Jenkins is a popular open source tool for DevOps automation (build/test/deploy), with more than 8.5 million defined jobs worldwide. Aside from a large and ever-growing community, Jenkins has a 1000+ plugin ecosystem and robust mechanism for building DevOps pipelines called "Pipeline." The Pipeline functionality offers a simple yet powerful, text-based DSL for creating multi-stage software delivery flows.
The CloudBees Jenkins Platform packages Jenkins core with additional enterprise-ready features and integrations --- including a CloudBees-specific feature that integrates the Red Hat OpenShift command line interface into your Pipelines. OpenShift aims to modernize the way enterprises develop, host, and scale their applications. Layering a light, well-thought-out container application platform layer on top of Kubernetes, OpenShift is an easy way to host and scale apps.
While OpenShift has some basic Jenkins facilities built in, using OpenShift and CloudBees Jenkins Platform together is not only a natural fit but a key success factor for your OpenShift implementation.
This blog walks you through a reference deployment pipeline automated with the Pipeline plugin for deploying to OpenShift, complete with source to image creation, advanced test phases, gated approvals, and deployments, using the best of OpenShift and the CloudBees Jenkins Platform.
The Idea: Reference Pipeline
OpenShift Layout
The OpenShift platform will be set up with separate projects per environment stack. This model is recommended by Red Hat for OpenShift environment isolation to test / validate your projects before deploying a project and its applications to production.
In our example, we’re building a fictitious mobile web site for the Mobile Team at a bank, so we’ll create projects as follows:
- Mobile Team - Development
- Mobile Team - Test
- Mobile Team - Production
Within your projects, you’ll want to set up your OpenShift service accounts with the appropriate permissions to handle the CLI tasks you’ll use in your pipeline (primary view/edit access for deployment config / route creation, etc.).
Don’t worry about adding applications yet, that’s where Pipeline comes in.
Jenkins Pipeline
OpenShift does have some basic build facilities built in, but the default Maven-based build (for JEE projects) within OpenShift is quite simple. In a production setting, you need a more robust build automation capability - capable of running your unit, integration, functional, etc. tests. Say hello to the Jenkins Pipeline plugin.
Getting Started
Start by creating a Pipeline:
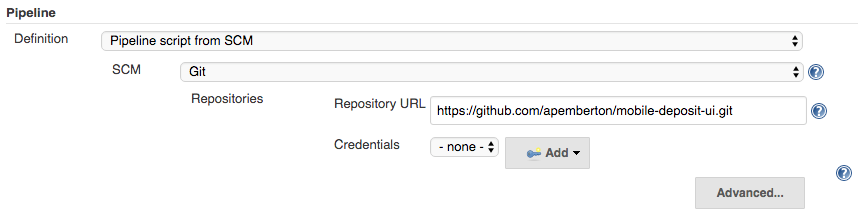
Then, treat your Pipeline as code, by simply selecting “Pipeline Script from SCM”:
This tells Jenkins to look for a file named "Jenkinsfile" alongside your application’s source code.
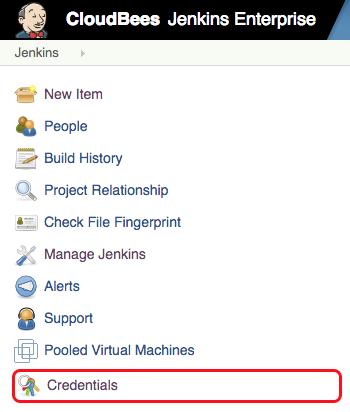
To integrate with OpenShift, you’ll need to add your OpenShift credentials in Jenkins. Luckily, Jenkins manages credentials safely and easily:
For our Pipeline, we’ll have a basic, 3-stage deployment cycle through the development, test, and production OpenShift projects. In my example, I’ve added Credentials in Jenkins for service accounts from my three OpenShift projects. We’ll also have explicit stages for testing and validation before proceeding with additional deployments.
Our initial build stage will simply checkout the application’s source (from the same source code manager as it found the Jenkinsfile:
stage 'build'
node{
checkout scm
sh 'mvn -DskipTests clean package'
stash name: 'source', excludes: 'target/'
archive includes: 'target/*.war'
}
Subsequent stages of our pipeline can then further validate that the application’s source is really ready for production - for example, running unit (or other) tests and scanning for quality:
stage 'test[unit&quality]'
parallel 'unit-test': {
node {
unstash 'source'
sh 'mvn -Dmaven.test.failure.ignore=true test'
step([$class: 'JUnitResultArchiver', testResults: '**/target/surefire-reports/TEST-*.xml'])
}
if(currentBuild.result == 'UNSTABLE'){
error "Unit test failures"
}
}, 'quality-test': {
node {
unstash 'source'
sh 'mvn sonar:sonar'
}
}
You’ll notice using the Pipeline plugin with Jenkins provides a really easy way to run builds in parallel. Jenkins can also easily capture your test results for trending:
Now that we’ve further validated our source code (beyond a basic build), let’s deploy to OpenShift.
Deploying to OpenShift
To make integrating with OpenShift from Jenkins even easier, CloudBees has launched a plugin for calling the OpenShift CLI from within Jenkins. More documentation is available on the CloudBees Network.
Its primary features are to:
- Treat the OpenShift CLI as a tool within Jenkins, easily installing and exposing the OpenShift CLI from your Jenkins build agents
- Integrate with Jenkins Credentials to securely manage credentials (username/password or oauth tokens) in your OpenShift pipelines
Our first use of the OpenShift CLI will be to push our application source code to our development project:
node{
unstash 'source'
wrap([$class: 'OpenShiftBuildWrapper', url: OS_URL, credentialsId: OS_CREDS_DEV]) {
oc('project mobile-development -q')
def bc = oc('get bc -o json')
if(!bc.items) {
oc("new-app --name=mobile-deposit-ui --code='.' --image-stream=jboss-webserver30-tomcat8-openshift")
wait('app=mobile-deposit-ui', 7, 'MINUTES')
oc('expose service mobile-deposit-ui')
} else {
oc("start-build mobile-deposit-ui --from-dir=. --follow")
}
}
}
In this example, we check to see if a buildconfig already exists for our application, starting a build if so, otherwise creating a new app in development from the source code we’ve already checked out in the Jenkins workspace.
One will note, this flow does cause the initial application binary to be built twice: once on your Jenkins agent for testing and again on OpenShift for deployment. While there are some workarounds to allow more easily deploying pre-built binaries, we felt it was important to show a more native source-2-image build. We look forward to enhancements in this area (eg: a binary-2-image build) from OpenShift in future releases.
Test Deployment
After you’ve checked out, built, and unit tested your source, you can use the CLI to perform a deployment to your test project. In this scenario, we’ll simply create a new app and deployment in test using the Docker image published in the development project’s Docker registry:
stage name:'deploy[test]', concurrency:1
input "Deploy mobile-deposit-ui#${env.BUILD_NUMBER} to test?"
node{
wrap([$class: 'OpenShiftBuildWrapper', url: OS_URL, credentialsId: OS_CREDS_TEST]) {
def project = oc('project mobile-development -q')
def is = oc('get is -o json')
def image = is?.items[0].metadata.name
oc("tag $image:latest $image:test")
project = oc('project mobile-test -q')
def dc = oc('get dc -o json')
if(!dc.items){
oc("new-app mobile-development/$image:test")
wait('app=mobile-deposit-ui', 7, 'MINUTES')
oc('expose service mobile-deposit-ui')
}
}
}
From here, you can trigger any number of additional layers of tests and deployments, per your team’s preferred delivery approach. For example, integrating with Selenium for functional tests after the test project deployment:
stage 'test[functional]'
node {
unstash 'source'
sh 'mvn verify'
}
checkpoint 'functional-tests-complete'
CloudBees Jenkins Enterprise offers proprietary extensions to Jenkins Pipeline DSL, such as the ‘checkpoint’ DSL above. Checkpoints allow you to restart a Pipeline from a known place, for example, after a successful deployment or test suite completes.
Putting it altogether: Example Pipeline
With that, we’ve built a Jenkins Pipeline for Red Hat OpenShift! By combining CloudBees Jenkins Enterprise and Red Hat OpenShift with your organization’s tools of choice for validating your software (jUnit tests, Sonar, and Selenium in this example).
When viewed from Jenkins Enterprise:
Of course, because our application is now running on OpenShift, it’s easy to scale either through the OpenShift console or via the CLI through further refinements to your Jenkins file:
For example, it’d be easy to layer in a blue/green deployment strategy from here.
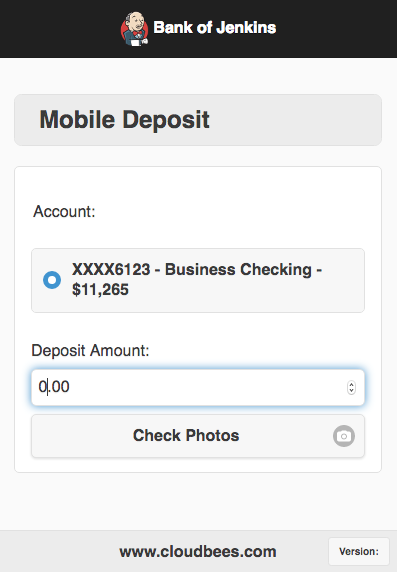
Hitting your production route, you should now see your production application deployed:
If you're interested to learn more, attend my DevNation session, Ultimate DevOps with Jenkins and OpenShift. We've also added the full source code for the example Pipeline to https://github.com/cloudbees/openshift-example.
Learn more about our integration on OpenShift Hub.
저자 소개
유사한 검색 결과
Redefining automation governance: From execution to observability at Bradesco
Introducing OpenShift Service Mesh 3.2 with Istio’s ambient mode
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
Lightspeed automation with generative AI | Technically Speaking
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래