It has been over two years since Red Hat acquired StackRox, turned it into Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security for Kubernetes (RHACS), and grew it into the Kubernetes-native security leader it is today. Those two years saw UI enhancements and many new features and improvements (such as updated Log4Shell policies, enforcing Cosign signature verification at runtime and the netpol CLI policy workflow), but we are excited for the first major release of Red Hat ACS’s tenure!
What to expect in the 4.0 release!
The 4.0 release contains one significant product transformation with many feature additions and updates. Still, the architecture and storage change is the reason for the major version update in line with the semantic versioning specification. The 4.0 release contains the following:
- A change in default databases, with a switch to PostgreSQL
- An updated and improved Network Graph (Tech Preview)
- Complete host-level scanning for Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) nodes
- Secured cluster support for IBM Power, IBM zSystems and IBM LinuxONE systems
- Enhanced runtime events and reporting
- Updated search capabilities
- Improved Syslog integration capabilities
- A new collections feature for easier reporting
- A "Policy Category" label for greater scoping of violations and vulnerabilities
- An API to report all processes listening on ports in a secured cluster
- FIPS Compliance validation
We are ecstatic to be sharing all of these updates. Let's dive into each feature update below!
PostgreSQL becomes the default database for RHACS in 4.0
When the StackRox 3.0 release was first launched, it laid the groundwork for Kubernetes security with features for configuration and vulnerability management. The latest version, 4.0, uses PostgreSQL, replacing the in-memory default database, RocksDB, used in previous versions. This approach has many benefits, including performance improvements, and also helps introduce many new features to the platform, which are covered below.
The benefits of using PostgreSQL as the RHACS backend include:
- Support scale and performance improvements
- Allow using standard tooling for backup and restore
- Minimize use of Persistent Volumes
For RHACS customers, PostgreSQL will be the default database starting with 4.0. Upgrading to 4.0 will include a database migration from RocksDB to PostgreSQL which will happen as part of the upgrade. Before upgrading, be sure to back up your database following the existing documented procedure so you can restore the backed-up database if you run into trouble.
ACS subject matter experts (SMEs) are available to guide on-prem customers to test the functionality to complete the necessary steps through the Red Hat Customer Portal.
Network Graph 2.0 has arrived!
As mentioned in the 3.74 release, RHACS network graph has been upgraded with the Patternfly library, providing improved functionality and crisp graphs. The graph provides detailed information about environment deployments, network flows and policies. There are two views:
- The Active flows (default) view shows flows with observed traffic focused on the selected namespace or specific deployment.
- The Inactive flows view shows flows that your network policies allow, although they have not served traffic in the observed time window. This view helps you identify changes needed to your network policies to achieve tighter isolation.
Filters and controls can be used to customize the displayed information. The graph includes a legend to explain icon usage. Below is an example showing deployments and traffic flows between them, with a red badge indicating missing policies.
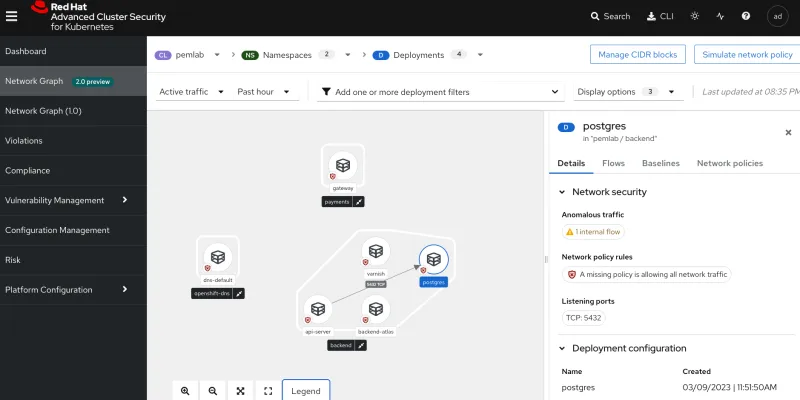
This visual update and the added roxctl CLI netpol generate feature (tech preview) enable a more effective network policy creation workflow to help developers, operations and security teams meet their zero trust network goals.
The Network Graph update and netpol features can be viewed in a short demo here.
Full host-level scanning for RHCOS nodes
You read that right! RHACS will now have full host-level scanning for RHCOS nodes.
Before this update, the RHACS platform only scanned Red Hat OpenShift cluster nodes for vulnerabilities in core Kubernetes components and container runtimes. But now, RHACS will provide Red Hat customers with vulnerability scanning of the entire host (node) operating system, beyond just the Kubernetes components, using Red Hat provided vulnerability data for scan accuracy.
RHACS will now:
- Identify all installed RPM packages, including Kubernetes components for the OpenShift cluster nodes secured with ACS running on RHCOS
- Identify known vulnerabilities impacting those packages and Kubernetes components
- Consume Red Hat-provided vulnerability data for RHCOS components to provide accurate scan results
This is the first step in enhancing our vulnerability management workflow process on RHACS. Stay tuned to future releases for more updates and tips on improvements to the vulnerability management workflow.
IBM Power, IBM zSystems and IBM LinuxONE support for RHACS Secured Cluster Services
RHACS has an extremely comprehensive support policy for various Kubernetes platforms and architectures. We’ve increased that support matrix to include OpenShift on IBM Power, IBM zSystems and IBM LinuxONE systems. Please review the RHACS support matrix for more details.
You can install the RHACS Secured Cluster Services on Red Hat OpenShift on IBM Power, IBM zSystems and IBM LinuxONE using the RHACS Operator. With release 4.0, RHACS supports scanning multi-arch builds with roxctl and extends support for RHACS secured clusters for:
- Red Hat OpenShift 4.12 to IBM Power (ppc64le)
- Red Hat OpenShift 4.10 and 4.12 to IBM zSystems (s390x) and IBM LinuxONE (s390x)
API to report all processes listening on ports in a secured cluster
Security-conscious Kubernetes users need a list of all processes listening on ports on the secured cluster. ACS already provides information on which deployments and namespaces have open ports. With 4.0, we’ve added information about processes listening on ports to help assess the security posture of the cluster more effectively.
This feature will be visible in the UI in a future release.
Updated global search in the dashboard
A proper search bar is an extremely powerful tool. In RHACS 4.0, we’ve enhanced the search experience to make finding and using security information much quicker and more targeted.
Our updated Global Search feature has been redesigned and is now presented on a dedicated search page, providing an extensive list of search criteria to help you quickly find what you need. With over ten search categories and individual search results presented as line items, you can easily zoom in on areas of interest and explore the results further. And the best part? Search now uses URLs, allowing you to navigate with your browser, open results in new tabs and even share search links with your team.
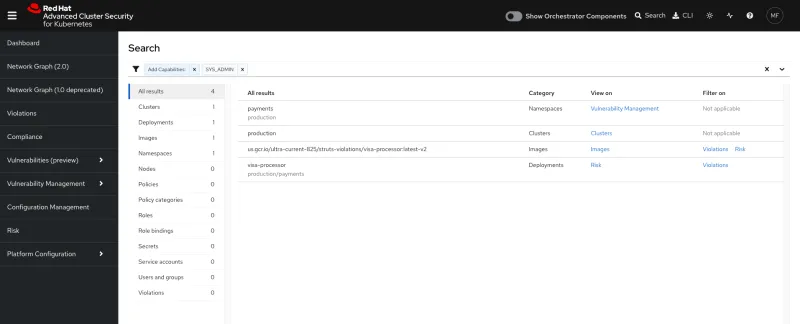
For example, with RHACS global search, users can search for deployments with SYS_ADMIN capabilities and share the link with other professionals, allowing them to find and quickly share information across teams efficiently. RHACS is committed to providing the best user experience, and our updated Global Search feature is just one example of that commitment.
Extra fields for improved syslog integration
When integrating with a syslog receiver, RHACS automatically sends all violations and audit events to the configured syslog receiver. With RHACS 3.74, you can specify custom key-value pairs to send to the external system. The new extra fields allow you to customize the data you can filter in your syslog receiver.
For more information, see Integrating by using the syslog protocol.
RHACS Collections
The introduction of PostgreSQL comes with the introduction of a brand new feature the RHACS team calls “Collections.” The collections feature allows users to define a collection of deployments using matching patterns, name it for repeatable use and eliminate the need for cloning and repetitive editing of RHACS properties. It defines a logical grouping by using selection rules, offering you the power of expression as follows:
- Rules can match by using the name or the label of a deployment, namespace or cluster.
- You can specify rules by using exact matches or regular expressions.
- Collections are resolved at run time. The rules can refer to objects that do not exist at the time of definition.
- Collections can be constructed by using other collections to describe complex hierarchies.
- Identify any group of deployments in your system by team, environment labels, namespaces, cluster names, etc.
In the 4.0 release, collections are only available in the updated Vulnerability Report feature. Over time, collections will be available in dashboards, network graphs and everywhere an RHACS search or filter is used, making it easy to focus on areas of interest.
Policy categories update
The RHACS team is updating the “Policy Categories” feature to help you manage related policies. This feature comes with the new Policy Categories tab, which allows viewing, creating, renaming or deleting categories. This workflow protects system-defined policies, ensuring you cannot delete them while granting the fine-grained ability to adjust groupings as needed. The same actions for policy categories available in the RHACS portal are also available through the API using the PolicyCategoryService service. For more information, see the API documentation by navigating to Help > API reference in the RHACS portal.
FIPS compliance
RHACS has now been validated on OpenShift 4.12 in FIPS (Federal Information Processing Standard) enabled mode. This helps meet compliance requirements for various customers.
Try out RHACS 4.0 today!
The 4.0 release notes are available to browse through, and as always, RHACS is available for a 60-day free trial (self-managed).
But if you are not currently using RHACS, we recommend you start with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security Cloud Service, a fully managed SaaS version of RHACS, by visiting the Amazon Marketplace or requesting a demo.
关于作者
Michael Foster is a CNCF Ambassador, the Community Lead for the open source StackRox project, and Principal Product Marketing Manager for Red Hat based in Toronto. In addition to his open source project responsibilities, he utilizes his applied Kubernetes and container experience with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Security to help organizations secure their Kubernetes environments. With StackRox, Michael hopes organizations can leverage the open source project in their Kubernetes environments and join the open source community through stackrox.io. Outside of work, Michael enjoys staying active, skiing, and tinkering with his various mechanical projects at home. He holds a B.S. in Chemical Engineering from Northeastern University and CKAD, CKA, and CKS certifications.
