Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization 4.20 is now generally available, helping organizations modernize their virtualization strategy with greater speed and confidence through expanded platform availability, enhanced virtual machine (VM) management, and new capabilities for hybrid cloud infrastructure. With networking enhancements, optimized live migration, and improved user experience, OpenShift Virtualization 4.20 enables teams to deliver more agile, cloud-ready, and consistent operations wherever they choose to run their workloads.
Our collaborations with customers and partners on their migration journeys have helped deliver significant value. Get an inside look from leaders at Ford and Emirates NBD on how their unified modern platform helped power critical workloads for their business. Additionally, you'll learn how both companies benefit from an efficient, security-focused, and reliable infrastructure that integrates with their existing infrastructure, IT tooling, and development platforms, positioning them for success with newer projects like AI adoption and enablement.
Hybrid cloud flexibility
With the release of OpenShift Virtualization 4.20, customers can more easily extend their VM workloads from on-premise environments to multiple clouds, giving them greater flexibility as they modernize their infrastructure.
OpenShift Virtualization on Microsoft Azure Red Hat OpenShift
As organizations work to simplify their platforms and reduce operational complexity, the general availability of OpenShift Virtualization on Azure Red Hat OpenShift offers a security-focused path forward. Built and backed jointly by Red Hat and Microsoft, this solution enables customers to migrate and run VMs alongside containers on a single, enterprise-grade platform. Tools such as the migration toolkit for virtualization and Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform help automate migrations from legacy systems with minimal disruption. This collaboration streamlines operations, strengthens security, and helps optimize cloud spending—empowering teams to modernize faster across hybrid and multicloud environments. Azure NetApp Files is also available in public preview as a storage option for this solution.
Watch the demo below to see how you can now deploy your VMs on Azure Red Hat OpenShift.
OpenShift Virtualization on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
Additionally, our expanded cloud availability for OpenShift Virtualization across Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) offers a powerful option for running enterprise workloads with high performance and flexibility. Designed for demanding applications, OCI provides bare-metal, VM, and container-based compute options, making it ideal for both traditional and cloud-native workloads.
Two-node OpenShift with arbiter
As organizations push more applications and data processing into retail stores, factories, and industrial sites, edge deployments must balance tight physical constraints with the need for resilient, cost-efficient infrastructure. With OpenShift 4.20, Red Hat introduces two-node OpenShift with arbiter (TNA), a topology designed specifically to solve this challenge at scale. TNA delivers full high-availability behavior while reducing the hardware footprint from 3 full nodes down to 2 primary nodes, plus a lightweight arbiter that hosts only the third etcd instance. This allows edge locations to maintain quorum, avoid split-brain scenarios, and tolerate single-node failures, all while dramatically lowering cost and simplifying operational overhead. With support for both x86 and Arm architectures, flexible installation methods, and integration with storage partners like Portworx for unified data services, TNA provides a practical, production-ready foundation for running critical virtualized and containerized workloads at the edge.

Support for ARM
Organizations are increasingly choosing ARM-based hardware because it’s power-efficient, cost-effective, and well-suited for space-constrained edge and datacenter environments. Until now, that often meant keeping VM-based workloads on separate, x86-only infrastructure. With OpenShift Virtualization now supported on ARM, customers can bring those existing VMs onto the same platform they already use for lightweight, efficient ARM deployments. This gives teams a unified way to manage workloads across architectures and simplifies how they scale applications wherever ARM makes the most sense. Watch this demo to learn more.
Intuitive installation
OpenShift 4.20 introduces a new installation method (Tech Preview) designed to simplify cluster deployment with an intuitive, self-contained experience. Instead of juggling multiple tools and relying on an external registry, users boot every node, control plane, and workers from a single ISO image. Once the nodes come online, configuration is handled entirely through a built-in graphical interface, even in disconnected environments. This eliminates the need for CLI commands and externally-hosted websites during installation, while allowing users to monitor deployment progress directly from the same interface.
The GUI experience is the same as the Assisted Installer, bringing its streamlined, YAML-free workflow to fully local installs. Users no longer need to craft or manage configuration files; instead the installer guides them through cluster setup with clear prompts and automation. This Tech Preview feature is optimized for OpenShift Virtualization today, enabling teams to stand up bare-metal clusters quickly and consistently while reducing the complexity typically associated with cluster provisioning.
View the demo below for more information.
Upgrades and workload mobility
As environments grow and teams scale, customers need smoother upgrades and simpler lifecycle management to keep OpenShift Virtualization running reliably in production. Organizations can now perform direct upgrades within a minor release, eliminating the need for intermediate steps and reducing both downtime and operational overhead. This streamlined upgrade path helps teams stay current with less disruption while maintaining consistent performance across clusters.
Cluster upgrade prechecks and upgrade status reporting are now generally available, giving administrators clearer visibility before and during an upgrade. Prechecks proactively identify configuration or resource issues that could block the process, while detailed status reporting keeps teams informed throughout the upgrade itself. Together, these capabilities turn upgrades into a more predictable and transparent experience.
Cross-cluster live migration (Tech Preview) moves running VMs between clusters without disruption. This new flexibility supports scenarios like cluster consolidation, hardware refreshes, and regional workload mobility, allowing organizations to modernize their infrastructure while keeping critical applications online.



Customers need flexible, scalable, and low-overhead networking options as they modernize virtualized workloads on OpenShift. OpenShift Virtualization 4.20 delivers several improvements that make VM networking easier to manage and better aligned with evolving datacenter and edge architectures.
One of the key additions is Plug a Simple Socket Transport (passt) binding for user-defined networks in tech preview, providing a simpler, more efficient way to connect VMs with better integration with the Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform networking ecosystem. This reduces overhead, speeds up network configuration, and offers a lightweight connectivity option for customers who want to streamline their VM networking footprint.
Networking control also improves with routed ingress for Layer 2 UDNs, enabling traffic to reach VMs over routed paths—supported by BGP—rather than only through bridging. This gives customers a more scalable and predictable network design, especially in multitenant or large-scale deployments where clear routing boundaries are essential.
Customers also gain more operational flexibility with the ability to change the virtual NIC link state of a running VM, allowing teams to simulate failures, perform network maintenance, or troubleshoot issues without shutting down workloads. Together, these enhancements give organizations a more adaptable and modern networking foundation for running their VMs.
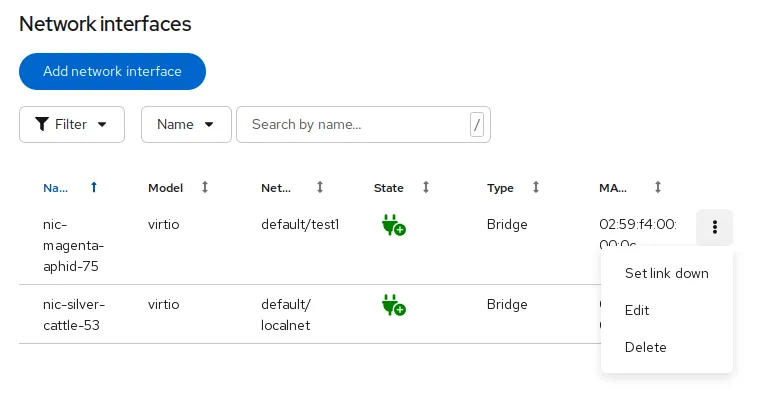
Advancing VM operations
Customers want consistent performance and efficient resource utilization, even as workloads fluctuate. With CPU Load Aware Rebalancing with Descheduler, now generally available, OpenShift Virtualization automatically redistributes VMs across nodes based on real CPU usage, preventing hot spots and reducing contention on over-loaded hosts. This feature helps maximize hardware efficiency, maintain workload stability, and helps ensure smoother operations across clusters automatically.
Legacy and diagnostic workflows still depend on ISO-based tools. The eject/inject CD-ROM support lets administrators mount or replace CD-ROM images on running VMs without rebooting, streamlining software installs, updates, and maintenance for older or specialized applications.
As workloads grow, teams often need to expand storage without taking applications offline. Disk hotplug support for virtio-blk devices makes this possible by allowing administrators to add or remove virtual disks on running VMs. This capability improves flexibility for scaling and maintenance, ensuring continuous availability even during dynamic infrastructure changes.
Simplified management
As organizations scale their virtualized environments across hybrid and multicloud deployments, simplifying management becomes increasingly critical. OpenShift Virtualization continues to evolve, bringing intuitive visibility, automation, and operational efficiency to administrators. The new multicluster tree-view provides a unified interface for monitoring and managing resources across multiple clusters, helping teams quickly identify and resolve issues without switching contexts. With a clear, hierarchical view of environments, administrators can make more informed decisions and maintain consistency across all deployments.
OpenShift Virtualization now includes the ability to optimize clusters for virtualization with a curated set of recommended operators, ensuring that environments are configured with the right components for stability and performance. Additionally, new VM metrics and alerts for CPU and storage latency enhance observability, enabling proactive performance tuning and faster troubleshooting. Together, these updates make managing large-scale virtualization workloads on OpenShift simpler, smarter, and more efficient.
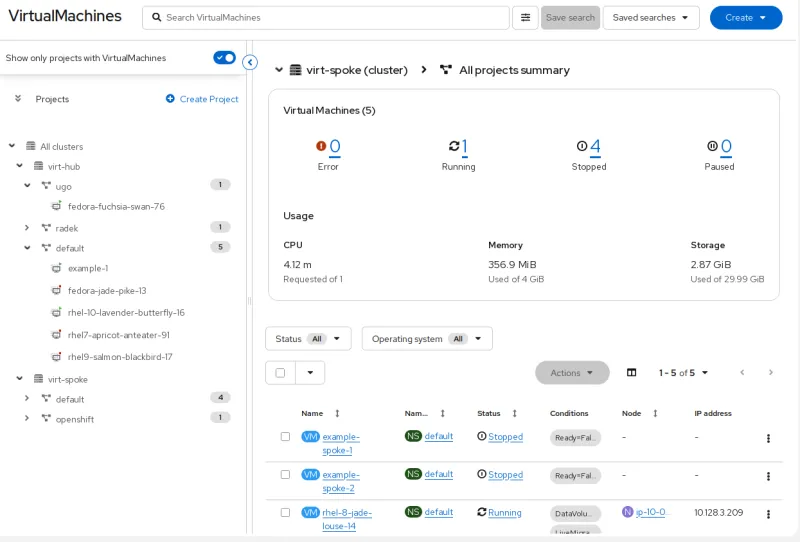
To further streamline day-to-day operations, administrators can now use the UI to live migrate a VM directly to a specific node, giving them precise control when balancing workloads, preparing for maintenance, or aligning VMs to specialized hardware such as GPUs or high-performance storage. This targeted migration option reduces operational friction and makes resource optimization far more intuitive for teams managing mixed VM and container environments.
At a broader fleet level, Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management 2.15 introduces a new Fleet Virtualization view (Tech Preview), enabling organizations to centrally oversee VM resources, configurations, and health across large numbers of OpenShift clusters. This unified perspective helps teams standardize operations, enforce policy governance consistently, and confidently scale VM workloads. The combination of improved local cluster tooling and fleet-level visibility delivers a more cohesive, end-to-end management experience for virtualization administrators and users.
Supercharge VM migration with storage offloading
Storage offloading is now available in Tech Preview in the migration toolkit for virtualization 2.10, significantly accelerates VM migrations from legacy storage solutions to OpenShift. This is ideal for migrating large databases with a significantly reduced maintenance window. Customers can take advantage of this feature with our growing list of compatible, certified storage providers, including Dell, Pure, Hitachi, HPE, and NetApp.

Beyond storage offloading, users can access new features to make the migration process even smoother and more flexible, including live cross cluster migration, migration to namespaces with UDN, BTRFS VM migrations, and support for network-bound disk encryption. These updates are designed to ensure the best performance and most stable migration experience for the widest range of workloads.
Together, these updates make migrations faster, more predictable, and easier to manage, especially for organizations modernizing large-scale, storage-heavy workloads. Read more about the latest migration toolkit virtualization 2.10 release.
Learn More
Explore the documentation.
Read about additional resources for getting started.
Watch the webinar.
Upstream project and community
Red Hat initiated and continues to be a leading contributor to KubeVirt, the upstream Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) project that users and vendors are adopting to integrate VMs in Kubernetes. We're also seeing additional companies choosing KubeVirt as a proven key technology. Explore the upstream innovation from the KubeVirt 2024 Summit.
Become a certified specialist
As with other Red Hat platforms, such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) and Red Hat OpenShift, modernizing your infrastructure and operations is a skill set that is valuable for both your company and your career. You can continue your training to become a Red Hat Certified Specialist in OpenShift Virtualization, and check out these additional resources:
리소스
Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization을 도입해야 하는 15가지 이유
저자 소개
Peter is a product manager in Cloud Platforms, focused on virtualization. He has been in high tech for storage, virtualization, databases, and hyperconverged solutions for longer than he cares to admit.
Courtney started at Red Hat in 2021 on the OpenShift team. With degrees in Marketing and Economics and certificates through AWS and Microsoft she is passionate about cloud computing and product marketing.
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래

