A Compressed Summary
- Enhanced Performance: DeepSeek models see up to 3x throughput and 10x memory capacity improvements with MLA and FP8 kernel optimizations in vLLM v0.7.1.
- Scalable Long-Context Inference: Optimized memory boosts token capacity from 54,560 to 512,000, enabling horizontal scalability with pipeline parallelism.
- New Innovations: MLA’s "matrix absorption" algorithm and other optimizations reduce memory usage while improving efficiency for complex, high-batch workloads.
Introduction
The vLLM community has rolled out its latest batch of enhancements to DeepSeek models, including support for MLA (Multi-Head Latent Attention) and optimized CUTLASS Block FP8 kernels. Kudos to Neural Magic’s team at Red Hat for their hard work, specifically Lucas Wilkinson, Tyler Smith, Robert Shaw, and Michael Goin. These improvements increase both generation throughput and memory efficiency, making long-context inference more scalable and cost-effective. In this post, we’ll walk through the key highlights and technical benchmarks.
Performance Gains: 3x Throughput and 10x Memory Capacity
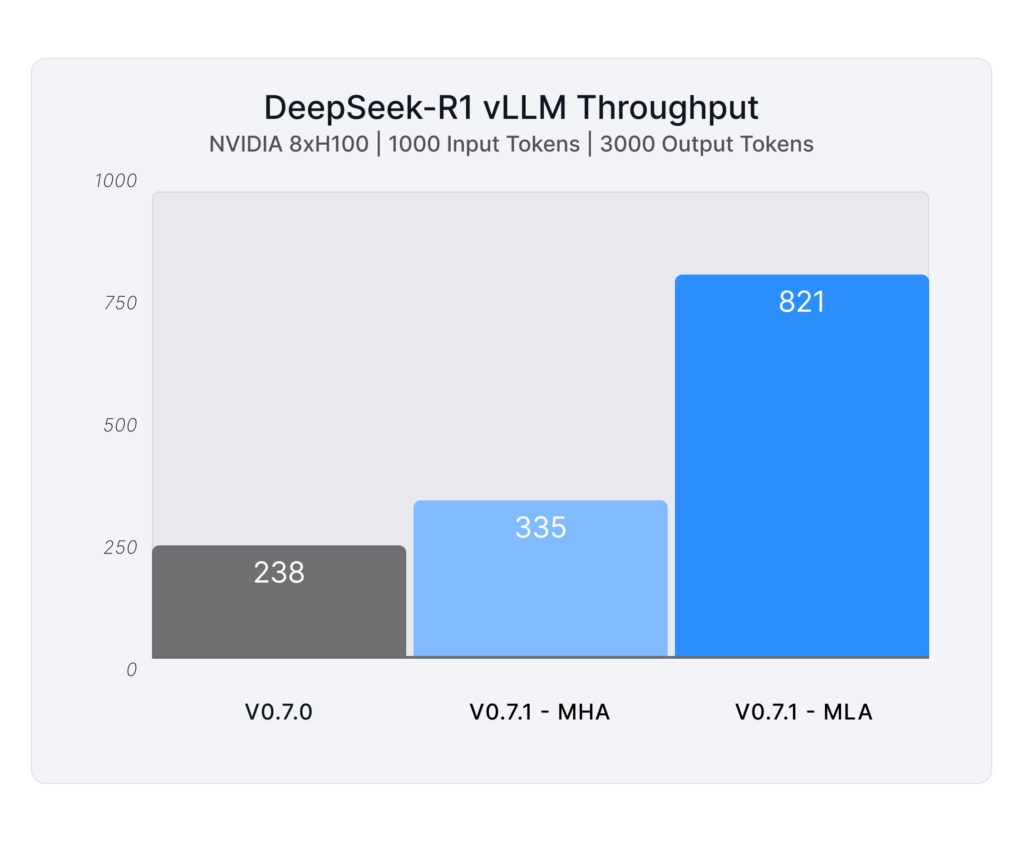
The latest enhancements in vLLM deliver impressive DeepSeek results compared to v0.7.0, and are optimized for long-context generation workloads:
- 3x increase in generation throughput
- 10x increase in token memory capacity
- Horizontal scalability via vLLM’s pipeline parallelism
For example, on an 8x NVIDIA H200 setup, generation throughput increased by 40% with FP8 kernel optimizations and by 3.4x with MLA. In TP8PP2 (Tensor Parallelism 8, Pipeline Parallelism 2) settings with H100 GPUs, we observed a 26% improvement from FP8 kernels and a 2.8x boost from MLA.
Memory Optimization and Token Capacity Expansion
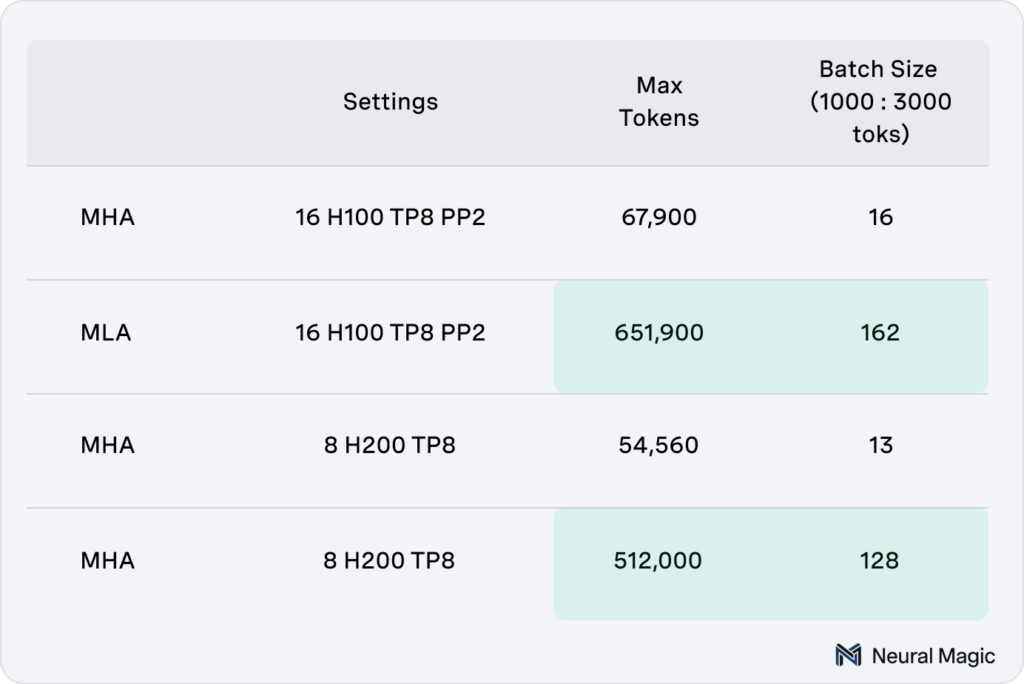
The secret to these throughput gains lies in memory optimization. MLA offers approximately 9.6x more memory capacity for key-value (KV) caches, which allows for significantly larger batch sizes during generation. On an 8x H200 setup, token capacity expanded from 54,560 to 512,000 tokens, enabling batch size growth from 13 to 128.
Trade-Offs in Low QPS Scenarios
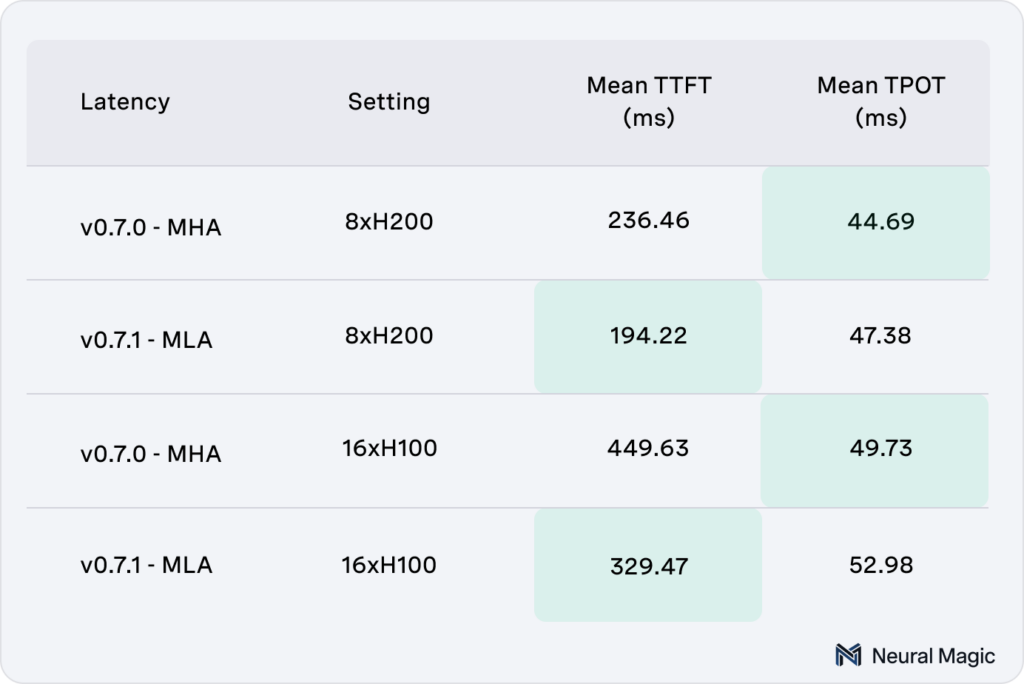
While MLA excels in large-batch, high-throughput scenarios, it faces some limitations at low queries per second (QPS). Multi-Head Attention (MHA) currently outperforms MLA in these settings, offering better time-to-first-token (TTFT) performance. However, MLA makes up for it by delivering higher efficiency in time-per-output-token (TPOT) under sustained loads. We’re actively working to address this limitation to ensure consistent performance across all workloads.
About the MLA Algorithm
MLA’s core advantage is its ability to compute directly on latent cache values, bypassing the need to up-project KV cache values. This innovation, based on the "matrix absorption" algorithm introduced in the DeepSeek V2 paper, reduces memory overhead while maintaining accuracy. For those interested in a more technical breakdown, we recommend checking out this explanation of MLA from Tsu Bin.
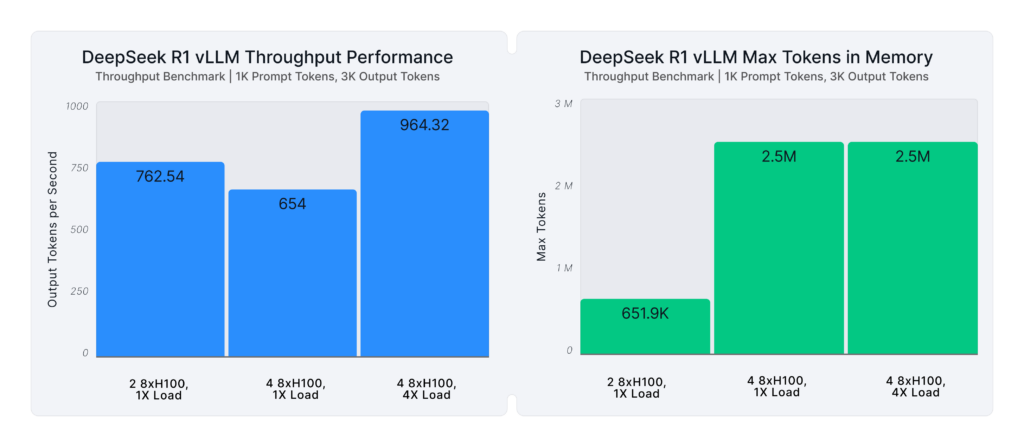
Horizontal Scaling with Pipeline Parallelism
One of vLLM’s standout features is its pipeline parallelism, which supports horizontal scalability for extremely long generations (watch our recent office hours video to learn about vLLM’s tensor and pipeline parallelism). You can now connect multiple machines—without requiring Infiniband connections—to increase both KV cache capacity and throughput. This makes it easier than ever to serve models like DeepSeek R1 for complex, long-form tasks.
Try It Today with vLLM v0.7.1
These improvements are already live in vLLM v0.7.1 and are compatible with DeepSeek models that leverage MLA, including DeepSeek Coder, V2-Lite, V3, and R1. Update your vLLM installation to start benefiting from the enhanced throughput and memory efficiency.
What’s Next for MLA and DeepSeek Models?
The vLLM community is just getting started. Ongoing work includes optimizations like prefix caching with MLA, expert parallelism, multi-token prediction, and attention data parallelism. Our mission is to provide users with high-efficiency model serving and streamlined usability.
Acknowledgments and Open-Source Collaboration Call-Outs
This implementation of MLA was led by Lucas Wilkinson from Neural Magic’s team at Red Hat. Additionally, we’re grateful to the teams at SGLang, CUTLASS, and FlashInfer for contributing optimized kernels. None of this would be possible without the open-source ecosystem, which continues to drive consistent innovation in vLLM performance engineering.
리소스
엔터프라이즈를 위한 AI 시작하기: 입문자용 가이드
저자 소개
Saša Zelenović is a Principal Product Marketing Manager at Red Hat, joining in 2025 through the Neural Magic acquisition where he led as Head of Marketing. With a passion for developer-focused marketing, Sasa drives efforts to help developers compress models for inference and deploy them with vLLM. He co-hosts the bi-weekly vLLM Office Hours, a go-to spot for insights and community around all things vLLM.
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래
