Through open source innovation, Red Hat OpenShift has incrementally enabled Precision Time Protocol (PTP) use cases. Initially, an Ordinary Clock (OC) was provided in Red Hat OpenShift 4.7. This supported a single follower clock port which synchronized the system clock to an upstream time leader system. This functionality used the open source driver and hardware provided by Intel for the x710 Fortville Network Interface Card (NIC) and the ptp4l and phc2sys software elements from the Linux PTP Project. Eventually, this evolved to support the Boundary Clock (BC) use case in Red Hat OpenShift 4.9.
The BC builds on the OC by not only having a single follower clock port but also multiple leader clock ports to synchronize systems downstream. This was enabled by the open source driver included in the Linux kernel and e810 Columbiaville NIC family. These specific NICs offer a single PTP Hardware Clock (PHC) shared across all physical interfaces avoiding the need for software level synchronization. As this PHC is synchronized through the follower clock port, the PHC time is shared with the local master clock ports for the downstream devices. Red Hat OpenShift 4.11 expanded this BC functionality on Dual Intel e810 NICs (without high availability, which we plan to deliver in 2024). All of these use cases were initially needed for the Distributed Virtual Radio Access Network (D-vRAN) Far Edge use case. However, these capabilities need not be limited to telecommunications use cases.
With 4.14.6, Red Hat OpenShift is ready to provide a technical preview of a Telecom Grandmaster (T-GM). This system will be the leader clock for an entire domain of systems. A T-GM has 2 additional capabilities over a BC:
- It can synchronize itself to a very accurate time source such as GNSS.
- It contains a digital phase-locked loop (DPLL), an electronic circuit with an oscillator that constantly adjusts the frequency output to match the frequency of an input signal (like the GNSS).
For 4.14, these new components are provided by Intel through their Westport Channel (WPC) NIC (E810-XXVDA4T).
To bring this software to market, Red Hat collaborated on 2 upstream projects to enable this functionality. The first collaboration was between Intel and the Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) Networking Services Team to enable the DPLL Configuration API in the Linux kernel. The teams worked very closely to not only provide upstream acceptance, but also the successful backporting of the new functionality into the RHEL 9 Linux kernel. This provides a more consistent, tested, and stable experience which RHEL customers have come to expect. The second collaboration was with the Linux PTP Project project to add ts2phc. This software synchronizes the Physical Hardware Clock (PHC) to external time stamp signals like the GNSS module on the Intel WPC NIC.
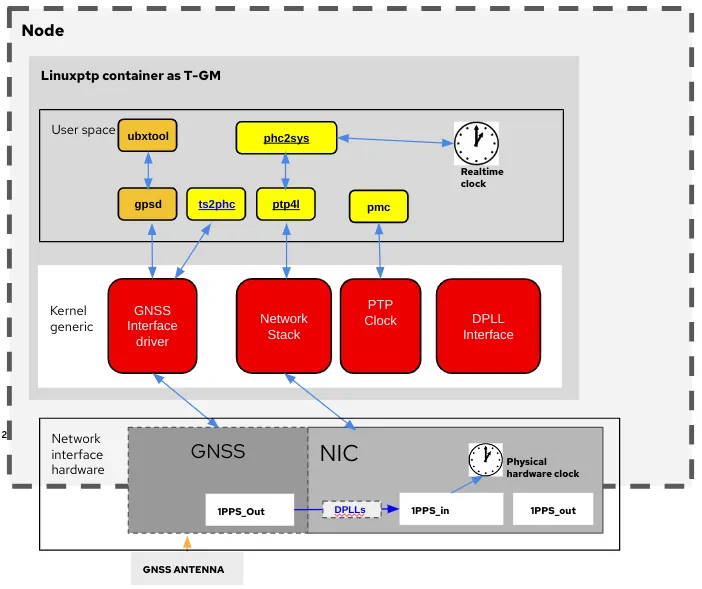

Open Source Software Elements Needed to Provide a T-GM
To simplify the configuration of all these elements, a single Custom Resource Definition (CRD) is provided by the PTP Operator to deploy the T-GM. The PTP Operator also handles the determination of the PTP clock class based on the T-GM state and events and metrics related to the operation of the T-GM.
Red Hat OpenShift 4.14.6 supports a T-GM built upon a single Intel WPC. Red Hat is currently working on expanding this technical preview to support a T-GM built upon two Intel WPCs. As these capabilities mature, this can alleviate the need for GNSS in the Cell Site Router in the D-vRAN Far Edge use case reducing total cost of ownership.
As you can see, Red Hat continues to demonstrate our leadership in precision timing and has greatly evolved the OpenShift PTP capabilities release over release. This achievement can only be delivered leveraging the power of community collaboration and open source software. As such, we’d like to extend a big thanks to Intel and the linuxptp community for helping to pull this solution together.
저자 소개
Ken Young has 30 years of Telecommunication product development experience across many technologies including Ethernet, multi-protocol label switching and router fast datapath. He joined Red Hat in 2020 to enable Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform for usage in the Telecom VRAN Far Edge. His current focus is on high performance timing in this operator use case.
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래