Let’s say you’d like to test or deploy a new version of an API, without having to point users at a new hostname or abandoning the old version of the API. In this post, I’m going to show you how you can do just that using paths on Red Hat OpenShift.
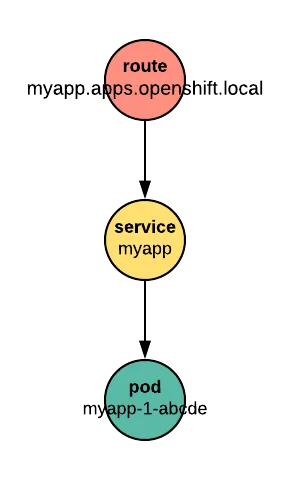
OpenShift routes connect users from the real world to an application running in an Red Hat OpenShift cluster. A route has two faces. A unique hostname, like myapp.apps.openshift.local, is seen by the outside world. Inside the cluster, the route connects to a service. The service is provided by one or more Pods running application code.
If we have a new version of our application to test, we can publish it with a new route, like myapp-beta.apps.openshift.local.
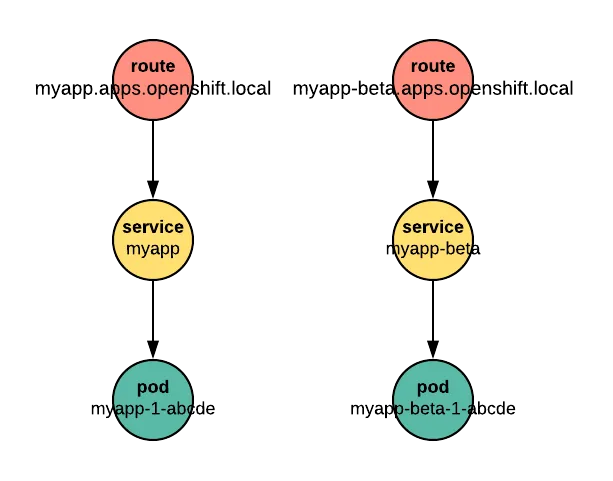
Then we run tests against it or let users try it at the “-beta” hostname. However, publishing the application with a new route and a new hostname can cause trouble. It may break Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) rules, complicating the handling of sessions and cookies, and it can introduce more Transport Layer Security (TLS) certificates to manage. It's probably easier to use one route with different paths to deliver requests to the beta version of the application. For example, the beta app could be reached at myapp.apps.openshift.local/beta.
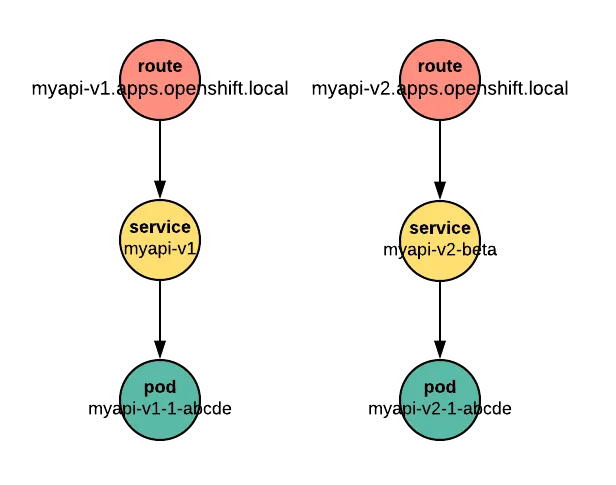
The pattern of one route per service is also awkward for APIs. APIs often follow a naming convention that segregates versions by URL path, for example myapi.apps.openshift.local/*v1*/health or myapi.apps.openshift.local/*v2*/health. It’s less common to see two versions of an API with two different hostnames, such as myapi-v1.apps.openshift.local/health and myapi-v2.apps.openshift.local/health.
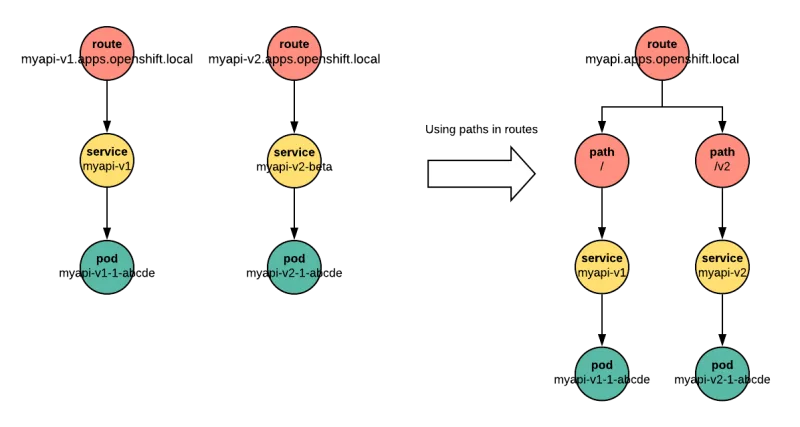
This post uses an example API server written in Node.js to show how you can deploy more than one version of an application beneath a single OpenShift route, by distinguishing each version with its own path.
We use minishift to spin up a local OpenShift 3.9 (or later) cluster for testing. The local Class C network represents the internet, but restricts our name resolution to the local scope for demonstration purposes. Replace the “.local”-based hostnames in the examples according to your internet domain and environment when exposing services publicly.
$ minishift start
-- Starting profile 'default'
-- Check if deprecated options are used ... OK
-- Checking if https://github.com is reachable ... OK
-- Checking if requested OpenShift version 'v3.9.0' is valid ... OK
-- Checking if requested OpenShift version 'v3.9.0' is supported ... OK
...
Using public hostname IP 192.168.99.10 as the host IP
Using 192.168.99.10 as the server IP
Starting OpenShift using openshift/origin:v3.9.0 ...
OpenShift server started.
The server is accessible via web console at:
https://192.168.99.10:8443
Through a bit of DNS magic outside the scope of this post, our base domain name for this example cluster will be 192.168.99.10.nip.io.
Example application
Nodejs-echo is an echo server. It provides a trivial API: Send it a message and it sends the same message back. Nodejs-echo source is available on GitHub.
Our *echo* API has two endpoints:
- /health Returns the API version as a demonstration of readiness.
- /echo/:msg Returns a duplicate of the received message msg.
Creating a portable application
The echo server is configured with three environment variables:
- IP
- PORT
- PREFIX
The first two variables control the IP and port on which the server listens. By default, it listens on the IP alias for all interfaces, 0.0.0.0, at port number 8080. These values don’t usually need adjustment when deploying the app on OpenShift.
PREFIX, the third environment variable, sets a path prefix for every endpoint. With PREFIX=/api, for example, nodejs-echo will respond to requests at the endpoints /api/health and /api/echo.
Deploy it on OpenShift
Let's create a new project to host our echo server:
$ oc new-project echo
Now using project "echo" on server "https://192.168.99.10:8443".
You can add applications to this project with the 'new-app' command. For example, try:
oc new-app centos/ruby-22-centos7~https://github.com/openshift/ruby-ex.git
to build a new example application in Ruby.
Then we deploy version v1 as the default version (which is in a branch named v1), with no PREFIX set:
$ oc new-app https://github.com/soukron/nodejs-echo#v1 --name api-v1
--> Found image 4cf5860 (3 weeks old) in image stream "openshift/nodejs" under tag "8" for "nodejs"
...
--> Creating resources ...
imagestream "api-v1” created
buildconfig "api-v1" created
deploymentconfig "api-v1" created
service "api-v1" created
--> Success
Build scheduled, use 'oc logs -f bc/api-v1' to track its progress.
Application is not exposed. You can expose services to the outside world by executing one or more of the commands below:
'oc expose svc/api-v1'
Run 'oc status' to view your app.
Finally, expose the api-v1 service to outside traffic with a route:
$ oc expose svc/api-v1 --hostname=api-echo.192.168.99.10.nip.io
route "api-v1" exposed
Test that the echo server works:
$ curl http://api-echo.192.168.99.10.nip.io/health
{"result":"ok","version":"v1"}
$ curl http://api-echo.192.168.99.10.nip.io/echo/HelloWorld
{"result":"ok","msg":"HelloWorld"}
Develop a new version
Meanwhile, development continues with improvements to our echo API. But we need to maintain compatibility for older clients that expect the v1 API. We could implement both versions in the same code branch, and manage the endpoints internally. But it can be easier to create a v2 branch where we implement the changes, and deploy it separately, without changing a single line of our frozen v1 branch.
We create a new branch, where we work on the following changes:
- Change the version string in the /health endpoint.
- Add a deprecation message about the /echo endpoint.
- Implement a new method, /say, that has some error handling.
Deploy the new version in OpenShift
Let's deploy our v2 version from our new branch:
$ oc new-app https://github.com/soukron/nodejs-echo#v2 --name api-v2
--> Found image 4cf5860 (4 weeks old) in image stream "openshift/nodejs" under tag "8" for "nodejs"
…
--> Creating resources ...
imagestream "api-v2" created
buildconfig "api-v2" created
deploymentconfig "api-v2" created
service "api-v2" created
--> Success
Build scheduled, use 'oc logs -f bc/api-v2' to track its progress.
Application is not exposed. You can expose services to the outside world by executing one or more of the commands below:
'oc expose svc/api-v2'
Run 'oc status' to view your app.
While our application image builds, we need to make two configuration changes to serve the new API version beneath its own path:
- Tell OpenShift to set the PREFIX environment variable to something like /v2, and inject it into our api-v2 deployment
$ oc env dc api-v2 PREFIX=/v2- Create a route with the same hostname as that for the v1 API, but with a path matching our PREFIX, /v2:
$ oc expose svc/api-v2 --hostname=api-echo.192.168.99.10.nip.io --path=/v2Now we can test the new version with our old methods:
$ curl http://api-echo.192.168.99.10.nip.io/v2/health
{"result":"ok","version":"v2"}
$ curl http://api-echo.192.168.99.10.nip.io/v2/echo/HelloWorld
{"result":"warning","reason":"this endpoint is deprecated, use say/ instead","msg":"HelloWorld"}
And the new method:
$ curl http://api-echo.192.168.99.10.nip.io/v2/say
{"result":"error","reason":"No message provided"}
$ curl http://api-echo.192.168.99.10.nip.io/v2/say/HelloWorld
{"result":"ok","msg":"HelloWorld"}
Summary
Using paths to distinguish different routes is a useful option, and might not be as obvious to OpenShift users as dedicating a hostname to every service. This post has tried to show how to configure an application to make different versions available under different paths.
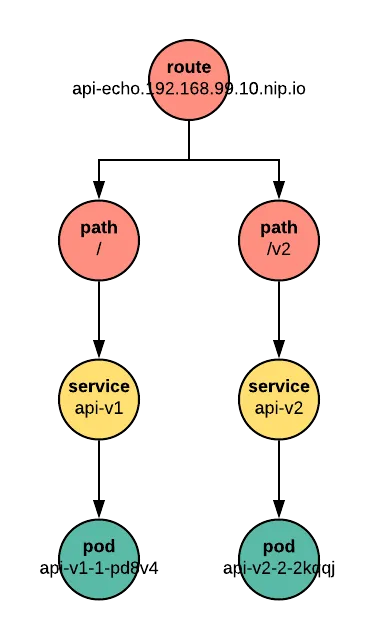
Let's take a last look at our project:
$ oc get pods,routes
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
api-v1-1-pd8v4 1/1 Running 0 26m
api-v2-2-2kqqj 1/1 Running 0 5m
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD
api-v1 api-echo.192.168.99.10.nip.io api-v1 8080-tcp None
api-v2 api-echo.192.168.99.10.nip.io /v2 api-v2 8080-tcp None
We see that we have two pods for our application, each built from a different branch. Both are exposed at the same hostname, but distinguished by their path.
Brand new to OpenShift? Check out the interactive tutorials complete with a hosted OpenShift environment at learn.openshift.com. Experienced application developer on the platform? Keep up to date and informed with theOpenShift documentation, or expand your OpenShift environment to Red Hat-hosted OpenShift Online or on-premise OpenShift Container Platform.
저자 소개
유사한 검색 결과
Simplify Red Hat Enterprise Linux provisioning in image builder with new Red Hat Lightspeed security and management integrations
F5 BIG-IP Virtual Edition is now validated for Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization
Air-gapped Networks | Compiler
Can Kubernetes Help People Find Love? | Compiler
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래
