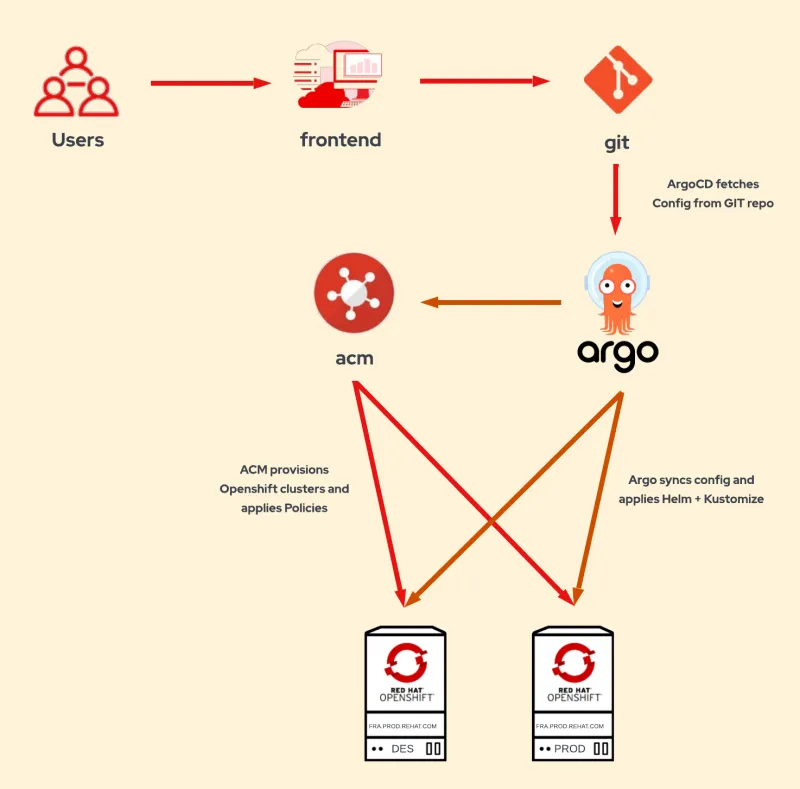
In the Introduction, we described a solution where ACM is used to provision Openshift clusters using Gitops. The users fill in the clusters parameters in a form, which are written to a yaml/json object and pushed to git. ArgoCD synchronizes these objects into the ACM cluster. The cluster is provisioned with ACM, which automatically adds the clusters to Openshift GitOps for Day 2. And then, the cluster is configured automatically with ArgoCD using Helm + Kustomize, and ACM policies.
In this article, we'll explain in more detail the first part of the solution: provisioning of Openshift clusters using GitOps with ACM.
If you're interested in the second part of the solution, Configuring Openshift cluster with ApplicationSets using Helm+Kustomize and ACM Policies, don't miss the next article.
Frontend
We need a frontend (web application) to create the objects needed by ACM to provision the clusters. This frontend can be Anible Automation Platform (Tower), Jenkins, or any custom web application with a form. Although ACM can be used as frontend to provision the clusters, there are some drawbacks: ACM stores the objects locally, not in git; ACM has a fixed form for cluster creation, which cannot be customized.

This solution doesn't rely on any specific application/orchestrator. This solution just need that this application writes 2 configuration files: conf.yaml and provision.yaml.
Cluster Parameters
Instead of creating all the objects needed by ACM in the frontend, we just need to create a 2 objects:
conf.yaml: contains all the configuration parameters of the cluster.provision.yaml: contains the parameters needed to provision the cluster, likeintall-config.yaml.
In our example repository, we can see these files for the cluster example zamora.dev.redhat.com:
├── clusters
│ └── dev
│ └── zamora.dev.redhat.com
│ ├── conf.yaml
│ ├── provision.yaml
│ └── overlay
│ └── kustomization.yaml
└── conf
└── dev
├── conf.yaml
└── provision.yaml
There are no specif format for conf.yaml and provision.yaml, but we follow these guidelines:
- In the folder
conf/<environment>, we sould add the common configuration for each environment. - In the folder
clusters/<environment>/<cluster>, we should add the specific configuration for the cluster. - In
conf.yaml, we should add the configuration needed for Day 2, explained in the next part: Configuring OpenShift cluster with ApplicationSets using Helm+Kustomize and ACM Policies. - In
provision.yaml, we should add the configuration needed for provisioning, for our Cluster-provisioning Helm chart. You can see an example of provision.yaml for the cluster here, and for the environment here.
Cluster-provisioning ApplicationSet
We’re using an ApplicationSet to search for provision.yaml files, and it’ll create an Argo Application for each file. Each provision application will create all the ACM objects needed to deploy an OpenShift cluster.

This application uses a Helm chart to deploy all the ACM objects needed:
- ClusterDeployment
- KlusterletAddonConfig
- MachinePool
- ManagedCluster
- Namespace
- Secrets: pull-secret, install-config, ssh-private-key and creds
The Helm ACM provision chart has these templates:
base
└── provision
├── Chart.yml
└── templates
├── ClusterDeployment.yml
├── KlusterletAddonConfig.yml
├── MachinePool.yml
├── ManagedCluster.yml
├── Namespace.yml
└── Secrets.yml
The ApplicationSet creates an Argo Application for each provision.yaml under clusters folder using the path: base/provision/openshift-provisioning and the config files:
/conf/{{cluster.environment}}/provision.yaml/clusters/{{cluster.environment}}/{{cluster.fqdn}}/provision.yaml
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: ApplicationSet
metadata:
name: cluster-provisioning
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
generators:
- git:
repoURL: https://github.com/albertogd/gitops-for-organizations.git
revision: main
files:
- path: "clusters/**/provision.yaml"
template:
metadata:
name: "provision-{{cluster.environment}}-{{cluster.name}}"
labels:
environment: "{{cluster.environment}}"
cluster: "{{cluster.fqdn}}"
region: "{{cluster.region}}"
cloud: "{{cluster.cloud}}"
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/albertogd/gitops-for-organizations.git
targetRevision: main
path: base/provision/openshift-provisioning
helm:
valueFiles:
- /conf/{{cluster.environment}}/provision.yaml
- /clusters/{{cluster.environment}}/{{cluster.fqdn}}/provision.yaml
destination:
server: 'https://kubernetes.default.svc'
namespace:
syncPolicy:
syncOptions:
- preserveResourcesOnDeletion=true
Use of preserveResourcesOnDeletion
Using an ApplicationSet to dynamically generate the provision applications has a risk involved: if the ApplicationSet is deleted. the following occurs (in rough order):
The ApplicationSet resource itself is deleted Any Application resources that were created from this ApplicationSet (as identified by owner reference) Any deployed resources (Deployments, Services, ConfigMaps, etc) on the managed cluster, that were created from that Application resource (by Argo CD), will be deleted.
To prevent the deletion of the resources of the Application, such as ManagedCluster, ClusterDeployment, etc, set .syncPolicy.preserveResourcesOnDeletion to true in the ApplicationSet. This syncPolicy parameter prevents the finalizer from being added to the Application.
Cluster Provision
Once the ACM objects are synchronized to the cluster, ACM will start to provision the new cluster.
Day 2 Configuration
To add each new cluster to GitOps, we need to create this 3 objects in ACM:
- ManagedClusterSetBinding
- Placement
- GitOpsCluster
These objects will be also stored in git, as explained in the next part, Configuring Openshift cluster with ApplicationSets using Helm+Kustomize and ACM Policies:
└── clusters
└── acm-hub
├── applications
....
└── gitops-cluster
├── GitOpsCluster.yaml
├── ManagedClusterSetBinding.yaml
├── Placement.yaml
└── kustomization.yaml
A ManagedClusterSetBinding resource allows us to bind a ManagedClusterSet resource to a namespace. In our example, we want to bind the clusterSet vmware to the openshift-gitops namespace:
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1beta1
kind: ManagedClusterSetBinding
metadata:
name: vmware
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
clusterSet: vmware
The Placement allows us to select clusters based on labels, in the case, platform = vmware:
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1beta1
kind: Placement
metadata:
name: vmware
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
predicates:
- requiredClusterSelector:
labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: platform
operator: "In"
values:
- vmware
The GitOpsCluster custom resource allows us to register the clusters selected with a Placement to an ArgoCD server:
apiVersion: apps.open-cluster-management.io/v1beta1
kind: GitOpsCluster
metadata:
name: argo-acm-clusters
namespace: openshift-gitops
spec:
argoServer:
cluster: local-cluster
argoNamespace: openshift-gitops
placementRef:
kind: Placement
apiVersion: cluster.open-cluster-management.io/v1beta1
name: vmware
namespace: openshift-gitops
Continue to the second part: Configuring Openshift cluster with ApplicationSets using Helm+Kustomize and ACM Policies
Return to the Introduction: GitOps for organizations: provisioning and configuring Openshift clusters automatically
저자 소개
Alberto Gonzalez de Dios is a Senior Cloud consultant: Automation and OpenShift specialist. He joined Red Hat in 2018, and he is certified in Azure, AWS and Red Hat (Red Hat Certified Architect Level II).
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래
