Red Hat blog
The global financial system has long been at the forefront of technological change. Initially, banking institutions had minimal systems and fewer products, instead, the focus was on regular in-person customer interactions. However, as the global reach of finance grew, so did the need for proxies and platforms.
At present, there is a need to simplify this multi-system approach within banks and streamline the flow of data among various banking platforms. The concept of distributed ledger on blockchain can help a bank share information across the board internally or with different banks under the same network. Blockchain ledgers are hard to tamper with. Transactions written to a blockchain cannot be amended, making it easier to establish accountability and reduce dispute among network participants.
Cross border transactions is an area that has been heavily looked upon as a blockchain use case and one of the most lucrative opportunities for innovation. Cross border payments account for $130 trillion USD annually as per The 2020 McKinsey Global Payments Report (PDF). Banks usually have to incur high charges for cross border transactions.
These charges can be as high as 10% of the transaction because of the hops a transaction goes into till it finally settles with the end customer. Using blockchain tokens, transactions can be done in real time with ledgers reflecting the transacted tokens between banks. This can be achieved using smart contract functionality where a smart contract can hold the business logic agreed between banks and once a transaction is executed, the shared ledger will keep the record immutable. These transaction records can help in reconciliation and faster settlements.
Another area that can bring high efficiencies in retail banking is customer identity management. Every financial institution performs KYC of their customers for different financial products. From the blockchain perspective, once a customer gets KYC’ed, all the other banks/participants on the network can utilize the same KYC on the ledger. This can save time, cost and effort for both banks and the customers.
We understand that blockchain can bring high levels of efficiency in the banking process, but banks need to modernize their existing landscape and build the blockchain ledger on top of it. This is where BIAN and blockchain can come together.
The Banking Industry Architecture Network
Banking Industry Architecture Network (BIAN) is a common architectural framework for enabling banking interoperability. It helps in creating standardized capabilities in banking to lower the cost and increase innovation. BIAN can be viewed as The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF) in enterprise architecture that defines not only the front-facing apps but also the back end. It can help build interoperability architecture with a bank while blockchain can create a ledger. This blockchain ledger can be integrated with the modern, interoperability infrastructure to deliver the promise of true banking transformation.
Banking Reference Architecture for New Age

The technology systems should be able to integrate well with the banks’ legacy systems and new applications. To bring upon transactional efficiency, BIAN standard reusable business services/APIs can act as a business innovation layer coupled with the blockchain ledger.
These APIs can integrate with legacy systems of records and external systems while the blockchain ledger can act as a parallel system to the existing application landscape of banks. Using the APIs, the blockchain ledger can write the relevant data to its shared ledger.
This shared ledger can act as a connecting layer with other banks in case the banks are working in a consortium and want to utilize common data for value creation. Leveraging the smart contract functionality on the blockchain, certain banking functions like account opening and loan sanctions can be automated using predefined logic to achieve operational efficiencies.
HCL CoTrust Blockchain Platform and Red Hat
HCL’s blockchain application development platform, called CoTrust, provides scaffolding services to create business use cases on top of standard blockchain platforms. An enterprise application can be integrated with CoTrust to support participation in a blockchain.
In case the enterprise decides to participate in another blockchain, it doesn’t have to go through another integration project for the same enterprise application. It can easily configure or customize the CoTrust instance that is already in use.
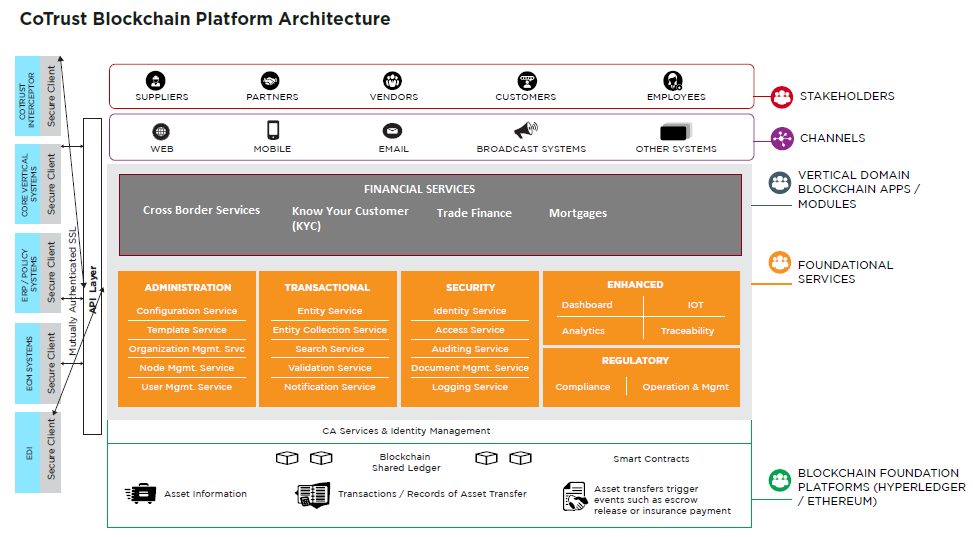
The foundational services of CoTrust are APIs, which can be easily customized for an organization depending on the use case. These APIs can integrate with existing systems of banks and can provide seamless experience on the layer above which vertical applications are written for specific use cases. At the platform layer, customers have the option to select the blockchain platform they prefer for their deployments.
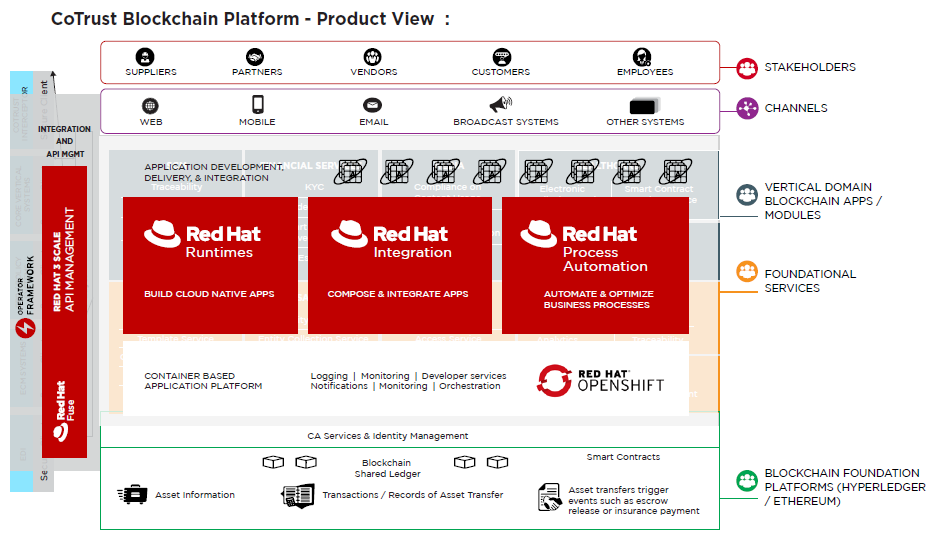
The CoTrust framework can be deployed on a Red Hat stack. The microservices-based cloud-native applications and services in the foundation layer, vertical apps and modules use the power of Red Hat Middleware to build, deploy, manage, and automate applications and processes. These microservices run as container-based applications on Red Hat OpenShift.
From the BIAN perspective, front-facing APIs are catered using Red Hat Integration–Red Hat Fuse and Red Hat 3Scale. The same suite can federate with blockchain services on CoTrust. For DevOps and IT operations management, organizations can use the Ansible Automation Platform and Tekton pipelines, along with Service Mesh for monitoring the complete environment.
In the end
As banks continue to evolve in their architecture journey, they need a trusted partner who can develop, migrate, and modernize their applications. HCL has experience in the banking and financial services space with dedicated practice and multiple accelerators. With a deep understanding of Red Hat’s practices and methods, HCL’s team of specialists can apply their collective knowledge and experience to a wide variety of enterprise blockchain scenarios.
To learn more about the clearing and settlement process using blockchain, read this whitepaper.
About the author
Shivendra Yadav is a Product Leader with the Digital and Analytics practice at HCL. He has extensive experience in enterprise IT consulting as well as in conceptualizing, incubating, and scaling product development initiatives in blockchain, hybrid cloud, public cloud and software defined infrastructure.

