Releasing software frequently to users is usually a time-consuming and painful process. Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) can help organizations to become more agile by automating and streamlining the steps involved in going from an idea, change in the market or business requirement to the delivered product to the customer.
Jenkins has been a center-piece for Continuous Integration and with the introduction of Pipeline Jenkins plugin, it has become a popular tool for building Continuous Delivery pipelines that not only builds and tests the code changes but also pushes the change through various steps required to make sure the change is ready for release in upper environments like UAT and Stage.
CI/CD is one of the popular use-cases for OpenShift Container Platform. OpenShift provides a certified Jenkins container for building Continuous Delivery pipelines and also scales the pipeline execution through on-demand provisioning of Jenkins slaves in containers. This allows Jenkins to run many jobs in parallel and removes the wait time for running builds in large projects. OpenShift provides an end-to-end solution for building complete deployment pipelines and enables the necessarily automation required for managing code and configuration changes through the pipeline out-of-the-box.
This example demonstrates how to setup a complete containerized CI/CD infrastructure on OpenShift and also how it integrates into the developer workflow. We will also explore a day in the life of a developer by adding a new REST endpoint to the application using the Eclipse-based JBoss Developer Studio and see how that propagates through the pipeline, being built, tested, deployed and promoted to upper environments.
In this example, we use the following tools to set up a CI/CD infrastructure on OpenShift:
- Jenkins: CI/CD engine
- Gogs: GIT server
- Nexus Repository: build artefact repository for managing JAR, WAR and EAR files
- SonarQube: static code analysis to detect bugs and anti-patterns
Although all above tools run in containers on OpenShift in this example, they can very well be running elsewhere on other type of infrastructure or be replaced by other popular tools like GitHub, BitBucket, GitLab, Bamboo, CircleCI, etc.
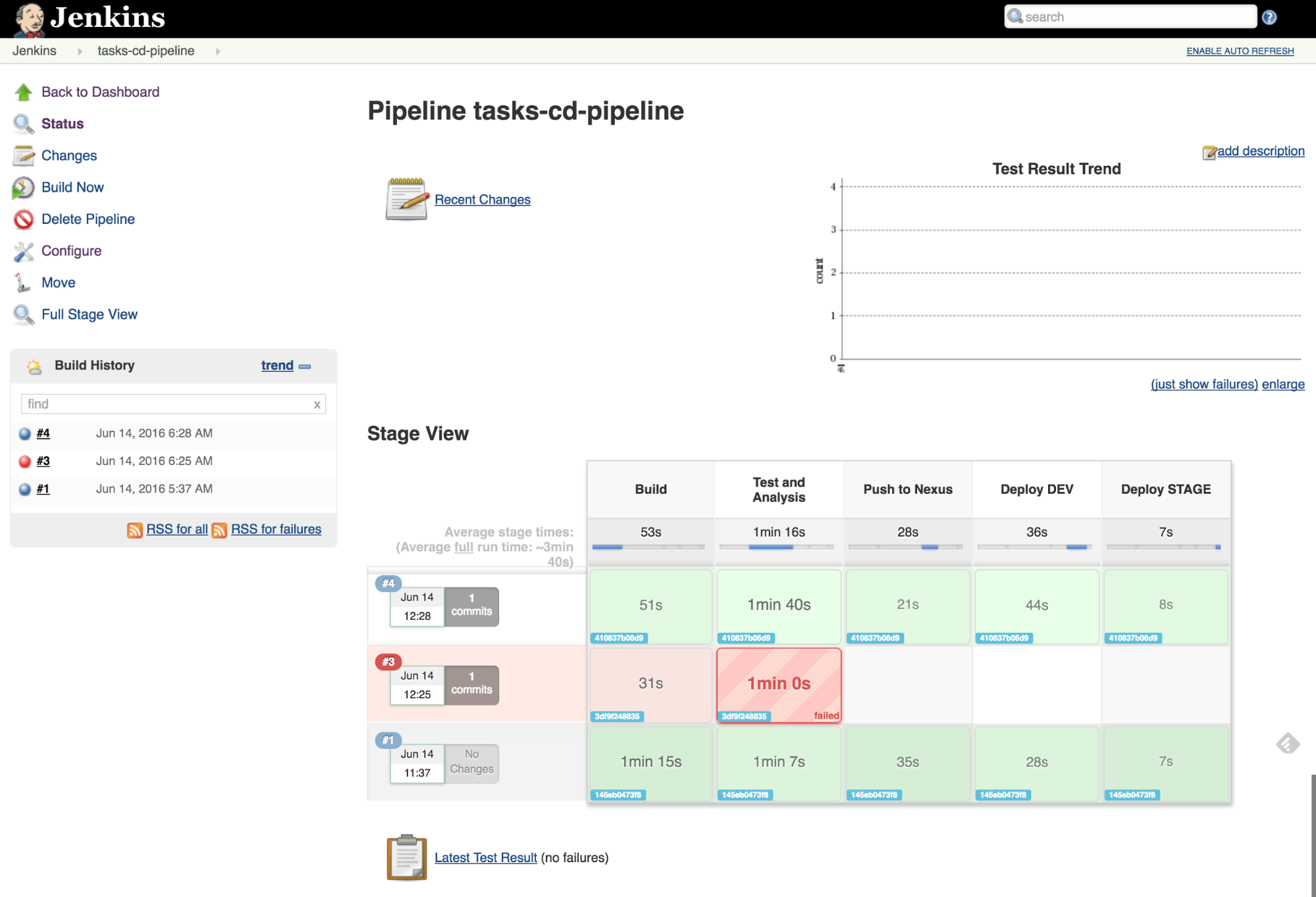
The following diagram shows the steps included in the example pipeline:

When a code or configuration commit triggers a pipeline execution:
- Code is cloned from Gogs git server, built, tested and analyzed for bugs and anti-patterns
- The WAR artifact build in the previous step is archived in Nexus Repository
- OpenShift takes the WAR artefact from Nexus Repository and builds a Docker image by layering the WAR file on top of JBoss EAP 6
- The Docker image is deployed in a fresh new container in DEV environment
- A set of automated tests run against the application container in DEV environment.
- If tests successful, the Docker image is tagged with the application version and gets promoted to the STAGE environment
- The tagged image is deployed in a fresh new container in the STAGE environment
All configuration for setting up this example is available in the following GitHub repository:
저자 소개
Siamak Sadeghianfar is a member of the Hybrid Cloud product management team at Red Hat leading the cloud-native application build and delivery on OpenShift.
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래
