Red Hat Satellite facilitates software synchronization in environments where connectivity to the Red Hat Content Delivery Network (CDN) is intermittent or slow. Inter-Satellite Synchronization (ISS) enables software synchronization for air gapped and indirect network environments, so your Red Hat Enterprise Linux hosts are patched and updated while conforming to security requirements or adapting to networking challenges.
This article discusses the different methods of network connectivity and how ISS enables software synchronization through air gapped and indirectly connected networks. Step-by-step instructions for setting up ISS for both network configurations are also provided.
For more information on software synchronization between Satellite servers, please refer to my previous article.
Air gapped environments - ISS export sync
Air gapped environments contain IT infrastructure assets in a network environment that is self contained where direct connections to the internet are not possible or not permitted.
ISS export sync requires that a Satellite server initially downloads software from the Red Hat CDN. An export is created from that initial download, then copied to the air gapped Satellite server. We call the first Satellite server the “upstream” server and the air gapped Satellite server the “downstream” server.
The exported software, or ISS export, can be copied to portable media from the upstream server and transported across the air gap, before it is imported into the downstream server.

Indirectly connected networks - ISS network sync
An indirectly connected network, or indirect network, is connected to the internet through a proxy in order to screen/filter traffic between a network and the internet. An indirectly connected network provides another layer of protection from malevolent external traffic.
ISS network sync enables software synchronization through an “upstream” server with a direct connection to the Red Hat CDN. First, software is synchronized to the upstream server. Next, a downstream server is configured to download software from the upstream server.

ISS Export Sync
Assumptions:
- Lifecycle environment named
Production - Content view named
RHEL9_BaseOS- Contains RHEL9 BaseOS repository.
- Published and promoted to
Productionlifecycle environment. - RHEL9 BaseOS repository must be configured with
Immediatedownload policy.
- The downstream Satellite server must have a manifest that is valid for the software repositories that will be synchronized from the upstream Satellite server.

Export the content view RHEL9_BaseOS
hammer content-export complete version --content-view "RHEL9 BaseOS" --version "1.0" --organization "Acme Org"
The exported data can be found in /var/lib/pulp/exports/Acme_Org/RHEL9_BaseOS/1.0/<date and time export was run>.
In other words, look for a naming scheme such as /var/lib/pulp/exports/<org>/<content view>/<content view version>/<date and time export was run>.
Copy the data to the downstream Satellite server
Once the data has been exported, three files will be created. They will be named similar to below.
export-ea7f2dc8-60b4-4136-bb15-5398f887aa39-20240419_1447.tar.gz export-ea7f2dc8-60b4-4136-bb15-5398f887aa39-20240419_1447-toc.json metadata.json
All three must be copied to the downstream server. You can copy them to removable media or via some means of network copy if available.
On the downstream server, the exported data must be copied into /var/lib/pulp/imports. Satellite will only import data from this directory root (unless configured otherwise).
In this example, I will create a directory called Acme_Org and copy the exported data into it.
Import the data on the downstream Satellite server
First, ensure that the pulp service owns the data on the downstream Satellite server.
Pre> chown -R pulp:pulp /var/lib/pulp/imports/Acme_Org/
Import the data.
hammer content-import version --organization "Acme Org" --path "/var/lib/pulp/imports/Acme_Org"
Here’s what the import operation looks like while it is in progress.

When this operation completes, you’ll find the content view RHEL9 BaseOS is created. Hosts registered to your downstream Satellite server will be able to access software imported from the upstream server in the RHEL9 BaseOS content view.
Incremental updates
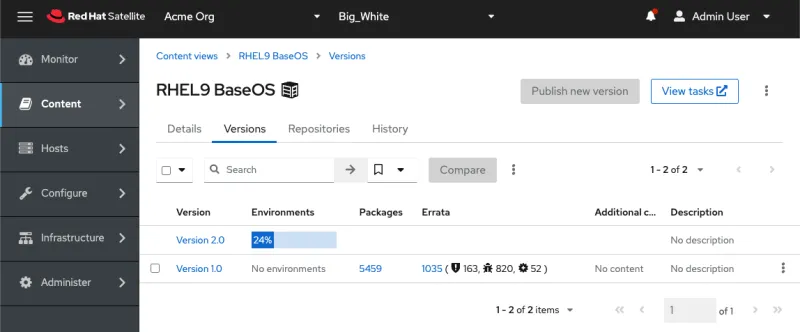
Subsequent updates can be performed incrementally.
In this example, we will publish and promote version 2.0 of the content view RHEL9 BaseOS on the upstream server. This step is not shown.
On the upstream server, run the following command after the content view RHEL9 BaseOS has completed the publish and promotion operation.
hammer content-export incremental version --content-view "RHEL9 BaseOS" --version "2.0" --organization "Acme Org"
Copy the data to the downstream server and then re-run the import command.
hammer content-import version --organization "Acme Org" --path "/var/lib/pulp/imports/Acme_Org/incremental_update_1"
In case you have performed multiple exports and you need to incrementally update multiple downstream servers, you must remember to apply incremental updates based on the last full or incremental update. You can view the history of the exports with the following command.
hammer content-export list
The output is as follows.
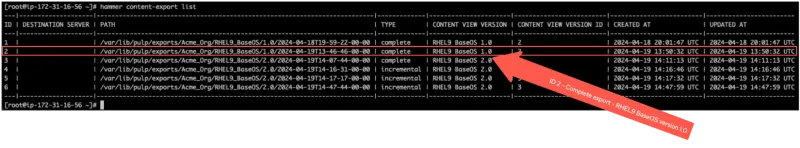
In this example, the export with ID 2 was imported into the downstream server. When this export was made, the content view RHEL9 BaseOS was published and promoted as version 1.0.
As you might recall, the content view RHEL9 BaseOS was published and promoted to version 2.0. The next incremental export on the upstream server must be made relative to ID 2, which denotes the id of the complete export of version 1.0 of the RHEL9 BaseOS content view. Thus, the export command must contain the --from-history-id flag.
hammer content-export incremental version --content-view "RHEL9 BaseOS" --version "2.0" --from-history-id=2 --organization "Acme Org"
On the downstream server, the content view RHEL9 BaseOS is published as version 1.0 as expected, using the content-export command above.
When the downstream server imports this data, it will create a content view version 2.0 based on previously imported data.
ISS Network Sync
Assumptions
Please refer to the Assumptions section for ISS export sync.
ISS network sync can be configured for repositories set to On-demand download policies.
Import upstream SSL certificates
ISS network sync is performed through an SSL encrypted connection between the upstream and downstream Satellite server. To ensure that the connection is secure and the encryption has not been compromised, the downstream server must import the SSL certificate chain from the upstream server.
First we’ll need to export the SSL certificate chain from the upstream server. You can obtain the upstream certificate with the following command.
curl http://<fqdn of upstream server>/pub/katello-server-ca.crt > katello-server-ca.crt/pub/katello-server-ca.crt > katello-server-ca.crt
The output, katello-server-ca.crt looks like this. Note that multiple certificates may be present in this file, depending on whether custom certificates are used.
[root@ip-172-31-24-152 ~]# cat katello-server-ca.crt -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- MIIHOzCCBSOgAwIBAgIUDXG3/qbr2MtMtTkVa6AA4HFOLLkwDQYJKoZIhvcNAQEL BQAwgZUxCzAJBgNVBAYTAlVTMRcwFQYDVQQIDA5Ob3J0aCBDYXJvbGluYTEQMA4G A1UEBwwHUmFsZWlnaDEQMA4GA1UECgwHS2F0ZWxsbzEUMBIGA1UECwwLU29tZU9y Z1VuaXQxMzAxBgNVBAMMKmlwLTE3Mi0zMS0xNi01Ni51cy13ZXN0LTEuY29tcHV0 ZS5pbnRlcm5hbDAeFw0yNDAzMDExOTI5NThaFw0zODAxMTcxOTI5NThaMIGVMQsw CQYDVQQGEwJVUzEXMBUGA1UECAwOTm9ydGggQ2Fyb2xpbmExEDAOBgNVBAcMB1Jh bGVpZ2gxEDAOBgNVBAoMB0thdGVsbG8xFDASBgNVBAsMC1NvbWVPcmdVbml0MTMw MQYDVQQDDCppcC0xNzItMzEtMTYtNTYudXMtd2VzdC0xLmNvbXB1dGUuaW50ZXJu YWwwggIiMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4ICDwAwggIKAoICAQDAWJFEZq9B21PoeOwb yU467mz3Byeg++7GrS4+ok4xjym0fJT5oO6uEBmANXTRA99cxS5BTy0hYJK/cC/H dDAcs6TfyvcA1HOaeZS3MPzW6WPwH1cR+ZORItJf70hewfMadiV4QN7JJQeRx4Xh AhAM2hS79/y1kyHnRpnejl6seMQmLmrm1ErR/4a0jkwYK9qpjjfMmSGYGaXzmHcY OKaENlXJAChW/MQScKH+9VB93M+UBqEoJWP3/7B77saTXw90Shw3GcCbcvsaLTpw 276EX0Dvo1DdQaLxR2Ex8WxRKfSDggfmqWycNa6B3s6V1ZhhAB3RT4skqFmf34bk /us+ZbuSdR6CjG52SD5RVMGZ66KbPtOSkXLmxEbO6hGKXh4XhjDCXrKMsfNUsc1v sbwR7pB9GJmYYjyHIP6w0SJZjq6VoRmTJKx0I9Uk+ph9GIBaEom0MAi/yLNFqyot oD85h3cr+O2UJ4pe3jqLjKKSX5wPHxBA06RTFhXX/3u8AVI2ouzbSwqWy3gEmEPU zdzHUKuR+ed1JD68m0HzfCa6nFDQVFbTnOQA8CzUO0Pp+6VUG4aWo6W0pJc8lWr4 QJbwPgNNHUIsJOTWhw3cTOyC473V7hGwo49oNCGImef9hGmSQ5I2uawSAk7Yo8nJ KNi6+AsTxiYpG0S1luF61OGjJwIDAQABo4IBfzCCAXswDAYDVR0TBAUwAwEB/zAL BgNVHQ8EBAMCAaYwHQYDVR0lBBYwFAYIKwYBBQUHAwEGCCsGAQUFBwMCMBEGCWCG SAGG+EIBAQQEAwICRDA1BglghkgBhvhCAQ0EKBYmS2F0ZWxsbyBTU0wgVG9vbCBH ZW5lcmF0ZWQgQ2VydGlmaWNhdGUwHQYDVR0OBBYEFAPNXOpt+xzlfS4fmMFCmaDg dt97MIHVBgNVHSMEgc0wgcqAFAPNXOpt+xzlfS4fmMFCmaDgdt97oYGbpIGYMIGV MQswCQYDVQQGEwJVUzEXMBUGA1UECAwOTm9ydGggQ2Fyb2xpbmExEDAOBgNVBAcM B1JhbGVpZ2gxEDAOBgNVBAoMB0thdGVsbG8xFDASBgNVBAsMC1NvbWVPcmdVbml0 MTMwMQYDVQQDDCppcC0xNzItMzEtMTYtNTYudXMtd2VzdC0xLmNvbXB1dGUuaW50 ZXJuYWyCFA1xt/6m69jLTLU5FWugAOBxTiy5MA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUAA4ICAQAC eO4VQCOyRuH8FJtA8jdfI5mRSq5sUtaUPFWE/wiKP7+2evEKxPrsuFlV74w/pYJE v7lkWy9MWEcoeBix/svQxLcGqsS9Mz/bsIaeKraQQnGC0zX7zk0JHcie92aVqFQx 0EE7ETQoHTVqPQjkqnmTXSZQzQB5bajtwZ8y/+TGDOXV0UnGhmTJn/CcD2EPooIl 8B80gLL0xOK5Vyowl9FYBLF5sMf1QNg74EupBFOAh6P3/SY6F0FZZzL+LHktmzKR 2AVL1RwMmteHmMvv5nrCvX/pJVyFPyY1y5f+oeUjxUASdY8Fw4a1IjA7lMjUaDt1 54sXG93riNHSa4SwDLhxIC0n9YDa9mqwHqOYtmlDjL1vTxjXd/1CYfckcerrW8s8 C+hszvQLT+WTEnxG48C8ctvUyQS3Ph4A+iiZ+2nFkePQbFVdlwvhQAEYoUmJh+ag 2D5GYjRjBb5N7r2ds2YDhnuWeXpXx+pzk7wc3zILf9yqOw1dwb1VWCVP6TS8NDeF TiRXUA/Qg5PV8//EaCBmMlSAfb9/L2UPXectzkVZeA6t24lGKgxmwlibiXhVLTYM 7Oql7+0DX9+BL/sqMBsShY5XpofDD7t881YLf2mo16jPlgxuSLvyCbdduWs8Iotf TJCRPBY1p/YRcGbdG0/Q7iBSBt+glD4pgyxjwN6IbA== -----END CERTIFICATE-----
To import the SSL certificate chain, copy it to the downstream server. Then enter the following command:
hammer content-credential create \
--content-type cert \
--name "<fqdn of upstream server>" \
--organization "<your org>" \
--path /<path to cert>/<name of cert>" \ --organization " " \ --path / /
The output should look something like this.

Configure the downstream server’s CDN to point at the upstream server
Navigate to the Subscriptions menu.

Click on Manage Manifest.

In the Manage Manifest menu, click on CDN Configuration.
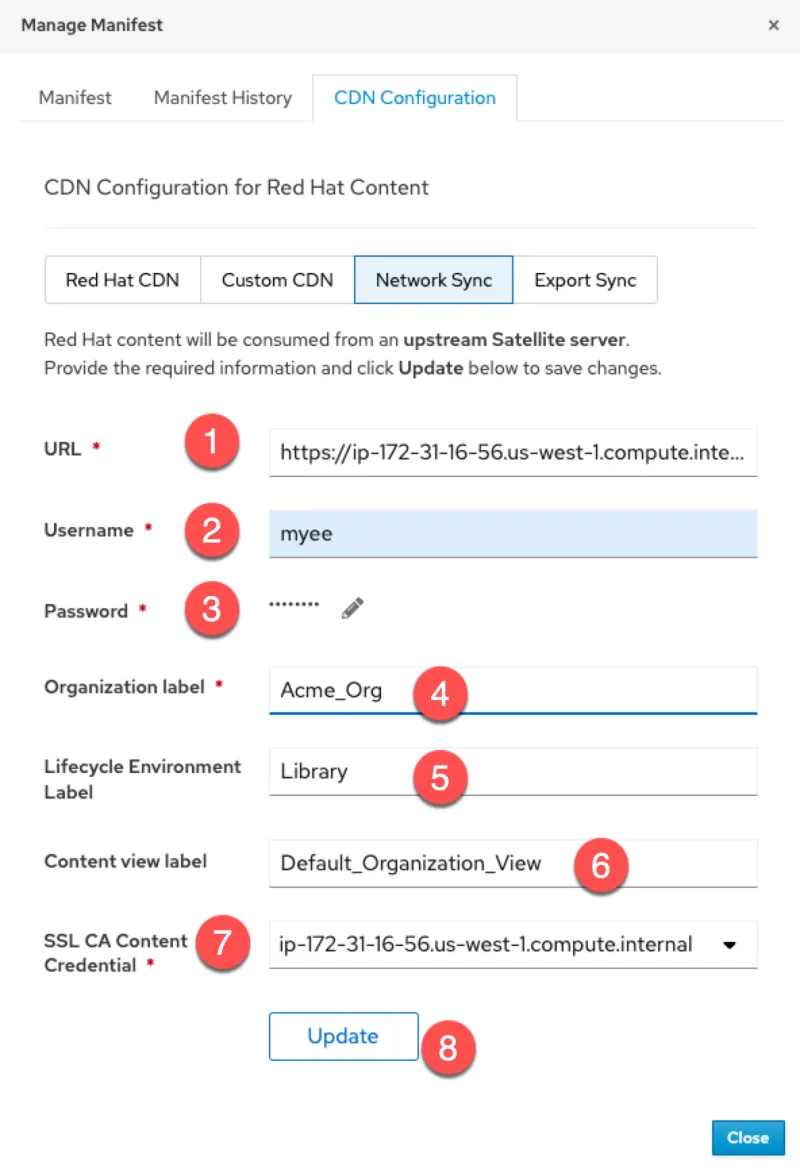
Click on the Network Sync tab.
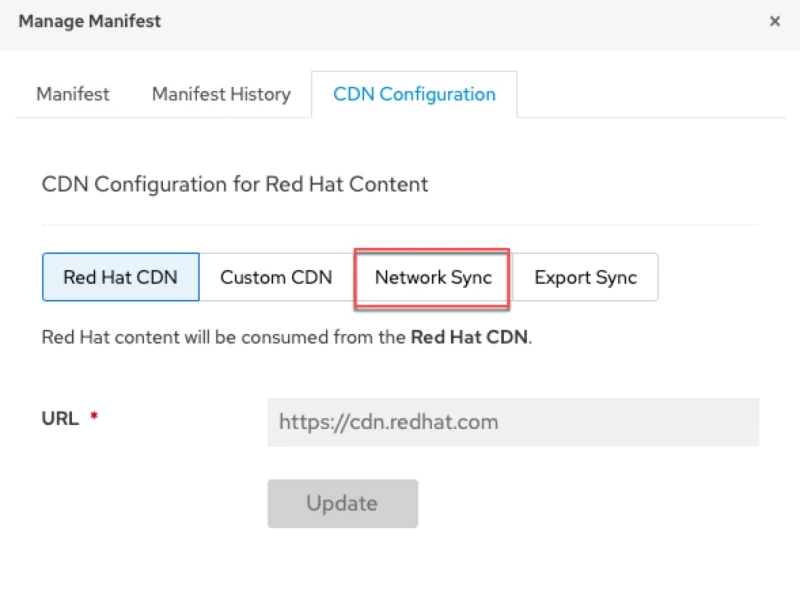
Configure the Network Sync.
- Enter the URL of the upstream server
- Enter the username. The user’s security privileges can be restricted
- Enter the password
- Enter the upstream organization label you wish to sync from
- Enter the upstream lifecycle environment you wish to sync from. To sync all content, enter “Library”
- Enter the upstream content view you wish to sync from. To sync all content, enter “Default_Organization_View”
- For SSL CA Content Credential, select the SSL certificate you imported earlier
- Click update
Add repositories from the upstream server on the downstream server
From the downstream Satellite server, navigate to the Red Hat Repositories menu.

Select the RHEL9 BaseOS repository.

Repositories that have not been synchronized to the upstream server are not available on the downstream server.

Synchronize the RHEL9 BaseOS repository and enable access to it with an activation key to test updates to RHEL9 hosts registered to the downstream server.
Red Hat Satellite simplifies software updates and management
Red Hat Enterprise Linux customers seek to integrate guardrails into their software supply chain and development life cycles to accelerate innovation without compromising security. Red Hat Satellite helps customers bring that secure software supply chain to on-premises and hybrid cloud environments. Inter-Satellite Sync export and network synchronization provide flexibility in conforming to security requirements in these environments.
References
关于作者
As a Senior Principal Technical Marketing Manager in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux business unit, Matthew Yee is here to help everyone understand what our products do. He joined Red Hat in 2021 and is based in Vancouver, Canada.
