Windows Machine Config Operator (WMCO) 6.0.0 available on OpenShift 4.11 will move from Windows Server configured with Docker runtime to Windows Server configured with containerd runtime. You can read more about Dockershim deprecation here. Switching from Docker to containerd runtime is relatively easy, and will have better performance and lower overhead. Because the Docker runtime is deprecated in Kubernetes 1.24, containerd is now the default runtime for WMCO-supported Windows nodes. Upon the installation of or an upgrade to WMCO 6.0.0, containerd is installed as a Windows service. The kubelet will now uses containerd for image pulls and as the container runtime instead of the Docker runtime.
Steps to configure containerd for Running Windows Container Workloads on OpenShift.
Install OpenShift 4.11
Follow these steps to install OpenShift Container Platform. Be sure the following pre-requisites documented here are followed.
Prerequisites
- You have access to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster using an account with
cluster-adminpermissions. - You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You have installed your cluster on a supported platform using installer-provisioned infrastructure, or using user-provisioned infrastructure with the
platform: nonefield set in yourinstall-config.yamlfile. - You have configured hybrid networking with OVN-Kubernetes for your cluster. This must be completed during the installation of your cluster. For more information, see Configuring hybrid networking.
Install Windows Machine Config Operator 6.0.0
You can install the Windows Machine Config Operator using either the web console or OpenShift CLI (oc). Refer to product documentation for steps on how to install WMCO from the inCluster Operator Hub.

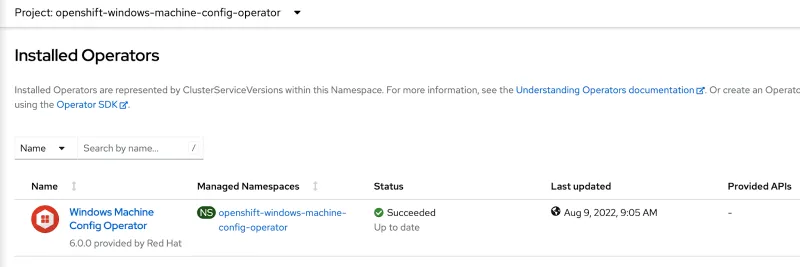
Be sure that the Windows Machine Config Operator is installed under Installed Operators.
Configure an instance using Windows MachineSets
You can create a Windows MachineSet object to serve a specific purpose in your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. For example, you might create infrastructure Windows machine sets and related machines so that you can move supporting Windows workloads to the new Windows machines. Here is a sample YAML that defines a Windows MachineSet object running on Microsoft Azure that the Windows Machine Config Operator (WMCO) can react upon. Please refer to the product documentation for the exact steps for configuring a Windows instance for your platform.
apiVersion: machine.openshift.io/v1beta1
kind: MachineSet
metadata:
labels:
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-cluster: <infrastructure_id>
name: <windows_machine_set_name>
namespace: openshift-machine-api
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-cluster: <infrastructure_id>
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-machineset: <windows_machine_set_name>
template:
metadata:
labels:
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-cluster: <infrastructure_id>
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-machine-role: worker
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-machine-type: worker
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-machineset: <windows_machine_set_name>
machine.openshift.io/os-id: Windows
spec:
metadata:
labels:
node-role.kubernetes.io/worker: ""
providerSpec:
value:
apiVersion: azureproviderconfig.openshift.io/v1beta1
credentialsSecret:
name: azure-cloud-credentials
namespace: openshift-machine-api
image:
offer: WindowsServer
publisher: MicrosoftWindowsServer
resourceID: ""
sku: 2022-datacenter
version: latest
kind: AzureMachineProviderSpec
location: <location>
managedIdentity: <infrastructure_id>-identity
networkResourceGroup: <infrastructure_id>-rg
osDisk:
diskSizeGB: 128
managedDisk:
storageAccountType: Premium_LRS
osType: Windows
publicIP: false
resourceGroup: <infrastructure_id>-rg
subnet: <infrastructure_id>-worker-subnet
userDataSecret:
name: windows-user-data
namespace: openshift-machine-api
vmSize: Standard_D2s_v3
vnet: <infrastructure_id>-vnet
zone: "<zone>"
Examine installed configured container runtime
From the command line, type oc get nodes -o widecode> and observe the output. You should be able to see that containerd is configured as the container runtime for the Windows node.

Upgrading from earlier versions of OpenShift and WMCO
The procedure for an upgrade that includes migration to containerd follows the regular upgrade process.
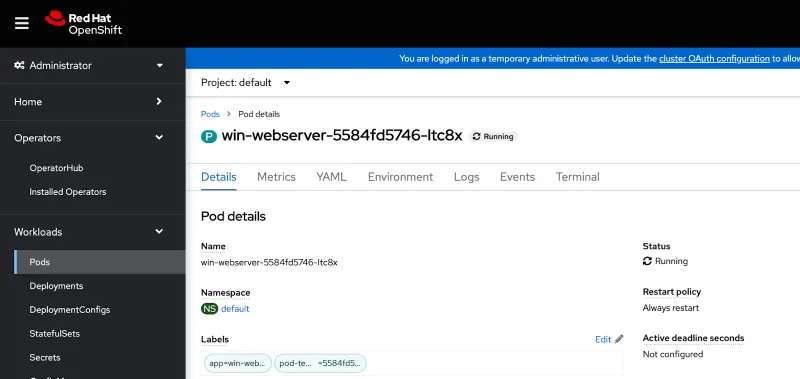
Run a sample workload
Deploy a sample application to the cluster and be surethe pod is running. Expose the application as a service.
Expand Networking->Services->Name of your service to note the external load balancer location as highlighted below.
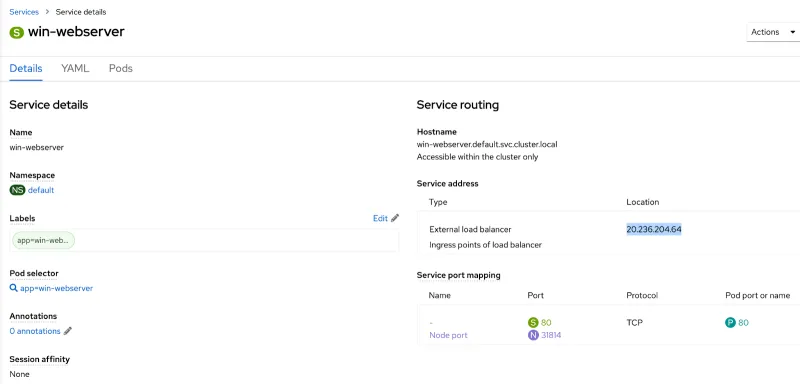
Hit that endpoint from a browser to be sure you can access the application.

저자 소개
유사한 검색 결과
Red Hat names Kevin Kennedy as global leader for the Red Hat partner ecosystem
Ford's keyless strategy for managing 200+ Red Hat OpenShift clusters
Machine learning model drift & MLOps pipelines | Technically Speaking
Building a foundation for AI models | Technically Speaking
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래
