What is a load balancer? A load balancer is an efficient way to distribute the network traffic among various backend servers. It is also known as a server farm or server pool. It distributes client requests or network load to target web servers. Load balancers work on the round-robin concept, which ensures high reliability and availability.

One scenario
You have a web server that can manage 100 clients at a time. Suddenly the requests to that particular server increase by 100 percent. It's likely that the website will crash or be terminated. To avoid this situation, set up a target web server. In this scenario, the client never goes to the target web server. Instead, their request goes to the master server, and the master server sends the request to the target web server. When the target web server replies to the master web server, which is known as a reverse proxy.
[ You might also like: Turn a Kubernetes deployment into a Knative service ]
Using HAProxy as a proxy
The port on the main web server is called the frontend port. HAProxy is an HTTP load balancer that can be configured as a reverse proxy. Here we'll look at how I configured HAProxy by using an Ansible playbook.
Check the system where you need to configure HAProxy
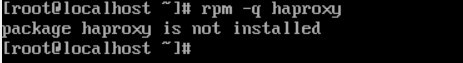
HAProxy is not installed on this system. You can confirm that with the following command:
rpm -q haproxy
Steps to configure HAProxy
Step 1 - Install HAProxy
To install HAProxy, you have to use a package module where you give the name of the service you want to install:
- name: "Configure Load balancer"
package:
name: haproxy
Step 2 - Copy the configuration file for the reverse proxy
Copy the configuration file so that you can modify it:
cp /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg /root/ws1/haproxy.cfg

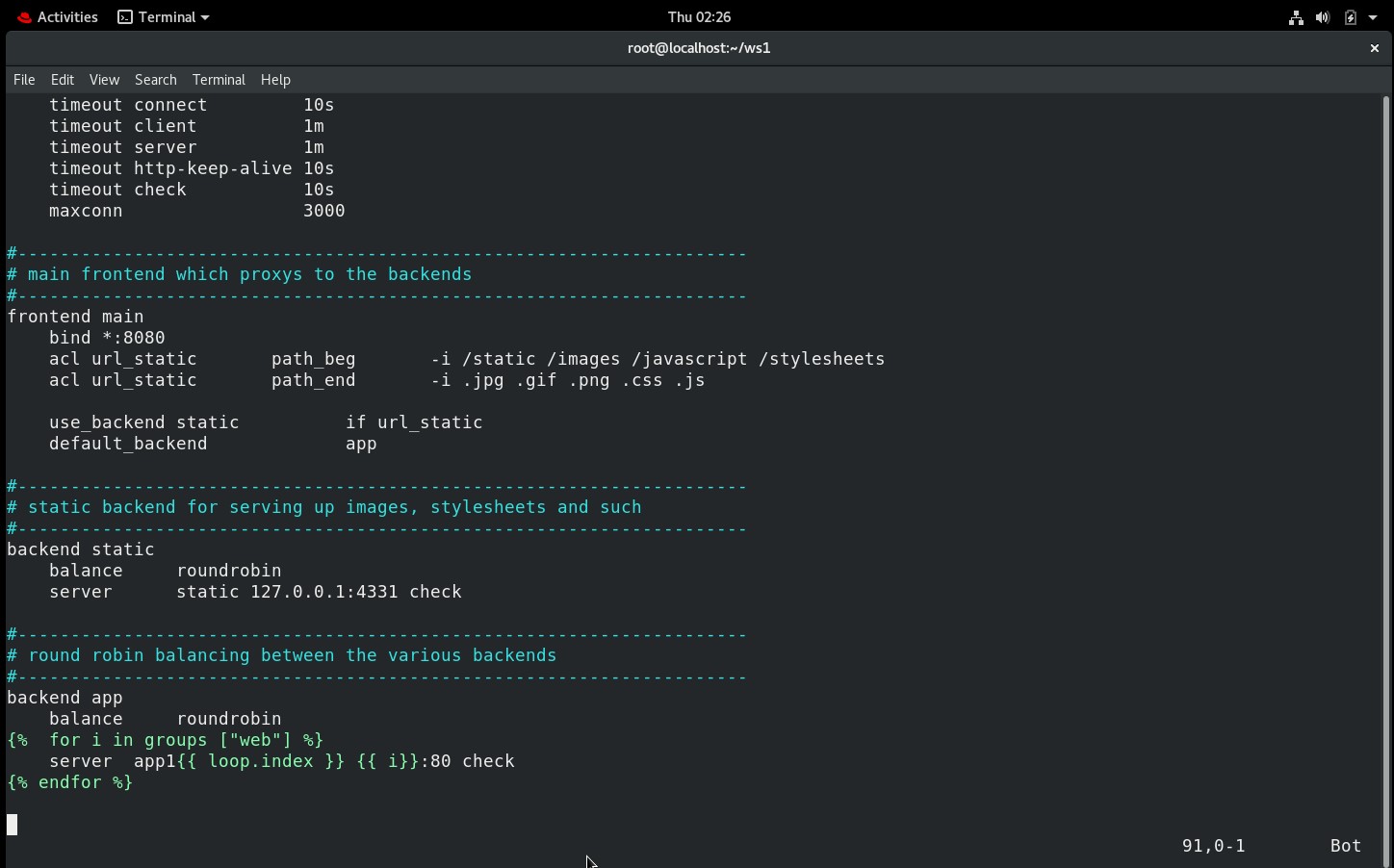
Step 3 - Change frontend port and assign backend IPs
By default, the frontend is bound to port 5000. I changed the port number to 8080. I also applied a for loop to configure the backend IP. Now you can launch as many web servers as you need, and there is no need to manually configure the IP inside the /etc/httpd/httpd.conf. It will automatically fetch the IP from inventory.
backend app
balance roundrobin
{% for i in groups ["web"] %}
server app1{{ loop.index }} {{ i}}:80 check
{% endfor %}
Step 4 - Copy haproxy.cfg to the managed node
Using template mode, copy the config file for HAProxy from the controller node to the managed node:
- template:
dest: "/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg"
src: "/root/ws1/haproxy.cfg"
Step 5 - Start the service
Use the service module to start the HAProxy service:
- service:
name: "haproxy"
state: restarted
Check the system where you need to install httpd webserver
For testing the HAProxy configuration, you will also configure httpd on your target node with the help of Ansible. To check that you don't already have httpd on your system, use the following command:
rpm -q httpd

Step 1 - Install httpd
The package module is used to install httpd on the managed node:
- name: "HTTPD CONFIGURE"
package:
name: httpd
Step 2 - Copy the webpage
The template module is used to copy your webpage from the source to the destination:
- template:
dest: "/var/www/html/index.html"
src: "/root/ws1/haproxy.html"
Step 3 - Start the service
The service module is used to start the httpd service:
- service:
name: "haproxy"
state: restarted
Complete the playbook to configure the reverse proxy
In this playbook, you have two different hosts with two different groups. One group is for the web server, and another is for the load balancer:
---
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: "HTTPD CONFIGURE"
package:
name: httpd
- template:
dest: "/var/www/html/index.html"
src: "/root/ws1/haproxy.html"
- service:
name: "httpd"
state: restarted
- hosts: lb
tasks:
- name: "Configure Load balancer"
package:
name: haproxy
- template:
dest: "/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg"
src: "/root/ws1/haproxy.cfg"
- service:
name: "haproxy"
state: restarted
Run the playbook
ansible-playbook haproxy.yml

Output
The playbook runs successfully, and the two target web servers can be accessed by the main web server using a load balancer.


[ Looking for more on system automation? Get started with The Automated Enterprise, a free book from Red Hat. ]
Conclusion
The load balancer and reverse proxy have now been configured by Ansible. You can add a layer of protection and availability to your web services by adding HAProxy to your infrastructure. Be sure to check out the documentation for your specific target to learn more.
Sobre o autor
Sarthak Jain is a Pre-Final Year Computer Science undergraduate from the University of Petroleum and Energy Studies (UPES). He is a cloud and DevOps enthusiast, knowing various tools and methodologies of DevOps. Sarthak also Mentored more than 2,000 students Regarding the Latest Tech trends through their community Dot Questionmark.
Mais como este
Strategic momentum: The new era of Red Hat and HPE Juniper network automation
Redefining automation governance: From execution to observability at Bradesco
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
You Can’t Automate Collaboration | Code Comments
Navegue por canal
Automação
Últimas novidades em automação de TI para empresas de tecnologia, equipes e ambientes
Inteligência artificial
Descubra as atualizações nas plataformas que proporcionam aos clientes executar suas cargas de trabalho de IA em qualquer ambiente
Nuvem híbrida aberta
Veja como construímos um futuro mais flexível com a nuvem híbrida
Segurança
Veja as últimas novidades sobre como reduzimos riscos em ambientes e tecnologias
Edge computing
Saiba quais são as atualizações nas plataformas que simplificam as operações na borda
Infraestrutura
Saiba o que há de mais recente na plataforma Linux empresarial líder mundial
Aplicações
Conheça nossas soluções desenvolvidas para ajudar você a superar os desafios mais complexos de aplicações
Virtualização
O futuro da virtualização empresarial para suas cargas de trabalho on-premise ou na nuvem
