AI adoption and development have accelerated with generative and agentic AI reaching the masses. As new markets emerge, businesses have been struggling to take advantage of AI for real returns on investment. Although GPUs have dominated the infrastructure, increasing costs and decreasing availability due to demand have prompted leaders to seek alternatives that still meet performance requirements and customer satisfaction standards.
Meanwhile, the developers and engineers working on AI face challenges in complex and time-consuming infrastructure setup and difficulty in building out software stacks and architectures for optimal large language model (LLM) inference with retrieval augmented generation (RAG). Ease of use, security of proprietary data, and even how to get started building AI are technical challenges that may bar developers from entry to AI.
The collaboration between Intel and Red Hat combines the performance of Xeon CPUs with the scalability of Red Hat OpenShift AI, offering a protected and flexible foundation for deploying agentic AI in the enterprise. On this platform, customers can build AI and machine learning models and applications more securely at scale across hybrid cloud environments.
To simplify the adoption process, Intel has created a number of AI quickstarts. AI quickstarts are examples of real-world business use cases that can quickly be deployed on Xeon with OpenShift, accelerating development and time-to-market. These quickstarts are available through the AI quickstarts catalog.
Why AI on Xeon?
Although GPUs have dominated deep learning, generative AI, and agentic AI, inference can use smaller and more cost-effective computing platforms to meet functional and performance requirements. CPUs have historically been the platform of choice for data processing, data analytics, and classical machine learning. This includes regression, classification, clustering, and decision trees using methods such as support vector machines, XGBoost, and K-means. Use cases include financial and retail forecasting, fraud detection, and supply chain optimization. This helps manage AI infrastructure costs over the long term. Intel Xeon is well-positioned as a head node for these sorts of smaller platforms.
Intel Xeon’s hardware features
The hardware features are what distinguishes Xeon as a viable CPU platform of choice for AI. The instruction set Advanced Matrix Extensions (AMX) and high memory bandwidth with Multiplexed Rank Dual In-line Memory Modules (MRDIMMs) are the most prominent components that set Xeon apart.
AMX was introduced in 4th Gen Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors as a built-in AI accelerator, a dedicated hardware block on the cores, to perform matrix math instead of relying on a discrete accelerator. It supports lower precision data types including Bfloat16 (BF16) and INT8. A major benefit of BF16 is improving performance without sacrificing accuracy compared to FP32. Accelerations with AMX reduce power and resource utilization and reduce development time with its optimizations upstreamed to AI frameworks including PyTorch and TensorFlow.
Recommender systems, natural language processing, generative AI, agentic AI, and computer vision use cases all benefit from AMX that result in greater end user and business value.

Figure 1: Intel® AMX features 2D register tiles with TMUL tile matrix multiply instructions to compute large matrices in a single operation.
In AI and LLM inference, the memory bottleneck is the key-value (KV) caching from high memory demand. MRDIMMS addresses this by shifting computational complexity from quadratic to linear, delivering more than 37% greater memory bandwidth than RDIMMs. This improves memory throughput and lowers latency when handling data-intensive tasks during AI inference. In systems where GPU memory is limited, Xeon CPUs can offload KV data, freeing expensive GPU resources while maintaining high performance.
Xeon has several practical use cases in AI—inference, RAG and secure data processing, and agentic AI. Both functional and performant, Xeon is a platform with supporting software to address needs in AI without the need of GPUs.
Xeon use case 1: AI inference
LLM inference powers applications including enterprise chatbots, document summarization, code assistants, and RAG pipelines. Mid-market enterprises and organizations seeking cost-effective gen AI without large GPU investments may find Xeon a more practical option. Xeon runs best with small to medium LLMs and mixture-of-experts (MOEs) up to 13B parameters while still meeting standards including time-to-first-token (TTFT) of 3 seconds and time-per-output-token of 100ms.
Intel has been working closely with the open source community to optimize AI inference, including vLLM and SGLang. vLLM is an inference serving engine for high throughput and memory efficiency. The vLLM dashboard for Xeon on Pytorch.org contains published performance numbers of popular LLMs including Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct on Xeon. Intel continues to improve performance and add support to a list of validated models. SGLang is another fast serving framework that Intel is working on integrating with Xeon.
Xeon also supports distributed LLM inference with llm-d where the prefill and decode stages are split across multiple nodes for higher scalability. llm-d is a Kubernetes-native, open source framework that speeds up distributed LLM inference at scale.
Xeon use case 2: RAG and secure data processing
RAG is effective for getting accurate outputs from LLMs without retraining models. The knowledge base is created by preparing data using document parsing, chunking, and metadata extraction to create embeddings that are then stored in a vector database. All operations can be done securely with Intel® Trust Domain Extensions (TDX), a hardware-based confidential computing technology. TDX uses hardware-isolated virtual machines (VMs) to protect data and applications from unauthorized access. This allows enterprises to quickly leverage available proprietary data for customer support automation, document retrieval, and legal research. Retrieval latency is low and concurrent queries can be handled with Xeon.
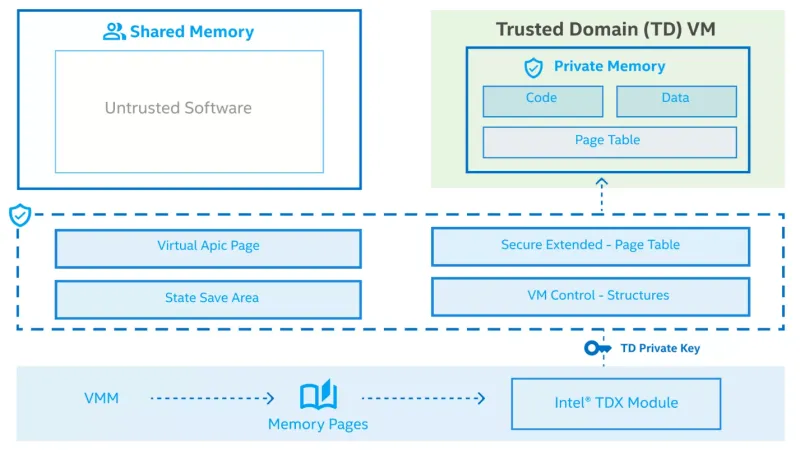
Figure 2: Intel® TDX uses hardware extensions for managing and encrypting memory to protect the confidentiality and integrity of data.
Xeon use case 3: Agentic AI
AI agents follow sequential logic of planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. It uses a mixed workload involving LLM inference and tools execution, from database queries, API calls, to file access. Xeon supports model context protocol (MCP) servers, LlamaStack agentic APIs, LangChain, and CrewAI frameworks. IT operations automation, financial decision support, and supply chain agents are target business use cases.
Xeon on OpenShift: What’s new
Red Hat OpenShift AI is an enterprise-grade AI platform for managing the full lifecycle of building, training, and deploying AI models and applications at scale across the hybrid cloud, on premises, and edge environments. Among the technologies included in OpenShift AI, vLLM provides optimized high-throughput and low-latency model serving while reducing hardware costs. There is a collection of optimized, production-ready, validated third-party models that gives development teams more control over model accessibility and visibility to meet security and policy requirements. This can all be automatically deployed with advanced tooling to jumpstart your AI projects and reduce operational complexity. Overall, AI applications can be brought to production at scale faster.

Figure 3: Red Hat OpenShift AI is a flexible, scalable artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) platform that enables enterprises to create and deliver AI-enabled applications at scale across hybrid cloud environments.
Features
It will take less time to manage AI infrastructure, where high-performing models can easily be deployed with Models-as-a-Service (MaaS) and accessed with API endpoints. There is flexibility across the hybrid cloud as protected and flexible self-managed software on bare metal, virtual environments, or all major public cloud platforms. Red Hat has tested and integrated common open source AI/ML tooling and model serving so it's easy for developers to use them. OpenShift AI also includes llm-d, an open source framework for distributed AI inference at scale.
vLLM CPU image
Intel has made available a vLLM image for CPU on Dockerhub built on top of the Red Hat universal base image. The image is built with AMX enabled. Therefore, 4th Gen Xeon® Scalable® processors or newer are required to run this image. Now, many open source models can be quickly deployed and run inference with high throughput and low latency out of the box.
AI quickstarts
Available in the AI quickstart catalog on redhat.com, are ready-to-run business use-case examples that run models optimally with vLLM on Xeon, powered by OpenShift AI. Developers can take these examples as starting points and customize to their needs or use as is. Early draft versions of several AI quickstarts are available on GitHub and run out-of-the-box on Xeon, with all finalized quickstarts released through the AI quickstart catalog.
- LlamaStack MCP Server – Deploys LLMs with vLLM with MCP servers such as weather reporting and HR tools
- LLM CPU Serving – A lightweight AI leadership and strategy chat assistant serving a small language model
- RAG – Use retrieval augmented generation to enhance LLMs with specialized data sources for more accurate and context-aware responses
- vLLM Tool Calling – Deploys LLMs using vLLM with function calling
Next steps
AI on Xeon is made easy with n Red Hat OpenShift AI. The managed and protected environment sets up the necessary AI infrastructure for development, deployment, and observability.
- View the vLLM dashboard for Xeon for performance numbers and vLLM documentation to build/download the vLLM images for CPU with AMX support.
- Use the vLLM for CPU based on the Red Hat Universal Base Image from DockerHub.
- Review list of supported models for Xeon.
- Explore the AI quickstart catalog for ready-to-run examples and visit the AI quickstart Github for AI quickstarts that are still under development.
- Visit the Red Hat OpenShift AI site.
Producto
Red Hat AI
Sobre el autor
Más como éste
AI insights with actionable automation accelerate the journey to autonomous networks
Cracking the inference code: 3 proven strategies for high-performance AI
Technically Speaking | Build a production-ready AI toolbox
Technically Speaking | Platform engineering for AI agents
Navegar por canal
Automatización
Las últimas novedades en la automatización de la TI para los equipos, la tecnología y los entornos
Inteligencia artificial
Descubra las actualizaciones en las plataformas que permiten a los clientes ejecutar cargas de trabajo de inteligecia artificial en cualquier lugar
Nube híbrida abierta
Vea como construimos un futuro flexible con la nube híbrida
Seguridad
Vea las últimas novedades sobre cómo reducimos los riesgos en entornos y tecnologías
Edge computing
Conozca las actualizaciones en las plataformas que simplifican las operaciones en el edge
Infraestructura
Vea las últimas novedades sobre la plataforma Linux empresarial líder en el mundo
Aplicaciones
Conozca nuestras soluciones para abordar los desafíos más complejos de las aplicaciones
Virtualización
El futuro de la virtualización empresarial para tus cargas de trabajo locales o en la nube
