许多企业组织利用红帽 OpenShift 虚拟化在同一个统一的 OpenShift 平台上管理和部署虚拟化工作负载及容器化工作负载。对于那些优先考虑虚拟化的用户,红帽 OpenShift 虚拟化引擎作为 OpenShift 的新版本,提供了一个完全专注于虚拟化工作负载的专属解决方案。它通过删除虚拟机当前可能不需要的非虚拟化功能,简化了部署、管理和扩展虚拟机的流程。通过这种有针对性的方法,团队可最大限度地发挥 OpenShift 虚拟化的价值,同时满足其特定的基础架构要求。
OpenShift 虚拟化引擎仅专注于虚拟化,降低了不必要的复杂性和成本,与企业组织当前的虚拟化 IT 优先事项无缝衔接,同时在更广泛的应用平台上保留熟悉的 OpenShift 体验。
对于那些希望在未来进行扩展的企业组织,OpenShift 虚拟化引擎提供了一条便捷途径,通过升级到更广泛的 OpenShift 版本,实现容器化与现代化改造。借助跨红帽产品组合的集成以及来自广泛合作伙伴生态系统的扩展功能,OpenShift 虚拟化引擎可提供强大的企业虚拟化解决方案,以满足现代企业组织的需求。
OpenShift 专注于虚拟化,具备面向未来的灵活性
OpenShift 虚拟化引擎仍然提供与其他版本相同的 OpenShift 体验,并且具有满足仅虚拟化需求所需的精简功能。与所有 OpenShift 版本一样,用户可以利用 OpenShift 虚拟化功能来满足他们对虚拟机的即时需求。准备就绪后,您可以在更广泛的 OpenShift 解决方案中无缝探索容器化和应用现代化选项,无需重新安装或重新部署 OpenShift。
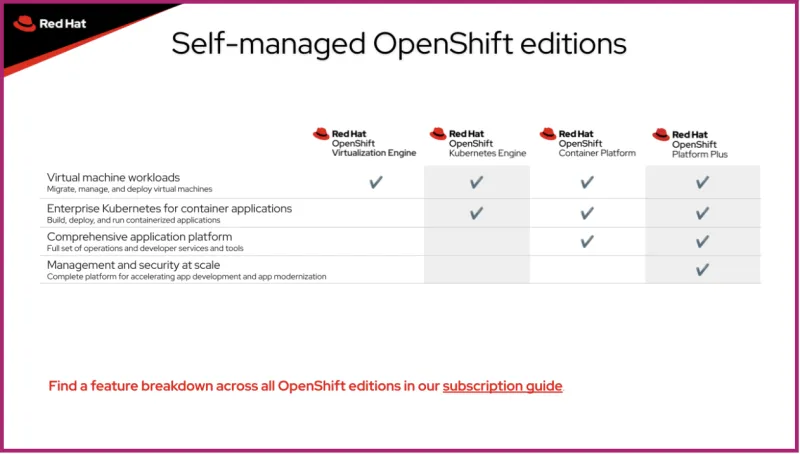
OpenShift 虚拟化引擎中提供的关键 OpenShift 功能包括:
OpenShift 虚拟化
OpenShift 虚拟化是所有 OpenShift 版本都包含的一项功能,它使用开源项目 KVM 和 KubeVirt 为虚拟机提供了一个现代化的基础架构平台。这使得企业组织能够通过单个平台管理所有应用(无论是虚拟化应用还是容器化应用),只需单个管理界面和一套工具即可处理全部工作负载,从而最大限度地降低开销。
裸机 OpenShift 部署和管理
OpenShift 虚拟化需要裸机集群节点,所有版本的 OpenShift 都提供强大的管理功能,以简化集群中物理服务器的部署和管理。这包括支持通过 OpenShift 自动化安装程序体验(IPI)、辅助安装程序、基于代理的安装程序等多种方式部署集群,让您可以根据自己的实际环境和需求定制安装体验。
OpenShift 的无线更新功能适用于裸机 OpenShift 虚拟化引擎集群,就像虚拟化的 OpenShift Kubernetes 引擎和 OpenShift 容器平台集群一样。这意味着,管理员只需点击几下或执行一个 CLI 命令,就能对集群和支持虚拟机基础架构的所有组件服务进行无中断更新。
为了进一步简化日常管理,OpenShift 虚拟化引擎在基于 Web 的管理 UI 中添加了一个专门的虚拟化管理员视图。这个量身定制的界面为专注于虚拟化的管理员提供了一个直观的环境,使他们能够轻松管理虚拟机、监控性能和执行日常任务,从而提高整体工作效率。
此外,OpenShift 强大的节点管理功能(如机器配置 Operator、NMstate Operator,以及使用机器集自动纵向扩展或缩减集群的原生功能等),也都适用于用于虚拟化的裸机集群。这些功能结合在一起,使管理员能够专注于更重要且级别更高的任务(如容量和性能管理),而不是对虚拟化环境的日常配置进行微观管理。
企业存储和网络功能
虚拟机需要具备存储空间以存储其磁盘和应用数据,并需要具备连通外部世界的能力。OpenShift 基于红帽企业 Linux CoreOS 和 KVM 虚拟机监控程序构建,使用长期以来备受信赖的 Linux 网络技术来连接虚拟机,连接方式与红帽企业 Linux 和 OpenShift 上的红帽 OpenStack 服务等其他基于 KVM 的产品如出一辙。这包括使用 Linux 网桥和 OVS 虚拟交换机,将虚拟机与 VLAN 和其他网络结构连接起来。事实上,基于 Kubernetes 的 OpenShift 虚拟化提供了更多高级功能。例如,OpenShift 的网络策略引擎为虚拟机提供原生平台级微分段,无论虚拟机是通过 VLAN 直接连接到外部世界,还是连接到软件定义网络。在存储方面,OpenShift 利用上游 Kubernetes 中的 CSI(容器存储接口)范式,并受到企业存储领域一些知名企业组织的物理和软件定义解决方案的支持,这些企业组织包括 Dell/EMC、HPE、IBM、NetApp、Portworx、Hitachi 和 Infinidat 等。每个存储供应商都可以通过实施 CSI 来表达其存储系统的原生功能,而 OpenShift 虚拟化唯一依赖的是 RWX(ReadWriteMany)卷(无论是基于文件还是基于块协议),以便为解决方案中部署的虚拟机和应用数据提供磁盘。
了解红帽的合作伙伴生态系统如何通过网络、备份和灾难恢复等其他领域的产品,帮助您完善虚拟化解决方案。
专注于改进和增强虚拟化体验的其他功能包括:
- 按命名空间监控用户工作负载:专为具有自动故障转移和主机修复功能的多租户虚拟化环境而设计,默认启用用户工作负载监控,以允许配置隔离代理修复。这样可以在节点故障情况下实现更快速的过渡,并使虚拟机能够快速重新调度到可用的节点。
- 增强的虚拟机平台日志记录功能:借助增强的平台日志记录功能,虚拟机管理员可以在整个部署过程中查看和收集他们有权管理的所有虚拟机的日志。通过利用专用于虚拟化的红帽多集群管理工具、红帽虚拟化高级集群管理和 Grafana,以可视化方式呈现受管集群上部署的虚拟机的日志和遥测数据,从而进一步强化此功能。
- 借助 OpenShift GitOps 自动置备虚拟机:用户可以利用内置的 GitOps 功能,从虚拟化高级集群管理控制台以代码形式自动部署虚拟机。截至目前,此功能为红帽 OpenShift 容器平台中的容器化功能所独有。借助 OpenShift 虚拟化引擎,用户现在能够受益于虚拟机自动化部署,以即时满足其虚拟化需求。
查看所有 OpenShift 版本的功能:
如何利用红帽产品组合优化 OpenShift 虚拟化引擎
OpenShift 虚拟化引擎可轻松集成红帽产品组合中的工具,以提供完整的自动化和管理解决方案。借助红帽 Ansible 自动化平台,您可以加速虚拟机组的大规模迁移,并自动执行相关基础架构(网络、存储等)的迁移和管理工作。虚拟机的日常任务也可以实现自动化,从而减少手动工作负载、提高一致性并提升运维效率。此外,企业组织还可以利用红帽的多集群管理工具红帽虚拟化高级集群管理来减少运维开销。通过这种集成,可跨多种虚拟机环境集中管理集群和应用,并一致地应用预配置的监管政策。通过结合使用红帽产品组合中的不同工具,管理员能够提供一个完整的生态系统,在整个 Day2 运维生命周期内管理和自动化虚拟机及相关基础架构。
关于作者
Carolyn May is a Product Marketing Manager at Red Hat, specializing in OpenShift, the leading hybrid cloud application platform powered by Kubernetes. With a background in sales, Carolyn spearheads initiatives aimed at highlighting the value of OpenShift.
Ben has been at Red Hat since 2019, where he has focused on edge computing with Red Hat OpenShift as well as private clouds based on Red Hat OpenStack Platform. Before this he spent a decade doing a mix of sales and product marking across telecommunications, enterprise storage and hyperconverged infrastructure.
更多此类内容
Improving VirtOps: Manage, migrate or modernize with Red Hat and Cisco
Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization: The strategic platform for virtualization customers
了解更多
- 增强混合云安全性
- 红帽被评为 2023 年 Gartner® 魔力象限™ 容器管理领导者
- 试用红帽 OpenShift


