Ceph is often deployed with OpenStack as a back-end storage method. These two open source projects work together to make a well-integrated and robust solution for infrastructure.
OpenStack is an open source Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) platform that can provide public and private clouds in your datacenter or on the edge. OpenStack contains multiple projects; the most commonly installed are Nova (compute), Keystone (identity), Neutron (networking), Glance (image), Cinder (block storage), and Swift (object storage).
Ceph is an open source project that provides software-defined storage with unified (object, block, and file) storage. You can scale out this storage, and it is self-healing with the ability to anticipate failures.
[ Get an overview of OpenStack's history, community, and 7 of its core projects. ]
How Ceph and OpenStack work together
Ceph Storage Clusters, which are based on Reliable Autonomic Distributed Object Store (RADOS), can provide back-end storage for OpenStack. This image shows how they work together.
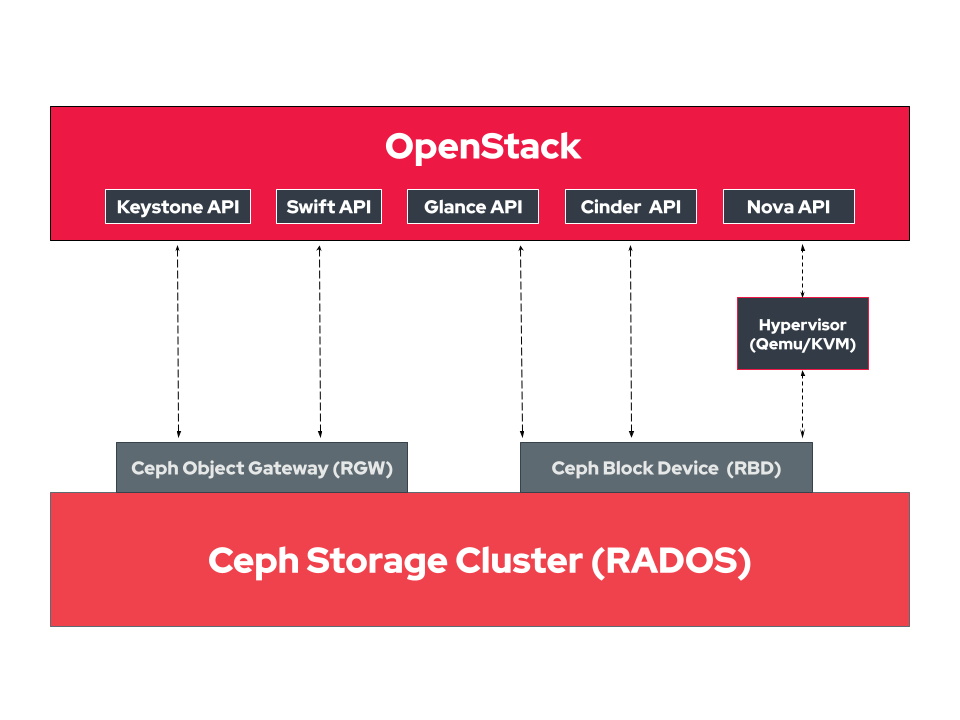
OpenStack's Keystone and Swift take advantage of Ceph by using the Ceph Object Gateway (a RADOS Rest Gateway, or RGW). This integration with Keystone allows the gateway to accept Keystone tokens for validation. This same gateway enables Swift to store its objects within Ceph.
On the other hand, Cinder, Glance, and Nova utilize Ceph block devices (RADOS block devices, or RBDs) for their back-end storage needs. Glance stores its images within Ceph, building virtual machines (VMs). Block storage devices created within Cinder for these VMs are provisioned within Ceph. And finally, Nova stores the virtual disk images of the running VMs within Ceph.
Open source makes it possible for these projects to integrate smoothly now and to maintain and improve their integration over time.
[ Download now: A system administrator's guide to IT automation. ]
Helpful resources
The following resources are a good place to start to learn more about Ceph and OpenStack:
- Getting started with RDO (community-supported version of OpenStack)
- RDO Twitter
- RDO community blog
- Ceph and OpenStack in a nutshell
- Storing containers with Kolla and Ceph
- Deploy OpenStack and Ceph on Kubernetes with Helm Charts
저자 소개
Amy Marrich is a Principal Technical Marketing Manager at Red Hat. She previously worked at a small open source e-assessment company in Luxembourg, where she was the Open Source Community and Global Training Manager. Previously, she was the OpenStack Instructor at Linux Academy and a Linux System Engineer on the Platform Engineering Cloud Operations team at Rackspace. She currently serves on the OpenStack Board, is an active member of the Openstack Ansible project, and was previously the chair of the OpenStack User Committee. Amy spends her free time competing in performance events (agility, FASt Cat, and dock diving) with her Dalmatians and competing in dressage with her Connemara pony.
유사한 검색 결과
Strategic momentum: The new era of Red Hat and HPE Juniper network automation
AI in telco – the catalyst for scaling digital business
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
A composable industrial edge platform | Technically Speaking
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래
