The journey to enterprise-wide Kubernetes adoption can be a "wild, wild west" of disparate environments and challenging security for some organizations. That's the landscape Northrop Grumman faced in 2020. At Red Hat OpenShift Commons Gathering, software engineering managers Joe McConnell and Randy Ellefson shared the lessons they learned while building a modern, multicloud Kubernetes platform for Northrop Grumman built on Red Hat OpenShift.

Image 1: From Left, Randy Ellefson and Joe McConnell, Northrop Grumman’s Chief Information and Digital Office
Standardizing on Red Hat OpenShift
Initially, Northrop Grumman was looking for a highly available, low-cost, multicloud, secure environment for containerized applications. They chose Red Hat OpenShift to be the central part of their core infrastructure, taking advantage of its comprehensive suite of modern application tools to create a holistic, single platform. This strategic relationship with Red Hat was essential for support, as the company aimed to reduce labor requirements by building a fully self-service platform.
A year after the initial deployment, the team achieved high availability and a fully self-service platform, allowing customers to trigger any request via an automated API. They also successfully implemented GitOps managed releases. This transition empowered the organization to achieve the following results:
- Red Hat OpenShift successfully enabled a self-service model, automating all customer requests via a streamlined API.
- By taking advantage of Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security within the Red Hat OpenShift ecosystem, the team moved beyond a failed centralized model to a more flexible, automated process that allowed individual programs to efficiently scan and adjudicate their own vulnerabilities.
- The platform’s versatility allowed the team to pivot from complex, legacy migrations to rapidly onboarding greenfield applications and modern Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) tools for AI and machine learning (M/L), providing customers with all the capabilities of a modern infrastructure, including a security-hardened environment.
They choose Red Hat to help them navigate the complexity of their Kubernetes adoption. “We chose Red Hat OpenShift because it offered a holistic approach to Kubernetes. By integrating a full suite of tools into a single platform, Red Hat enabled us to move away from disparate environments toward a solution that is both reliable and highly effective," said Joe McConnell.
Embracing a managed service for velocity and scale
The rise of COTS apps, like Microsoft Copilot and augmented reality tools, presented a new challenge: many required kubeadmin or admin-level privileges, which couldn't be allowed in shared tenancy clusters. Furthermore, customers' demands for cluster delivery shrank from weeks to hours.
This led Northrop Grumman to adopt Microsoft Azure Red Hat OpenShift Cluster-as-a-Service (CaaS). Adopting Azure Red Hat OpenShift—a managed service jointly operated by Red Hat and Microsoft—accelerated cluster automation by offloading the infrastructure burden to specialized Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) teams. While this shifted the focus toward application delivery, the team initially struggled with inconsistent deployments caused by varying versions of the Azure CLI and WSL on individual admin laptops. To solve this, they took advantage of OpenShift’s container-native strengths to develop 'build containers'—a collection of portable images containing standardized tools. This ensured that every OpenShift cluster was delivered as a consistent, compliant market product, effectively turning their deployment process into a reliable, repeatable Infrastructure as Code (IaC) pipeline.

Image 2: Northrop Grumman’s shared enterprise Kubernetes platform
The push to hybrid cloud and GitOps
Building on this momentum, the team expanded their scope to deploy Red Hat OpenShift clusters across Microsoft Azure, AWS, and on-premise environments. Even in complex, disconnected settings, they maintained rigorous compliance with NIST 800-53 and CMMC 2 standards by applying the same GitOps principles and 'build container' concepts that had proven successful in their initial Azure Red Hat OpenShift rollout.
For bare-metal deployments, they used a multilayer approach:
- Layer 1: Ensuring hardware, network, and storage are in place, followed by a vanilla CoreOS and vanilla OpenShift install.
- Layer 2: Using ArgoCD to build out governance and common capabilities.
- Top stack: Laying down observability tools (Grafana, Prometheus, Loki), single sign-on (Keycloak), and a customer CI/CD pipeline using ArgoCD and Tecton. Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes and Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes are also installed for governance, compliance, and vulnerability scanning.
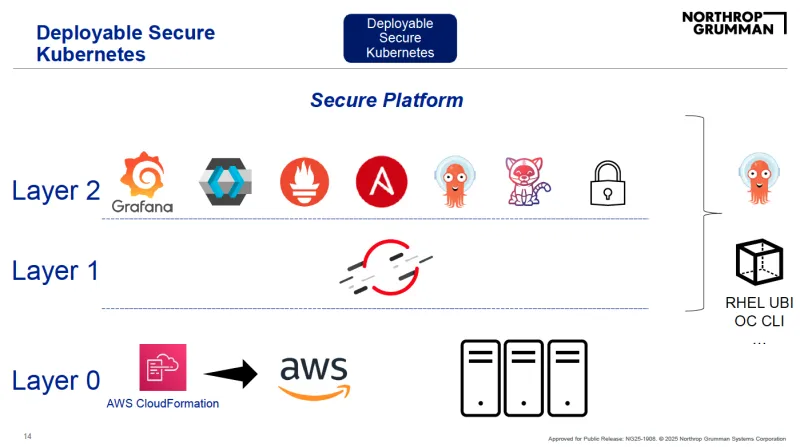
Image 3: Northrop Grumman’s layered approach for deploying security-focused Kubernetes
The decision to pivot to using ArgoCD strictly for installation automation (at Layer 2) proved highly beneficial. This standardized approach has drastically reduced Day 2 operational overhead, enabling a single operations team to manage many day-to-day tasks, such as patching, across all clusters.
Next stop: Red Hat OpenShift AI and high-performance computing
Looking ahead, Northrop Grumman is focused on maximizing its current investments by integrating Red Hat OpenShift AI to streamline its AI/ML data processing and platform capabilities.
This will be central to their next major milestone: delivering a 30,000-core, on-premise GPU farm for high-performance computing (HPC) with an estimated 30,000 cores on an ambitious timeline. The rapid delivery of this GPU farm, in a matter of months, will be powered by OpenShift AI and through collaborations with Red Hat, Dell, Nvidia, and DDN. This collaboration will produce a single SKU—a standardized environment combining all necessary hardware, software licensing, and services in a bundle.
They are also exploring Red Hat OpenShift Dev Spaces and hosted control planes for disconnected and classified environments. For their next step in AWS, they plan to use Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS, which offers hosted control planes. This dedication to a hybrid strategy, unified by Red Hat OpenShift, is the foundation for their next generation of critical development.
Are you ready to build, run, and scale AI-enabled applications on the world’s leading enterprise Kubernetes platform? Explore Red Hat OpenShift and OpenShift AI today.
- Take the next step with Red Hat OpenShift and Red Hat OpenShift AI.
- Watch this session from OpenShift Commons in Atlanta.
- Read TechTarget’s article about Northrop Grumman's adoption of Infrastructure-as-Code and GitOps on Red Hat OpenShift.
关于作者
Debbie Margulies is a principal product marketing manager for Red Hat OpenShift and has been at Red Hat since 2019 through the acquisition of StackRox.
