In this post:
-
Get an overview of zero touch provision and why it’s beneficial for managing deployments at the edge.
-
See how GitOps can help you achieve hands-off deployments.
When pushing compute and cloud technologies to the edge of the network, the logistical approach to infrastructure provisioning needs to be hands-off. Is Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP) a possibility? Are things ever really “zero?”
This post will provide an overview of ZTP, why it’s important when working with thousands of edge nodes, and how GitOps practices and Red Hat solutions are enabling more rapid deployment of mobile infrastructure—helping you manage your infrastructure at the edge.
What is Zero Touch Provisioning?
Broadly defined, Zero Touch Provisioning describes a process to provision devices in a network automatically, with minimal manual intervention. Some benefits include freeing administrators to perform specialized tasks and the reduction of errors by eliminating the manual configuration efforts required. Additionally, provisioning can be performed at-scale and much more rapidly.
As an example, mobile Radio Access Networks (RAN) are complex and geographically distributed. They need to be deployed without manual intervention for a variety of reasons.
As one would expect, the physical build of a mobile tower and base station or addition of new radios requires direct access to the hardware and site location. All other provisioning, software deployment and configuration, however, should be completely hands-off to avoid downtime due to human error and travel time to physical sites, which can also be very expensive.
Technicians in the field should be focused on tasks that are directly related to being at the physical site, such as running power, connecting cables and troubleshooting connectivity issues. Time on site is costly as they can be remote, the work environments range from extreme cold or heat and inclement weather, so it is paramount to maximize productive time at the physical site whenever possible. This concept of site-efficiency and need for ZTP is magnified further when noting that the scale of a RAN deployment is typically going to consist of what could approach (or exceed) 1,000 nodes in a geographic region.
Achieving hands-off deployment with GitOps
Achieving hands-off deployment is enabled by defining the infrastructure as code, storing all configuration data in Git, and by utilizing the power, reliability, and consistency contained in a broad, proven set of automation tools. GitOps is a set of practices to manage infrastructure and application configurations using Git, an open source version control system.
This captures the essence of the advantage afforded by GitOps: a set of practices or principles that empowers developers or operators to leverage a declarative configuration to define the end state of the cluster they intend to deploy at a cell site. To provide context of the scale involved, and why its potential is so important, there are over 400,000 cell sites in the US alone.
In the framework of a mobile network, the operator's network—which typically starts out as a set of site plans—needs to be transformed into a set of yaml files that defines the end state of the entire network. There are hundreds of configuration parameters that need to be defined to successfully deploy the nodes, a portion of which are common to all the nodes, some are applicable to a group of nodes, and others which are site-specific. This variability quickly escalates into an n factorial problem (hundreds of parameters, thousands of nodes, hundreds of files).
A programmatic approach with Red Hat solutions
Any successful approach or solution to these challenges needs to be programmatic.
Templating is a good way to define and collect data in a structured way by outlining a way to separate the specific from the common configuration data. Policy generator tooling enables the creation of all of the custom resources (yaml files) for each site and stores them in Git. The operator is now ready to decide which clusters to deploy and when.
Because various GitOps approaches can be used to manage the deployment of clusters depending on the user’s desired outcomes, using Git to underpin continuous management of clusters can help realize significant operational savings.
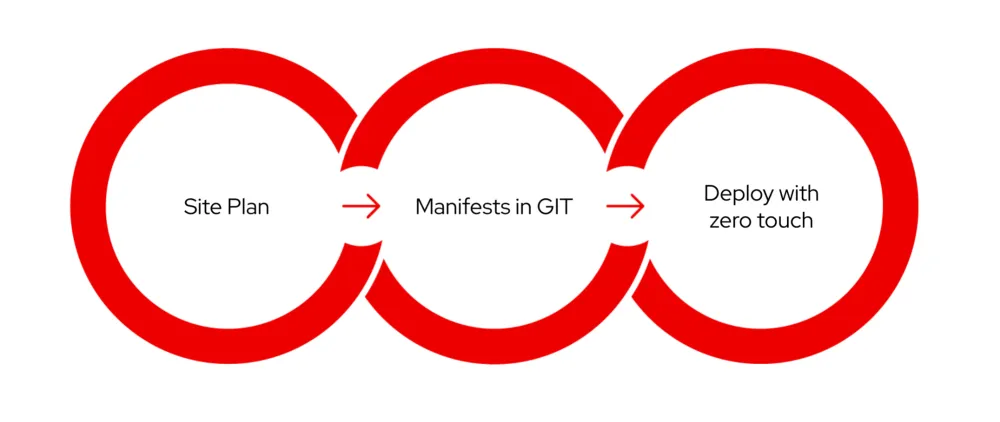 Mobile network operators should examine their site plans and determine distinctions between policies and configurations that are applicable to all nodes, a subset of nodes, or specific sites.
Mobile network operators should examine their site plans and determine distinctions between policies and configurations that are applicable to all nodes, a subset of nodes, or specific sites.
Examples of each include:
-
Common - the use of single root IO virtualization (SR-IOV) interfaces or precision time protocol (PTP) in the deployment.
-
Group - a set of policies that would be applicable based on different hardware vendors being used in part of the network.
-
Site-specific - static IPs, VLAN configurations
 The tooling that is utilized in this journey is diverse, and each component has a part to play in achieving success. The challenges our telco customers face include how to deploy thousands of Kubernetes clusters at the edge of the network on bare metal without having access to each node and creating a costly operational model.
The tooling that is utilized in this journey is diverse, and each component has a part to play in achieving success. The challenges our telco customers face include how to deploy thousands of Kubernetes clusters at the edge of the network on bare metal without having access to each node and creating a costly operational model.
Red Hat maintains working relationships with various hardware partners to ensure an ecosystem of servers is supported. Additionally, Red Hat has a strong focus on the ecosystem of RAN providers.
Concluding remarks
At Red Hat, we are enabling the rapid deployment of mobile infrastructure by leveraging cloud technologies to bridge the gap between the physical radios and the datacenter.
New RAN models as proposed in 3GPP and O-RAN look to leverage Kubernetes at the edge. With Red Hat OpenShift for RAN, we can help accelerate these new technology deployments with our focus on Zero Touch Provisioning. A blank server can now be deployed at the edge of the network, loaded with signed and secure software stack, configured with the appropriate tuning for performance, and with the needed site-specific data applied, all without any human intervention across thousands of nodes. The workflow is powered by open source, best practices and GitOps principles.
In Red Hat’s ecosystem of supported products, Red Hat OpenShift and Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes come together to provide a flexible and adaptable solution to all of these challenges.
We invite you to explore what Red Hat OpenShift can do for your environment here.
저자 소개
Ian Jolliffe has deep experience in the Telecom and Industrial verticals and has been contributing to various open source projects since 2013. Jolliffe is most active these days in defining solutions that take cloud technologies and compute resources to the edge. Jolliffe has been a committer to the OPNFV high availability project, contributor to Akraino, and frequent speaker at edge-focused events. He joined Red Hat in 2020 and is focused on delivering solutions for 5G edge.
유사한 검색 결과
Deterministic performance with Red Hat Enterprise Linux for industrial edge
Red Hat Enterprise Linux delivers deterministic performance for industrial TSN
What Can Video Games Teach Us About Edge Computing? | Compiler
How Do Roads Become Smarter? | Compiler
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래
