This is the second post of our blog series on Red Hat OpenShift and Splunk Integration. In the first post, we showed how to send application and system logs to Splunk. The second part is focused on how to use Splunk Kubernetes Objects.
Prerequisites
The prerequisites are the same as defined in the first part.
Architecture
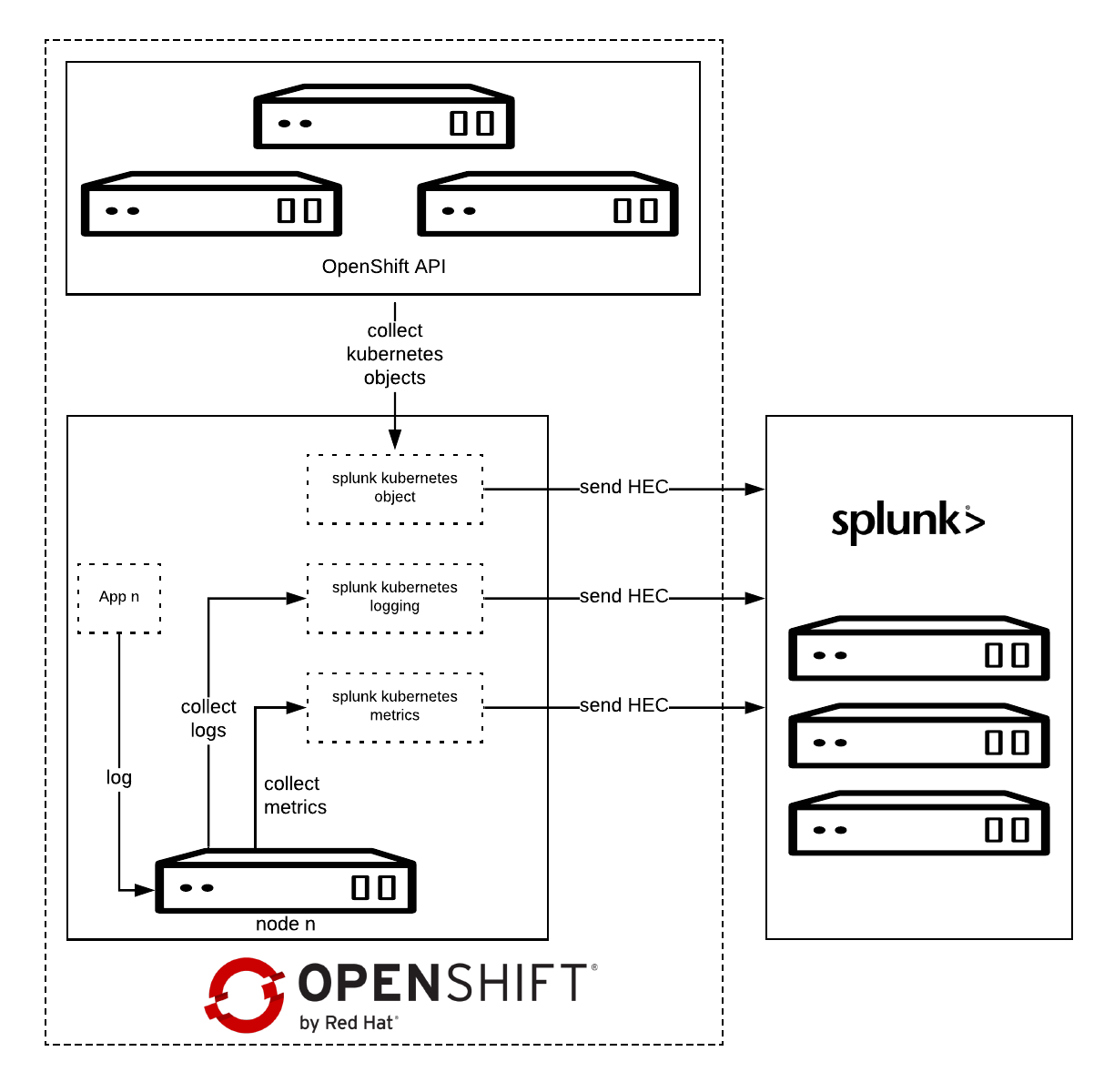
Splunk Connect for Kubernetes deploys:
- One DaemonSet on each OpenShift node for collecting log.
- One DaemonSet on each OpenShift node for collecting metrics.
- One Deployment to collect OpenShift Objects changes.
Installation
Before starting, please make sure you have already configured the Splunk Connect project as described in the first part.
Download the latest Helm Splunk Connect Helm package, which at the time of writing is 1.2.0.
wget <a href="https://github.com/splunk/splunk-connect-for-kubernetes/releases/download/1.1.0/splunk-kubernetes-objects-1.1.0.tgz">https://github.com/splunk/splunk-connect-for-kubernetes/releases/download/1.2.0/splunk-kubernetes-objects-1.2.0.tgz</a>
Download the source code as well; it is necessary to setup fine-grained permission.
wget https://github.com/splunk/splunk-connect-for-kubernetes/archive/1.2.0.zip
unzip 1.2.0.zip
cd splunk-connect-for-kubernetes-1.2.0/
Configure the variables for Helm; you can find sample values for the Splunk Connect on GitHub:
Minimal value example:
global:
splunk:
hec:
host: splunk.openlab.red
port: 8080
token: xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxx-xxxxxxxxx
protocol: https
rbac:
create: false
Splunk Kubernetes Objects
Splunk Kubernetes Objects collect Kubernetes objects that can help users access cluster status. Splunk collects the object data by calling the Kubernetes API. This supports two modes:
- Watch mode: the Kubernetes API sends new changes to the plugin. In this mode, only the changed data is collected.
- Pull mode: the plugin queries the Kubernetes API periodically. In this mode, all data is collected.
Setup
1: Assign cluster-reader permission.
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-reader -z splunk-kubernetes-objects --rolebinding-name=splunk-kubernetes-objects
Or Add fine-grained permission, check objects clusterRole manifests.
oc apply -f manifests/splunk-kubernetes-objects/clusterRole.yaml
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user splunk-kubernetes-objects -z splunk-kubernetes-objects --rolebinding-name=splunk-kubernetes-objects
2: Install Helm package.
helm install --tiller-namespace=splunk-connect --name splunk-kubernetes-objects -f objects-value.yml splunk-kubernetes-objects-1.2.0.tgz
Verify on Splunk
Conclusion
In this article we have explored how we can capture and send to Splunk the entire definition of Kubernetes objects, once they get created or modified.
In the next post will see how to collect OpenShift/Kubernetes metrics to Splunk.