In Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.5, we’ve introduced virtual data optimizer (VDO). VDO allows you to save disk space and reduce replication bandwidth with the help of data compression and data deduplication.
In this blog post I want to walk you through how you can use the cockpit Web admin console that comes with Red Hat Enterprise Linux, to set up VDO and save substantial amount of space for your virtual machine images.
If you run a lot of VMs of the same OS, then you typically have a lot of bits that are the same, over and over again. A lot of the data that makes up the operating system is identical between the hosts. As your deployment grows with new VMs, the more storage you need to buy, even though a lot of the bits in the VMs are the same.
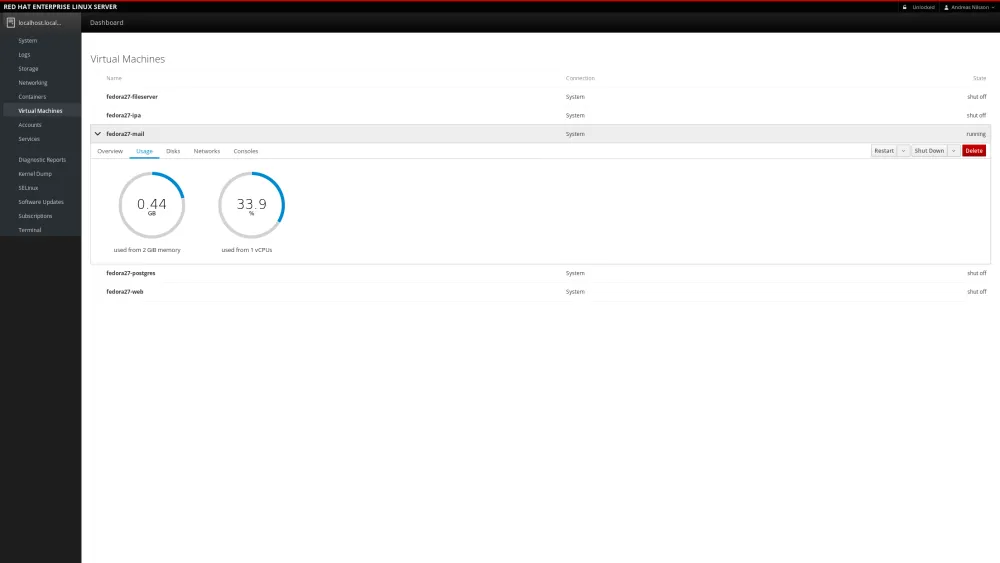
As you can see, I run a couple of Virtual Machines on this host.
If we go over to the storage page, we see that we’re using 100 GiB gigabytes to store these images. Running short on disk space.
So let’s try and see what happens if we move the VM images to a VDO device instead.
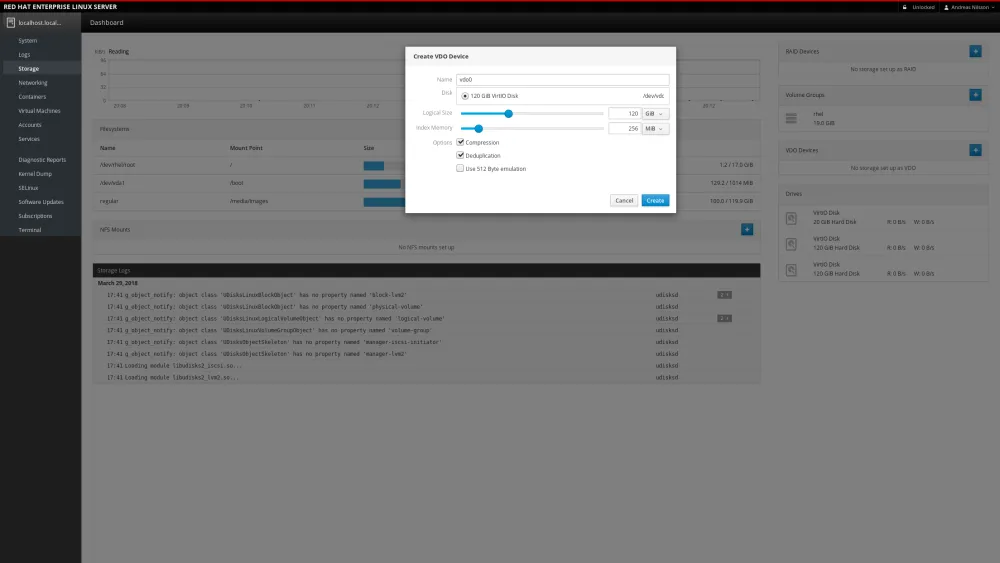
We create a new VDO device and select a empty block device.
We set both compression and deduplication. Most of the time this is the best choice, but both of these features have overhead. For example, compression consumes extra CPU resources. If data being stored is already compressed, as is the case with multimedia file formats (jpg, gif, mp3, mp4, etc..) , then the compression option should be disabled. Similarly textual database content (such as XML data) compresses well, but there aren’t likely to be duplicate 4K blocks in a single database instance. For the primary database application server, turning dedupe off and enabling compression can boost performance.
We then create the filesystem, and mount it on the temporary location /media/temporary/.
Then we copy the files from /media/images to /media/images2/.
Then unmount /media/temporary and mount the disk on /var/lib/libvirt instead.
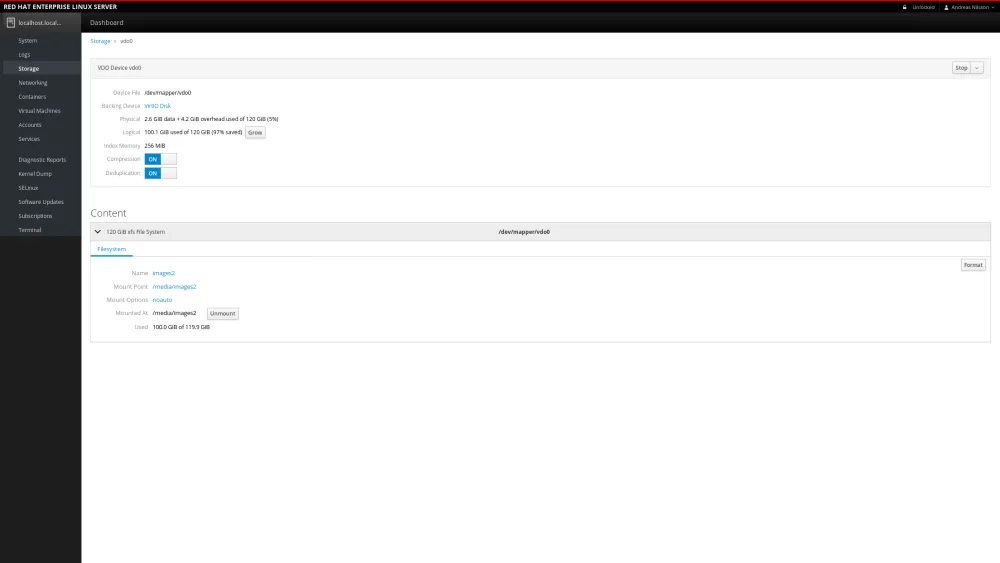
On the filesystem level, the logical space is still 100 GiB, but if we dive in to the VDO details page, we see that the physical size only takes up 2.6 GiB, making a space saving of 97%.
In this case, it’s possible to grow the logical size up to 600 GiB.
You can try this yourself on a Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.5 server, by installing the package cockpit, that gives you the web console, and log in to it with your web browser at https://<ip-address>:9090.
Learn more about cockpit administrator console and four troubleshooting tasks for Linux experts and beginners in this webinar April 19th: REGISTER.
저자 소개
유사한 검색 결과
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform: Measuring Business Impact with Dashboard and Analytics
Friday Five — December 5, 2025 | Red Hat
Technically Speaking | Platform engineering for AI agents
Technically Speaking | Driving healthcare discoveries with AI
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래