With Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform 3, you are usually working with three roles for nodes: master, compute, and infrastructure (infra). Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform 4 instead, by default, provides master and worker roles. There is no infra node in OpenShift 4. When migrating from OpenShift 3 to OpenShift 4, users frequently ask how to convert OpenShift 3 infra nodes to OpenShift 4 infra nodes. In this post we'll walk you through that.
2023 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™에서 리더로 선정된 Red Hat
Red Hat은 Gartner 2023 Magic Quadrant 컨테이너 관리 부문의 실행 능력 및 비전의 완성도에서 최고점을 획득했습니다.
The most common mistake that people make is just applying the infra label to the worker nodes:
oc label node $NODE_NAME node-role.kubernetes.io/infra=After applying the label, there is no output to suggest that this is a problem. However, when you upgrade the OpenShift cluster, you will notice that the worker nodes that you applied the label to do not get upgraded. This is the expected behavior.
In this post we will discuss what Machine Config Pool is and how you should use it for OpenShift 4 infra nodes.
Bottom line
In order to understand the situation, you should understand the concept of Operators in OpenShift Container Platform 4.
As you may know, OpenShift Container Platform 4 is an operator-focused platform. On Red Hat CoreOS, the Machine Config Operator handles the operating system, managing OS updates and configuration changes. Understanding the Machine Config Operator is central to managing master and worker nodes properly according to the new management design of OpenShift Container Platform 4.
What is a Machine Config Operator?
The Machine Config Operator (MCO) is a cluster-level operator like any other operator, but it is a special one from an OpenShift Container Platform infrastructure perspective. It manages the operating system and keeps the cluster up to date and configured. Through MCO, platform administrators can configure and update systemd, cri-o/kubelet, kernel, NetworkManager, etc. on the nodes. To do so, the MCO creates a statically rendered MachineConfig file which includes the MachineConfigs for each node. It then applies that configuration to each node. Let’s examine some of the details.
Sub Components of Machine Config Operator
The Machine Config Operator is a complex component. There are several sub-components and each sub-component performs a different task. This blog does not explain all the sub-components in detail, but you can examine each of them by clicking the links below.
Template Controller
Update Controller
Render Controller
Kubelet Config Controller
 Red Hat의 UBI(Universal Base Image)를 활용해서 작업 효율성을 개선하세요
Red Hat의 UBI(Universal Base Image)를 활용해서 작업 효율성을 개선하세요
 Red Hat의 UBI(Universal Base Image)를 활용해서 작업 효율성을 개선하세요
Red Hat의 UBI(Universal Base Image)를 활용해서 작업 효율성을 개선하세요
What does Machine Config Controller do?
Of the above sub-components, the Machine Config Controller is relevant for the problem that we are discussing. The Machine Config Controller starts to play a role after OpenShift Container Platform 4 is installed.
Machine Config Controller Goals:
Coordinate upgrade of machines to the desired configuration defined by a MachineConfig Object.
Provide options to control upgrades for sets of machines individually.
In other words, this controller generates Machine Configs for pre-defined roles (master and worker) and monitors whether an existing Machine Config CR (custom resource) is modified or new Machine Config CRs are created. When the controller detects any of those events, it will generate a new rendered Machine Config object that contains all of the Machine Configs based on MachineConfigSelector from each MachineConfigPool.
The following are each controller’s role description:
Template Controller:
Generate the MachineConfigs for predefined roles of machines (master, worker).
Watch controllerconfig to generate OpenShift-owned MachineConfigs.
Render Controller:
Watch MachineConfigPool object to find all the MachineConfig objects.
Update CurrentMachineConfig with the rendered MachineConfig.
Detect changes on all the MachineConfigs and syncs all the MachineConfigPool objects with a new CurrentMachineConfig.
Update Controller:
Watch if MachineConfigPool .Status.CurrentMachineConfig is updated.
Upgrade machines to the desired MachineConfig by coordinating with a daemon running on each machine.
Machine Config
We have mentioned the Machine Config object, but what is it? It is the source of machine configuration and is used for installation and first-boot, as well as upgrades. The Machine Config should be static, i.e. it should not contain links or remote locations to generate configuration dynamically. In short, it defines OS level configuration if the machine uses RHCOS. Using the ignition config format, you can manage machines such as storage, systemd, kernel and so on.
Machine Config Pool
The Machine Config Pool is the main object to resolve the situation. The Machine Config Pool operates similarly to the Rolebinding object, which associates roles with users. The Machine Config Pool associates nodes with Machine Configs.
Let’s examine the following diagram to understand the Machine Config Pool.
The Machine Config Pool maps between nodes and Machine Configs. The Machine Config Pool has two selectors, and each selector matches machine configs with nodes.
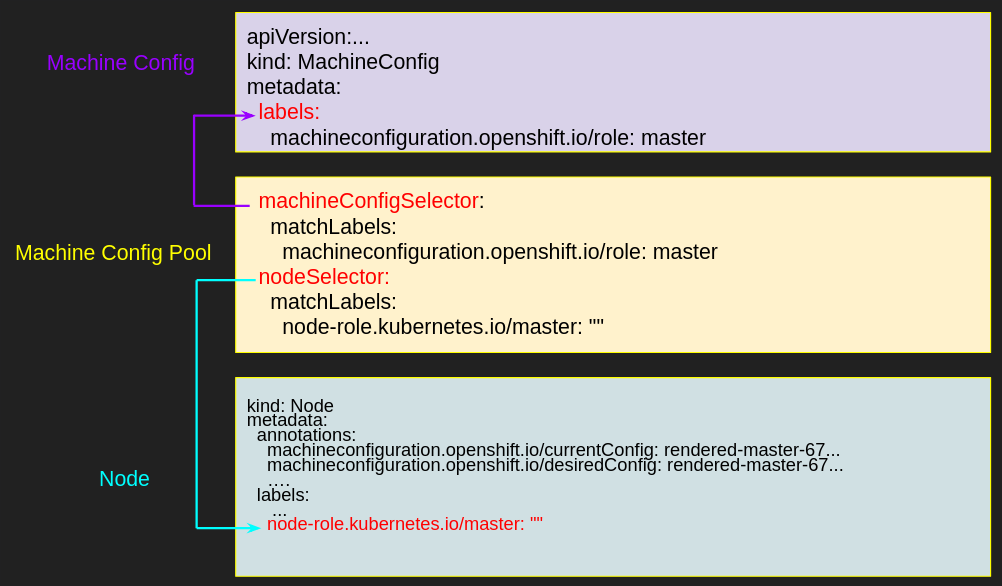
Figure 1. The relationship among Machine Config Pool/Machine Configs and Worker Nodes
The Render controller in the Machine Config Controller monitors the Machine Config Pool and generates static machine config objects named rendered-master-XXXX and rendered-worker-xxx. These objects can include multiple machine configs. The Render controller then checks whether the nodes in the pool have applied the latest rendered-xxxx machine config. If the machine config pool changes, then the render controller creates a new rendered-xxx and applies it.
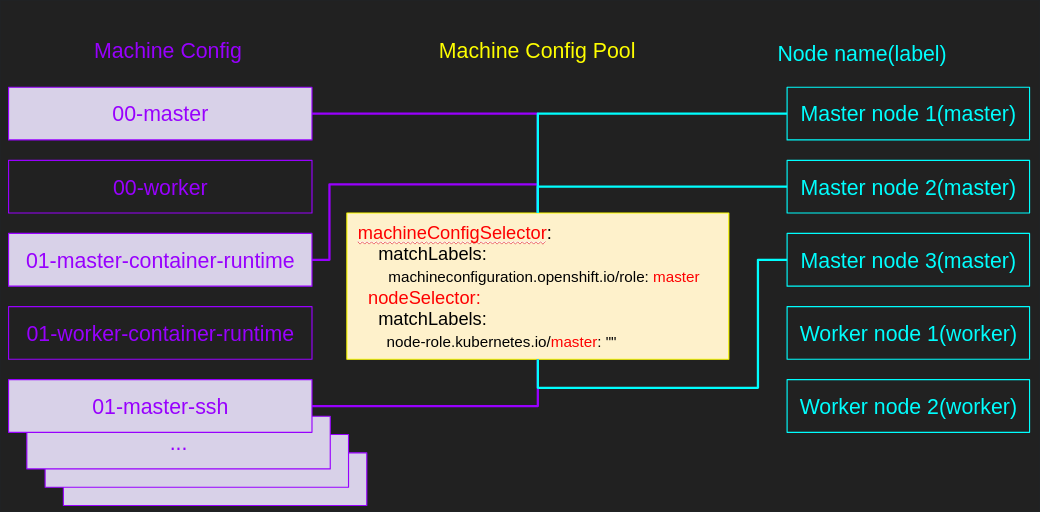
Figure 2. How Machine Config Pool selects Machine Configs and Worker
Infra worker node group
Now it is time to solve the infra role worker nodes issue. As I mentioned, there are only 2 roles in OpenShift 4 by default: master and worker. Therefore, the OpenShift 3 infra role needs to inherit the OpenShift 4 worker role in order for the upgrade to take place.
Step 1. Create a infra MachineConfigPool
apiVersion: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/v1
kind: MachineConfigPool
metadata:
name: infra
spec:
machineConfigSelector:
matchExpressions:
- {key: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/role, operator: In, values: [worker,infra]}
maxUnavailable: null
nodeSelector:
matchLabels:
node-role.kubernetes.io/infra: ""
paused: falseFrom MachineConfigSelector, you can see it tries to find worker and infra related Machine Configs. There are no infra related MachineConfigs by default but if you want to configure something only for infra worker nodes, you can create it according to Step 2.
Step 2. Create a infra MachineConfig (optional)
apiVersion: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/v1 kind: MachineConfig metadata: labels: machineconfiguration.openshift.io/role: infra name: 50-infra spec: config: ignition: version: 2.2.0 storage: files: - contents: source: data:,test filesystem: root mode: 0644 path: /etc/testinfra
Step 3. Update worker node role of the infra nodes.
oc label node <node> node-role.kubernetes.io/worker- oc label node <node> node-role.kubernetes.io/infra=
Conclusion
Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform 4 includes many operators and it is managed by them from installation, upgrade and so on. Unlike OpenShift Container Platform 3, you should follow the new ways of OpenShift 4 to manage worker nodes by Machine Config. Machine Config Operator is a main component to control and handle OpenShift worker nodes so you should understand this concept and use it properly for OpenShift Container Platform 4.
저자 소개
Jooho Lee is a senior OpenShift Technical Account Manager (TAM) in Toronto supporting middleware products(EAP/ DataGrid/ Web Server) and cloud products (Docker/ Kubernetes/ OpenShift/ Ansible). He is an active member of JBoss User Group Korea and Openshift / Ansible Group.
유사한 검색 결과
Migrate your VMs faster with the migration toolkit for virtualization 2.11
Friday Five — February 20, 2026 | Red Hat
Understanding AI Security Frameworks | Compiler
Data Security And AI | Compiler
자세히 알아보기
- 초보자를 위한 하이브리드 클라우드 전략
- 2023년 Gartner® Magic Quadrant™ 컨테이너 관리 부문 리더로 선정된 Red Hat
- Red Hat OpenShift 체험
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래
