Step-by-step Deploy of Single Node OpenShift (SNO)
Red Hat recently released a technology preview of an assisted installer for single node OpenShift (SNO). A Red Hat blog post about this is available here.
As stated in the blog, more and more organizations are looking to deploy and manage containers at the edge, and that can introduce challenges related to space, networking, and other limitations.
On the topic of space, and edge, the International Space Station is actually running a single node OpenShift instance for DNA sequencing. More about that in this article.
So, let’s get started. First of all, you need to decide where to install the node. Cloud, virtual, or physical machine? All is supported, as long as you can boot the machine from the generated image. The following hardware requirements must be considered:
Basic install without virtualization:
CPU: 8 cores (or 4 cores with hyperthreading enabled)
RAM: 32GB
HDD: 120GB
If you want to install with virtualization, CPU requirements are 12 cores/threads on bare metal.
And, of course, internet access, since SNO needs to communicate with our SaaS service.
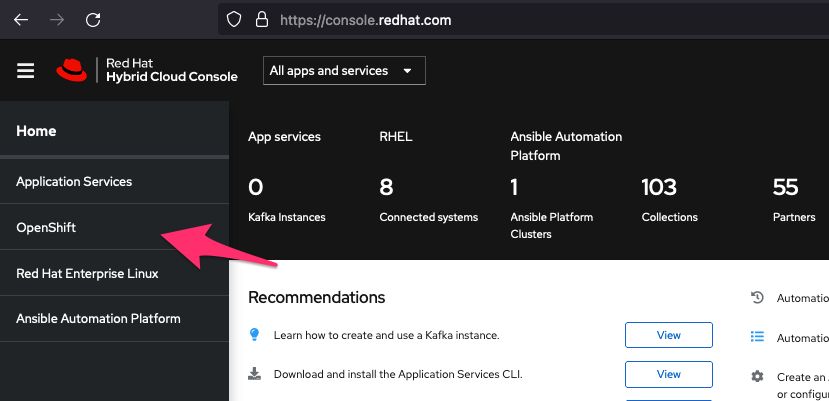
With that part sorted, logon to https://console.redhat.com with your Red Hat account. If you do not have one yet, you will be able to create one in the login page.
After logging in, select OpenShift as shown here:
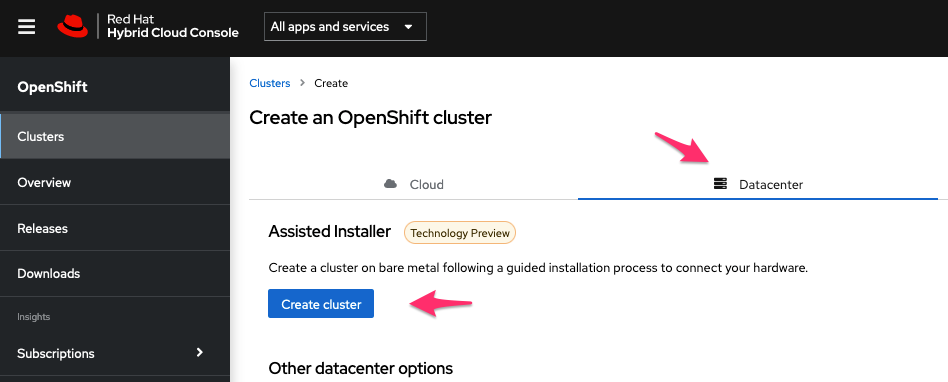
Then select to “Create Cluster,” choose “Datacenter” as target, and “Assisted Installer” should show up like in this screen capture:
This will start the wizard, where you need to enter:
- A cluster name
- A domain name
- And check boxes for SNO and that you understand the limitations of a technology preview.
Click “Next” when done.
If you have enough CPU cores (12), deploy on bare metal, and want virtualization integrated, select the checkbox for “Install OpenShift Virtualization.”
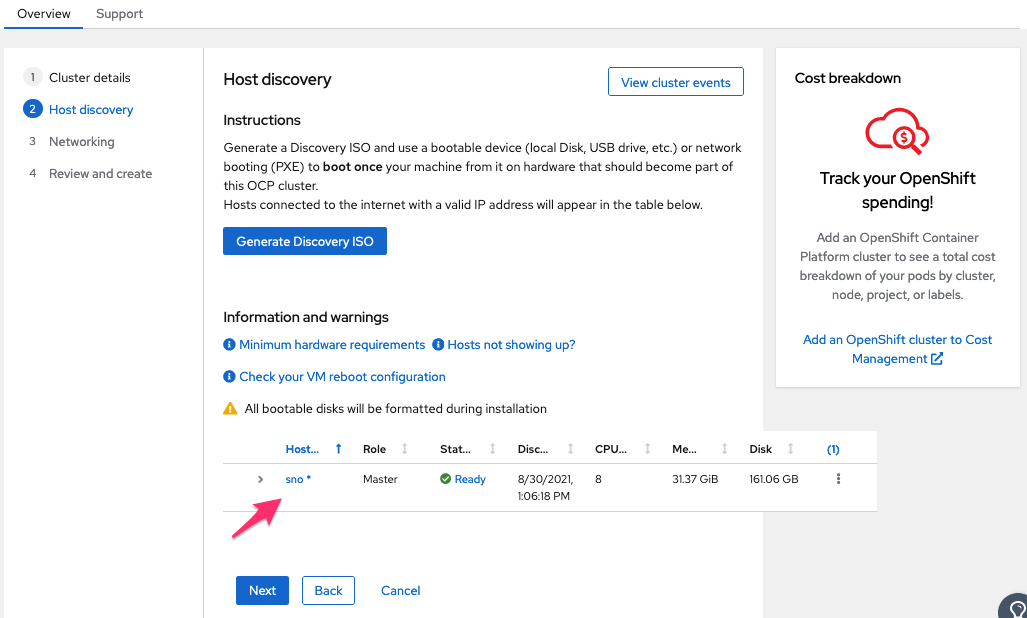
Then press “Generate Discovery ISO”:
In that dialogue, you select preferred media, USB or CD, and provide your public SSH key. For my environment, I just use the /.ssh/id_rsa.pub key on my desktop computer.
After pressing “Generate Discovery ISO” you will get links to download the image.
In my scenario, I copied the ISO to a suitable datastore, and mounted it in a virtual machine and booted the machine from the ISO. For bare metal, you can either use the same ISO to boot via remote management solutions, or just generate a bootable USB-stick with for instance BalenaEtcher or similar.
After the target has booted successfully, it will show up in your browser as “localhost”. Give it a desired hostname like this:
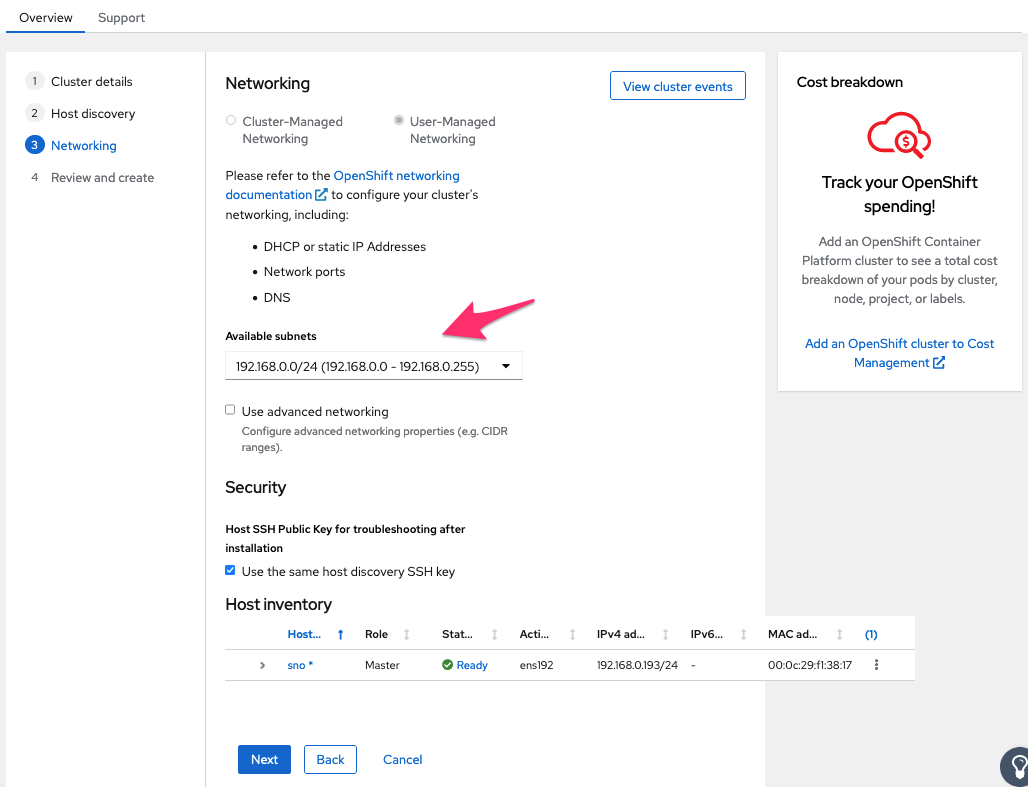
Next step is networking. I am doing this really simple, so I just select the desired available subnet in the pull down menu. You can enter advanced settings if you want to customize more related to networking.
I also select (default) to reuse my SSH key from the discovery host.
Clicking “Next” will show a summary like this:
Press “Install cluster” to start the install:
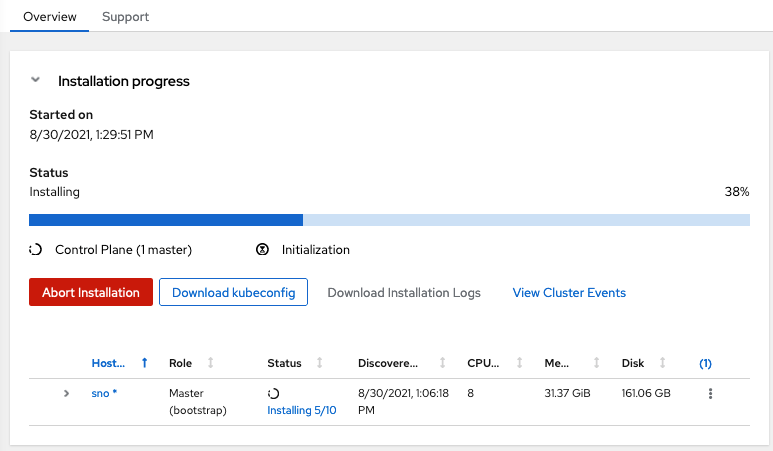
Depending on hardware and connectivity, the install will take around 45 minutes. When done, you will see a status like this:
Two things to remember before trying the URL and login:
Do you have a working DNS resolving for the host?
In my homelab, I just run a simple BIND server for that, so I added this, as described under “Not able to access the Web Console?” Remember to replace with your own domain/IP.
api.ocp1node.ekeberg.io A 193.168.0.193
*.apps.ocp1node.ekeberg.io A 193.168.0.193
ocp1node A 193.168.0.193
An even simpler solution is to add this to your local hosts file:
192.168.0.193 api.ocp1node.ekeberg.io
192.168.0.193 oauth-openshift.apps.ocp1node.ekeberg.io
192.168.0.193 console-openshift-console.apps.ocp1node.ekeberg.io
192.168.0.193 grafana-openshift-monitoring.apps.ocp1node.ekeberg.io
192.168.0.193 thanos-querier-openshift-monitoring.apps.ocp1node.ekeberg.io
192.168.0.193 prometheus-k8s-openshift-monitoring.apps.ocp1node.ekeberg.io
192.168.0.193 alertmanager-main-openshift-monitoring.apps.ocp1node.ekeberg.io
Now we are ready to check out your install.
Click the “copy to clipboard” to the right of the password.
Click the Web Console URL. (Accept the SSL-warnings)
Username should be populated with “kubeadmin” paste your password and select “Log in”
… and tap yourself on the shoulder for job well done if you are greeted with this dashboard:
Now you can start to explore and play with OpenShift in a pretty fast and simple way.
For those that want even simpler ways to have a look at OpenShift, there are more options.
Developer Sandbox for OpenShift
Get started in seconds with OpenShift as a Service. It is totally free, but pods will not live past 12 hours, so this is not for persistent testing and evaluation.
Link to sign up and test: https://developers.redhat.com/developer-sandbox
Code Ready Containers:
If you have a laptop/desktop or preferably a workstation, you can also run Code Ready Containers (CRC), a local desktop version of OpenShift tailored to that scenario. Not all the functions and features as the “real thing,” but as a developer you will get a taste of UI/TUI possibilities. Warning: On a “normal” laptop, performance will not be “excellent.” SNO might be a better option.
In addition to the above mentioned ways to access OpenShift, you can also have a look at Microsoft Azure, Amazon AWS, and IBM Cloud OpenShift offerings to get started in the public cloud, quick and easy.
Red Hat OpenShift is supported by most public cloud vendors globally, by most major service providers, and of course on a vast array of platforms and hardware on premise. Or in space.
저자 소개
Øivind Ekeberg has over 20 years of experience in IT with hands on experience in sales, logistics, service, deployment and maintenance. Ekeberg's main focus is on the services and applications that users need to do their work, and to try to design cost-efficient solutions that give flexibility to customers.
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래