This is a guest post by Michael Mattsson Principal Tech Marketing Engineer at HPE.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise and Red Hat have over two decades of innovation in our joint alliance partnership spanning a wide variety of infrastructure solutions built on open source software and high performance hardware backed by a customer-focused joint support engagement that ensures an unsurpassed product experience.
We are excited today to formally introduce a new solution as both teams have been heads down delivering the first Operator to achieve Red Hat OpenShift container storage interface (CSI) certification. The upstream HPE CSI Driver for Kubernetes has been repackaged, hardened and delivered by HPE and certified by Red Hat. The HPE CSI Operator for Kubernetes is published in the Red Hat Ecosystem Catalog and can be deployed from the OpenShift OperatorHub. The HPE CSI Driver is a unified CSI driver supporting multiple enterprise block storage (iSCSI and Fibre Channel) platforms through a pluggable architecture. HPE Nimble Storage, HPE Primera and HPE 3PAR are currently supported and certified.
Technology Overview
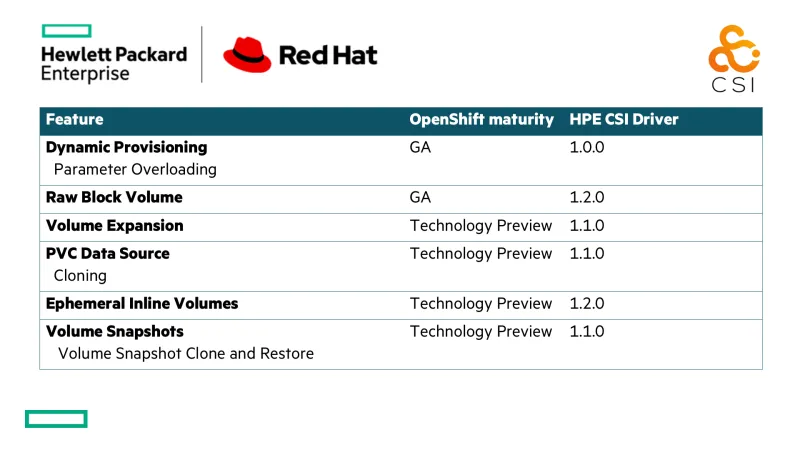
The HPE CSI Driver is a comprehensive CSI driver currently conforming to version 1.2 of the CSI specification. Data management capabilities such as snapshots and cloning are available through CSI or StorageClass parameter overloading during provisioning to allow Red Hat OpenShift users to immediately take advantage of their HPE storage platforms. CSI native cloning and snapshots is currently available as a “Technology Preview” in Red Hat OpenShift 4.4. Other notable features currently under “Technology Preview” in Red Hat OpenShift is CSI inline ephemeral volumes and expanding CSI volumes. All features are marked GA by the HPE CSI Driver and customer may rest assured they’ve invested in a future proof storage platform for Red Hat OpenShift.
The HPE CSI Driver is designed to support multiple storage backends and a clean separation has been created between CSI and the storage backends. This allows the backend storage teams to focus on making sure they present their platform capabilities in the most efficient way possible. A separate team is dedicated to ensuring all the Kubernetes, OpenShift and CSI minutia conforms to recent standards, conventions and certifications. The interface against the backend storage platforms is called Container Storage Providers (CSP). The CSP follows an open source specification that allows any vendor with a block storage (iSCSI or Fibre Channel) protocol to implement a CSP. Both Nimble and Primera/3PAR CSPs run on the Kubernetes cluster as ephemeral API gateways but the CSP may run embedded on the storage platform itself (or elsewhere) as long as it allows communication from the cluster and follow the CSP specification.
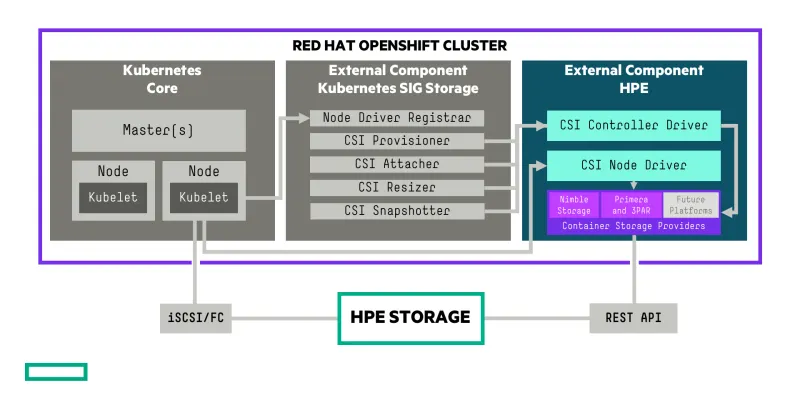
The architecture also allows building extensions either to CSI itself using traditional sidecars or extend functionality by other means. Any such extension will become available for existing CSPs automatically. HPE recently announced a beta of the NFS Server Provisioner feature in version 1.2.0 of the HPE CSI Driver. It allows the CSI driver to create ReadWriteMany or ReadOnlyMany (RWX/ROX) PersistentVolumeClaims by transparently spinning up a NFS server on the Kubernetes cluster served by a ReadWriteOnce (RWO) volume. This lends itself well for certain use cases where shared storage between Pods within the same Namespace is required which isn’t possible with strict block storage, which only supports RWO. Expect more innovations like these from HPE in the near future!
Get Started!
Installing the HPE CSI Operator may be performed either via the OpenShift Console or the OpenShift CLI. For the purpose of demonstrating the installation process, we’ll use oc. How to use the OpenShift Console to install the CSI operator is available on the HPE Storage Container Orchestrator Documentation portal (SCOD).
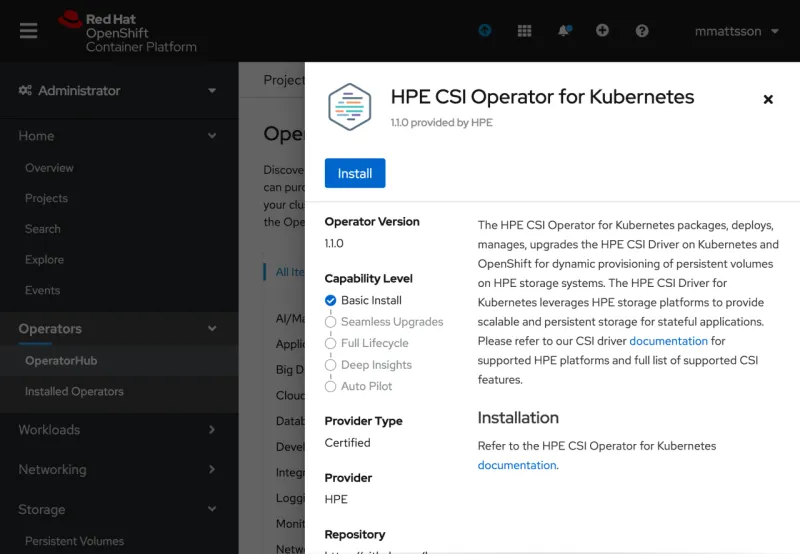
A preview of what the certified HPE CSI Operator for Kubernetes looks like in the OpenShift Console.
The CSI driver requires privileged access. For the driver to work correctly a custom SecurityContextConstraint needs to be applied. But, first let’s create a new Project where we would deploy the CSI operator.
oc new-project hpe-csi-driver --display-name="HPE CSI Driver for Kubernetes"
The next set of YAML stanzas may be created by running oc create -f- and paste the YAML into the terminal. Hit CTRL-D on a new line to apply it.
Create the custom SCC.
---
kind: SecurityContextConstraints
apiVersion: security.openshift.io/v1
metadata:
name: hpe-csi-scc
allowHostDirVolumePlugin: true
allowHostIPC: true
allowHostNetwork: true
allowHostPID: true
allowHostPorts: true
allowPrivilegeEscalation: true
allowPrivilegedContainer: true
allowedCapabilities:
- '*'
defaultAddCapabilities: []
fsGroup:
type: RunAsAny
groups: []
priority:
readOnlyRootFilesystem: false
requiredDropCapabilities: []
runAsUser:
type: RunAsAny
seLinuxContext:
type: RunAsAny
supplementalGroups:
type: RunAsAny
users:
- system:serviceaccount:hpe-csi-driver:hpe-csi-controller-sa
- system:serviceaccount:hpe-csi-driver:hpe-csi-node-sa
- system:serviceaccount:hpe-csi-driver:hpe-csp-sa
- system:serviceaccount:hpe-csi-driver:hpe-csi-operator-sa
- system:serviceaccount:hpe-nfs:hpe-csi-nfs-sa
volumes:
- '*'
Next, an OperatorGroup and Subscription needs to be created.
---
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1
kind: OperatorGroup
metadata:
name: hpe-csi-driver-for-kubernetes
namespace: hpe-csi-driver
spec:
targetNamespaces:
- hpe-csi-driver
---
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: hpe-csi-operator
namespace: hpe-csi-driver
spec:
channel: stable
name: hpe-csi-operator
source: certified-operators
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
Watch the CSI operator being rolled out.
oc rollout status deploy/hpe-csi-driver-operator -n hpe-csi-driver
The next step involves creating a HPECSIDriver. This is where you need to make conscious choice if you want to use HPE Nimble Storage (nimble) or HPE Primera/HPE 3PAR (primera3par), which share the same backendType.
apiVersion: storage.hpe.com/v1
kind: HPECSIDriver
metadata:
name: csi-driver
namespace: hpe-csi-driver
spec:
backendType: nimble
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
logLevel: info
secret:
backend: 192.168.1.100
create: true
password: admin
servicePort: '8080'
username: admin
storageClass:
allowVolumeExpansion: true
create: false
defaultClass: false
name: hpe-standard
parameters:
accessProtocol: iscsi
fsType: xfs
volumeDescription: Volume created by the HPE CSI Driver for Kubernetes
Note: The backend parameter refers to the IP address of the management interface on the storage system.
The next step would be to create a StorageClass to allow dynamic PersistentVolume provisioning from PersistentVolumeClaims. Below is a basic StorageClass that will be marked as “default” on the cluster.
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
annotations:
storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class: "true"
name: hpe-storageclass
provisioner: csi.hpe.com
parameters:
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: xfs
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-name: nimble-secret
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-namespace: kube-system
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-publish-secret-name: nimble-secret
csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-publish-secret-namespace: kube-system
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-publish-secret-name: nimble-secret
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-publish-secret-namespace: kube-system
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: nimble-secret
csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: kube-system
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: nimble-secret
csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: kube-system
description: "Volume created by the HPE CSI Driver for Kubernetes”
fsMode: "0770"
reclaimPolicy: Delete
allowVolumeExpansion: true
The StorageClass parameters are unique for the different CSPs. These are documented on SCOD for HPE Nimble Storage and HPE Primera/HPE 3PAR.
Next steps could be to deploy any application from OperatorHub requiring persistent storage, such as MariaDB or MongoDB.
Learn More
The Red Hat OpenShift certified HPE CSI Operator for Kubernetes is available now. Current supported platforms are HPE Nimble Storage, HPE Primera and HPE 3PAR. Sign up to the HPE DEV Slack community at slack.hpedev.io (or login at hpedev.slack.com if you already have signed up) to chat with the HPE staff, partners and customers. Also stay informed via our announcements and updates, we hang out in #kubernetes, #nimblestorage and #3par-primera.
- Check out the HPE CSI Operator in the Red Hat Container Catalog
- Learn how to install the HPE CSI Operator on HPE Storage - Container Orchestrator Documentation (SCOD) portal
- Source code for the HPE CSI Driver is available on GitHub
- Explore how Persistent Storage works in the Red Hat OpenShift documentation
- Learn more about HPE Nimble Storage, HPE Primera and HPE 3PAR at hpe.com/storage
- Join the HPE Developer Community to learn from other HPE developers who use HPE products
저자 소개
Red Hatter since 2018, technology historian and founder of The Museum of Art and Digital Entertainment. Two decades of journalism mixed with technology expertise, storytelling and oodles of computing experience from inception to ewaste recycling. I have taught or had my work used in classes at USF, SFSU, AAU, UC Law Hastings and Harvard Law.
I have worked with the EFF, Stanford, MIT, and Archive.org to brief the US Copyright Office and change US copyright law. We won multiple exemptions to the DMCA, accepted and implemented by the Librarian of Congress. My writings have appeared in Wired, Bloomberg, Make Magazine, SD Times, The Austin American Statesman, The Atlanta Journal Constitution and many other outlets.
I have been written about by the Wall Street Journal, The Washington Post, Wired and The Atlantic. I have been called "The Gertrude Stein of Video Games," an honor I accept, as I live less than a mile from her childhood home in Oakland, CA. I was project lead on the first successful institutional preservation and rebooting of the first massively multiplayer game, Habitat, for the C64, from 1986: https://neohabitat.org . I've consulted and collaborated with the NY MOMA, the Oakland Museum of California, Cisco, Semtech, Twilio, Game Developers Conference, NGNX, the Anti-Defamation League, the Library of Congress and the Oakland Public Library System on projects, contracts, and exhibitions.
유사한 검색 결과
Ford's keyless strategy for managing 200+ Red Hat OpenShift clusters
F5 BIG-IP Virtual Edition is now validated for Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization
Can Kubernetes Help People Find Love? | Compiler
Scaling For Complexity With Container Adoption | Code Comments
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래
