Migrating a virtual machine (VM) from one platform to another is a complex task. Nevertheless, organizations are looking for a unified platform that provides the same benefits for VMs as what's available for containers. With Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization, you don't have to make the journey alone. The Assisted Installer for OpenShift supports deploying connected clusters with OpenShift Virtualization from the start, so you can begin your migration journey today and modernize at your own pace.
What is the Assisted Installer?
The Assisted Installer simplifies the process of deploying connected OpenShift clusters by providing a guided, automated experience. Instead of relying on a dedicated bootstrap machine, the installer handles cluster bootstrapping as part of the installation process, reducing complexity and time to deployment. Available through a web-based UI, or API, the Assisted Installer gives you flexibility in how you manage installations. You can also integrate it with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management to simplify deployment and ongoing management across multiple clusters, while still retaining the option to enable OpenShift Virtualization during installation.
Virtualization-ready from day one
With the Assisted Installer, you can enable OpenShift Virtualization during the cluster installation process. While some additional configuration may still be required, this approach simplifies deployment and shortens the path to running VM workloads alongside containers.
The Assisted Installer also provides built-in pre-installation validations, checking for hardware and system requirements (CPU virtualization flags, memory, storage, and so on) before installation begins. This helps ensure that your environment is properly configured for virtualization and reduces the risk of deployment errors.
Key benefits include:
- Simplified experience: Deploy OpenShift clusters with virtualization included through a single, guided workflow.
- Confidence through validation: Automated pre-checks ensure nodes meet cluster and Day 2 operator requirements before installation continues.
- Consistency across environments: Gain a streamlined deployment experience across connected environments. Support for disconnected environments is in Developer Preview with the Agent Installer for OpenShift Virtualization.
- Faster path to modernization: Accelerate your journey to running VMs and containers on a unified OpenShift platform.
Getting started with Assisted Installer
Using the Assisted Installer, deploying a connected OpenShift Virtualization cluster is straightforward:
- Click the Create cluster to access the Assisted Installer.
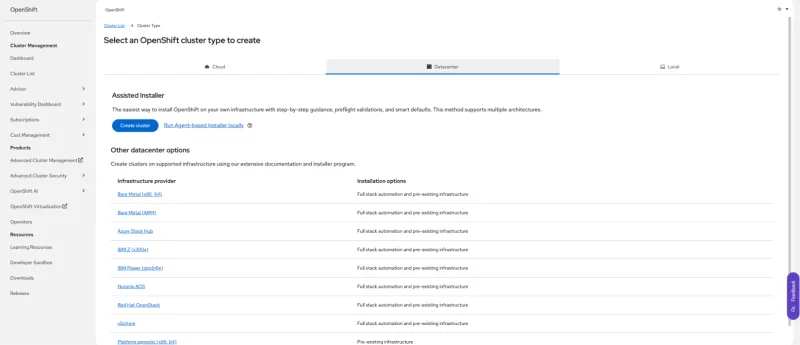
Alt text: Creating a cluster in the OpenShift web console.
- Define your cluster configuration.

Alt text: Defining cluster details in the OpenShift web console.
- Select OpenShift Virtualization bundle, or cherry-pick operators to be installed, during setup.

Alt text: Include operators you want to install.
- Add your host to the new clusters using a bootable image (ISO).
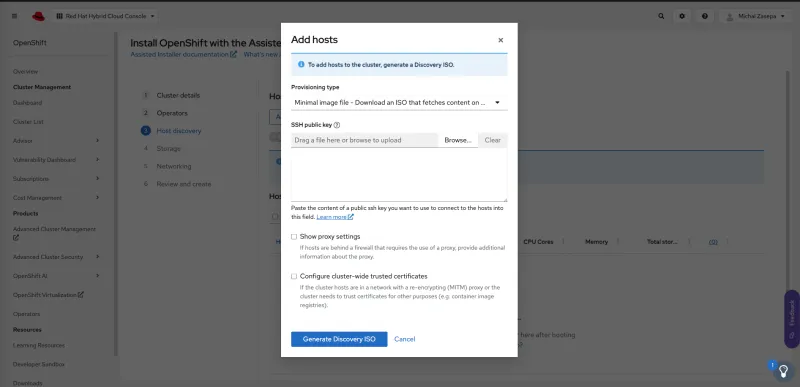
Alt text: Add an ISO as your bootable image.
- The auto-assigning feature in Assisted Installer can help you select which node should be used as the control plane, and you can adjust it to your needs.

Alt text: Assisted Installer can help you choose a control plane.
- Configure the storage and network settings.
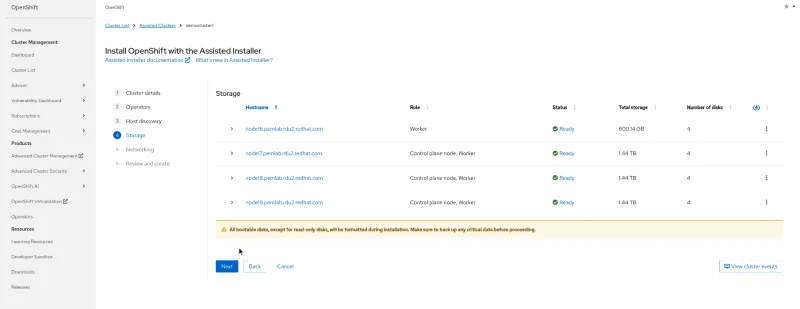
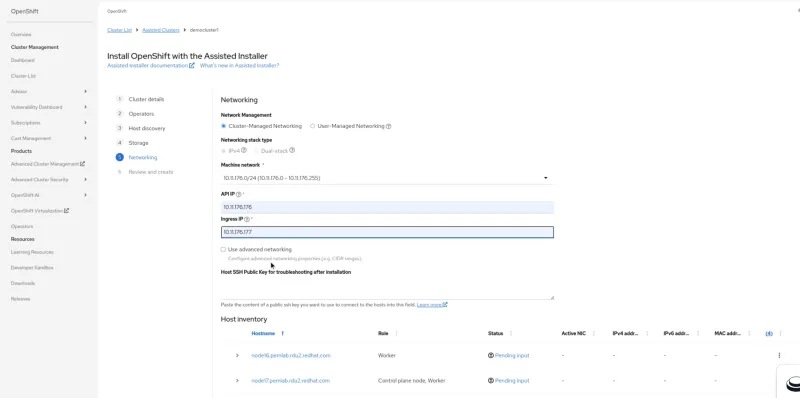
Alt text (for both images): Add your network and storage configuration.
- Run pre-install validations to confirm system readiness.
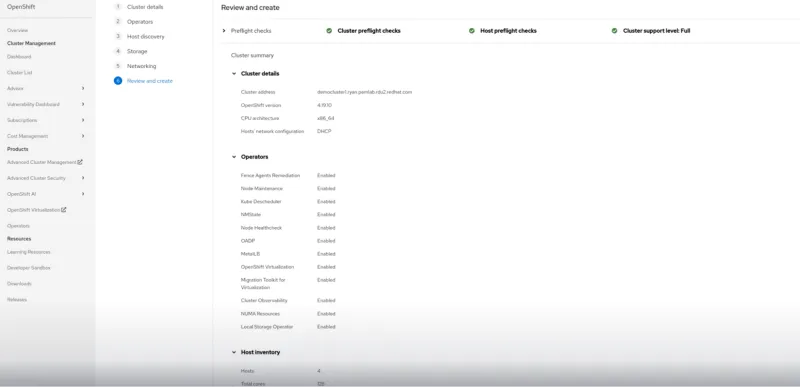
Alt text: Pre-install validations help confirm your configuration is ready.
- Launch your installation, and then log in to the deployed cluster to finish any configurations required by your application that are specific to your VM.
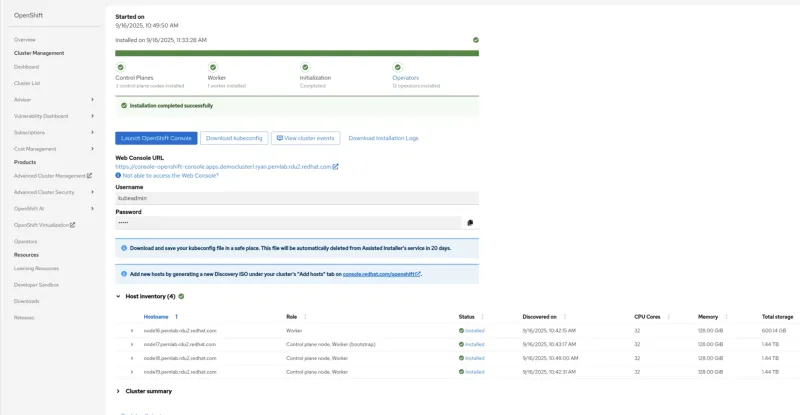
Alt text: After installation, you can configure your VM further, as required.
Migrate with confidence
The Assisted Installer is designed to help you deploy OpenShift clusters quickly and with confidence. With built-in support for OpenShift Virtualization, you can simplify operations and accelerate modernization by bringing your existing virtual machine workloads onto a cloud-native platform from day one.
Learn more about OpenShift Virtualization and the Assisted Installer:
关于作者
Courtney started at Red Hat in 2021 on the OpenShift team. With degrees in Marketing and Economics and certificates through AWS and Microsoft she is passionate about cloud computing and product marketing.

