Open Cluster Management
Open Cluster Management is a community-driven project that is focused on multicluster and multicloud scenarios for Kubernetes applications. Open APIs are included and evolving within this project for cluster registration, work distribution, dynamic placement of policies and workloads, and more.
The Open Cluster Management add-on enables any capability within the Kubernetes ecosystem to orchestrate itself across multiple clusters and cloud providers. Open Cluster Management provides core primitives to satisfy the previously mentioned requirements to ease the multicluster enablement.
In this blog, you will learn how to develop a custom add-on, which enables you to extend your custom actions by performing them on multiple clusters.
Hub cluster
The hub cluster is the common term that is used to define the central controller that runs on a Kubernetes cluster. The hub cluster aggregates information from multiple clusters by using an asynchronous work request model.
Managed cluster
The managed cluster provides a representation of the managed cluster on the hub cluster. The ManagedCluster resource controls whether or not the remote cluster is accepted by the hub cluster for management. After the managed cluster is accepted, it can retrieve information from the hub cluster to direct a set of manifests or actions to apply.
What is an add-on?
Open Cluster Management has a way to help you create an extension based on the foundation components so you can work with multiple clusters in different ways. Some examples of add-ons include:
-
A tool to collect alert events in the managed cluster and send them to the hub cluster.
-
A network solution that uses a hub to share the network information and establish a connection across managed clusters.
-
A tool to run security policies on multiple clusters.
In general, if a management tool needs a different configuration for each managed cluster or a secured communication between managed cluster and hub cluster, it can use the add-on feature of the Open Cluster Management to simplify the installation and improve day two operations.
Normally, an add-on contains two components:
- The
addon-hub-controller, which is a controller that runs on the hub cluster. - The
addon-agent, which is an agent that runs on the managed cluster.
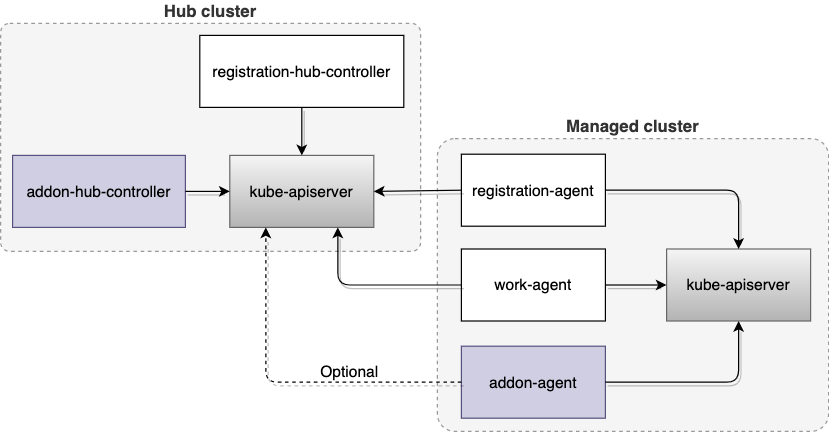
The following diagram shows how the two components fit in to the architecture of the add-on.
As shown in the previous diagram, some foundation components from Open Cluster Management are also required to manage the lifecycle of an add-on. The following list describes those components:
registration-hub-controller: This controller on the hub cluster updates the add-on status according to the status of the cluster's lease on the hub.registration-agent: This agent on the managed cluster helps to register the add-on with the hub cluster and creates a secret that contains the hub kubeconfig for the add-on on the managed cluster. The agent also continues updating the add-on status on the hub cluster based on the add-on lease created on the managed cluster.work-agent: This agent on the managed cluster distributes a list of manifests from the hub cluster to the managed cluster and applies the manifests on the managed cluster for the add-on.
How to develop an add-on
The easiest way to build an add-on is to leverage addon-framework, which is a library that contains the necessary interfaces and default implementations for add-on lifecycle management. In this section, you can develop an example helloworld add-on.
Step 1: Build your add-on hub controller
-
Start with the
AgentAddoninterface to develop anaddon-hub-controller.// AgentAddon defines manifests of agent deployed on managed cluster
type AgentAddon interface {
// Manifests returns a list of manifest resources to be deployed on the managed cluster for this add-on
Manifests(cluster *clusterv1.ManagedCluster, addon *addonapiv1alpha1.ManagedClusterAddOn) ([]runtime.Object, error)
// GetAgentAddonOptions returns the agent options.
GetAgentAddonOptions() AgentAddonOptions
}
The Manifests method is expected to return the manifest resources that are required to deploy the addon-agent on a managed cluster. The GetAgentAddonOptions method returns add-on configuration including add-on name and registration option.
-
Create a struct named
helloWorldAgentto implement the interface.type helloWorldAgent struct {
kubeConfig *rest.Config
recorder events.Recorder
agentName string
}
var _ agent.AgentAddon = &helloWorldAgent{} -
Create an
AddonManager, which is provided by addon-framework, and register the agent that you built before starting it.mgr, err := addonmanager.New(controllerContext.KubeConfig)
if err != nil {
return err
}
agentRegistration := &helloWorldAgent{
kubeConfig: controllerContext.KubeConfig,
recorder: controllerContext.EventRecorder,
agentName: utilrand.String(5),
}
mgr.AddAgent(agentRegistration)
mgr.Start(ctx)
Step 2: Build your add-on agent
-
Create an
agentController. This controller monitors configmaps in the cluster namespace on the hub cluster, and copies them to thedefaultnamespace on the managed cluster.type agentController struct {
spokeKubeClient kubernetes.Interface
hunConfigMapLister corev1lister.ConfigMapLister
clusterName string
recorder events.Recorder
} -
Start an
agentControllerand aLeaseUpdater. TheLeaseUpdatercreates a lease for the add-on in the add-on installation namespace and updates it every 60 seconds.// create an agent contoller
agent := newAgentController(
spokeKubeClient,
hubKubeInformerFactory.Core().V1().ConfigMaps(),
o.SpokeClusterName,
controllerContext.EventRecorder,
)
// create a lease updater
leaseUpdater := lease.NewLeaseUpdater(
spokeKubeClient,
"helloworld",
"default",
)
go agent.Run(ctx, 1)
go leaseUpdater.Start(ctx)
You just finished a major part of the helloworld add-on development. Visit the helloworld directory in GitHub to view the complete source code. Next, you can enable it.
How to enable your add-on
After you finish developing your add-on, you need to enable it on your managed cluster by using the ManagedClusterAddOn API. You can deploy the helloworld add-on using Open Cluster Management.
-
Follow the getting started instructions of
registration-operatorto prepare a kind cluster and deploy the Open Cluster Management instance on the kind cluster to manage itself.After you deploy Open Cluster Management successfully, a managed cluster (
cluster1) and its certificate signing request (CSR) are created on the hub:export KUBECONFIG=$HOME/.kube/config
kubectl get managedcluster cluster1
NAME HUB ACCEPTED MANAGED CLUSTER URLS JOINED AVAILABLE AGE
cluster1 true https://localhost True True 20m -
Accept the managed cluster and approve its CSR with the following command:
kubectl patch managedcluster cluster1 -p='{"spec":{"hubAcceptsClient":true}}' --type=merge
kubectl get csr -l open-cluster-management.io/cluster-name=cluster1 | grep Pending | awk '{print $1}' | xargs kubectl certificate approve -
Build a docker image of the
helloworldadd-on on your local host:make images
An image
quay.io/open-cluster-management/helloworld-addon:latestis created. -
Load the image to your kind cluster:
kind load docker-image quay.io/open-cluster-management/helloworld-addon:latest
-
Deploy the
helloworldadd-on controller on the hub cluster:make deploy-example
The pod of the
helloworldadd-on controller is created in theopen-cluster-managementnamespace:kubectl -n open-cluster-management get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
helloworld-controller-5857d64c7c-qxnzs 1/1 Running 0 47m -
Enable the
helloworldadd-on on the managed cluster by using theManagedClusterAddOnAPI:cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: addon.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ManagedClusterAddOn
metadata:
name: helloworld
namespace: cluster1
spec:
installNamespace: default
EOFThe
helloworldadd-on is then installed in thedefaultinstallation namespace on the managed cluster:kubectl -n default get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
helloworld-agent-79cf779b98-vgwz9 1/1 Running 0 36m
You enabled the helloworld add-on on the managed cluster. Next, try to use it.
How to use your add-on
After enabling your add-on, complete the following steps to use it:
-
Create a configmap for
helloworldin the managed cluster namespacecluster1on the hub cluster:cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: helloworld
namespace: cluster1
data:
value: helloworld
EOF -
The add-on synchronizes with the configmap of the managed cluster, you can find it in the YAML file of the managed cluster:
kubectl -n default get cm helloworld -oyaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
value: helloworld
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
creationTimestamp: "2021-07-06T06:42:04Z"
managedFields:
- apiVersion: v1
fieldsType: FieldsV1
fieldsV1:
f:data:
.: {}
f:value: {}
manager: helloworld
operation: Update
time: "2021-07-06T06:42:04Z"
name: helloworld
namespace: default
resourceVersion: "32967"
uid: f46d2e50-a29d-4b9b-9113-24219821b365
How does your helloworld add-on work?
Now that your add-on is enabled and working, you might be interested in the process that makes this add-on work. The order of the steps in the process doesn't matter, and some of the actions might happen simultaneously. After you applied the ManagedClusterAddOn called helloworld on the hub cluster, the following process starts:
-
On the hub cluster, the
AddonManagerthat is started in theaddon-hub-controllercalls back to theManifestsmethod of thehelloWorldAgent. This call back collects the manifest resources of thehelloworldadd-on and creates the manifest works on the managed cluster namespace.kubectl -n cluster1 get manifestworks
NAME AGE
addon-helloworld-deploy 8m27s -
On the hub cluster, the
AddonManagercalls back to theGetAgentAddonOptionsmethod ofhelloWorldAgentto get the registration information of thehelloworldadd-on and append it to the add-on status.kubectl -n cluster1 get managedclusteraddons helloworld -oyaml
apiVersion: addon.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ManagedClusterAddOn
...
status:
registrations:
- signerName: kubernetes.io/kube-apiserver-client
subject:
groups:
- system:open-cluster-management:cluster:cluster1:addon:helloworld
- system:open-cluster-management:addon:helloworld
- system:authenticated
user: system:open-cluster-management:cluster:cluster1:addon:helloworld:agent:8fmr7 -
On the managed cluster, the
work-agentwatches themanifestworkof thehelloworldadd-on and deploys theaddon-agentof thehelloworldadd-on on the managed cluster.kubectl get clusterrolebindings helloworld-addon
NAME ROLE AGE
helloworld-addon ClusterRole/helloworld-addon 49m
kubectl -n default get deploy,sa
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/helloworld-agent 1/1 1 1 37m
NAME SECRETS AGE
serviceaccount/helloworld-agent-sa 1 37m -
On the managed cluster, the
registration-agentcollects the registration information from the status of thehelloworldadd-on and creates a CSR on the hub cluster.kubectl get csr
NAME AGE SIGNERNAME REQUESTOR CONDITION
addon-cluster1-helloworld-pgmt4 8s kubernetes.io/kube-apiserver-client system:open-cluster-management:cluster1:sdcnn Pending -
On the hub cluster, the
AddonManagercalls back to the functionCSRApproveCheckof theRegistrationconfiguration to determine whether the CSR should be approved.kubectl get csr
NAME AGE SIGNERNAME REQUESTOR CONDITION
addon-cluster1-helloworld-pgmt4 8s kubernetes.io/kube-apiserver-client system:open-cluster-management:cluster1:sdcnn Approved,Issued -
After the CSR is approved, the
registration-agenton the managed cluster watches the approved CSR that is on the hub cluster and gathers the hub credentials from it. Then theregistration-agentuses the hub cluster credentials to create a hubkubeconfigand saves it as a secret in thehelloworldadd-on installation namespace.kubectl -n default get secrets
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
helloworld-hub-kubeconfig Opaque 3 5m45s -
The
addon-agentof thehelloworldadd-on mounts the secret and uses the hub cluster'skubeconfigof the secret to access to the hubkube-apiserver. In day two operation, when the certificate of thehelloworldadd-on is about to expire, theregistration-agentsends a request to rotate the certificate on the hub cluster. Theaddon-hub-controlleron the hub cluster automatically approves the certificate rotation request. -
After the
addon-agentof thehelloworldadd-on is deployed on the managed cluster, the agent creates aleasein its installation namespace.kubectl -n default get leases
NAME HOLDER AGE
helloworld 7m52s -
The
registration-agenton the managed cluster uses this lease to update the status of thehelloworldadd-on on the hub cluster.kubectl -n cluster1 get managedclusteraddons helloworld -oyaml
apiVersion: addon.open-cluster-management.io/v1alpha1
kind: ManagedClusterAddOn
...
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2021-07-09T02:52:49Z"
message: helloworld add-on is available.
reason: ManagedClusterAddOnLeaseUpdated
status: "True"
type: Available
In this blog, we introduced an approach to extend the capability of Open Cluster Management by developing and using an add-on. By following these steps, you can develop a sample add-on based on addon-framework and deploy it on both the hub cluster and the managed cluster. It also explains how an add-on registers itself on the hub cluster and updates its status with the lease. With this knowledge, you are able to change some settings and build your own custom managed cluster add-ons.
Sobre los autores
Más como éste
Introducing OpenShift Service Mesh 3.2 with Istio’s ambient mode
Looking ahead to 2026: Red Hat’s view across the hybrid cloud
Crack the Cloud_Open | Command Line Heroes
Edge computing covered and diced | Technically Speaking
Navegar por canal
Automatización
Las últimas novedades en la automatización de la TI para los equipos, la tecnología y los entornos
Inteligencia artificial
Descubra las actualizaciones en las plataformas que permiten a los clientes ejecutar cargas de trabajo de inteligecia artificial en cualquier lugar
Nube híbrida abierta
Vea como construimos un futuro flexible con la nube híbrida
Seguridad
Vea las últimas novedades sobre cómo reducimos los riesgos en entornos y tecnologías
Edge computing
Conozca las actualizaciones en las plataformas que simplifican las operaciones en el edge
Infraestructura
Vea las últimas novedades sobre la plataforma Linux empresarial líder en el mundo
Aplicaciones
Conozca nuestras soluciones para abordar los desafíos más complejos de las aplicaciones
Virtualización
El futuro de la virtualización empresarial para tus cargas de trabajo locales o en la nube