Observability is the ability to gain insights into the internal behavior of a system or application by analyzing its outputs. Especially with the rise of complex, distributed systems, observability is an essential element of modern software engineering. Implementing an observability solution requires careful consideration of the specific needs of your system and the available tools and technologies.
There are 2 approaches to implementing observability: using multiple observability solutions via heterogeneous implementation, and using a single solution via a unified observability solution. Heterogeneous and unified observability each have advantages and the choice between them depends on an organization's specific needs. In this article, I will explain the difference between the 2 approaches.
[ Build a resilient IT culture ]
Heterogeneous observability
Heterogeneous observability refers to the use of multiple specialized tools and systems to monitor and analyze different components and layers of an application or system. This pattern typically uses multivendor solutions in siloed implementations, and the solutions work independently. These patterns are more common in organizations that are early in realizing the value of observability.
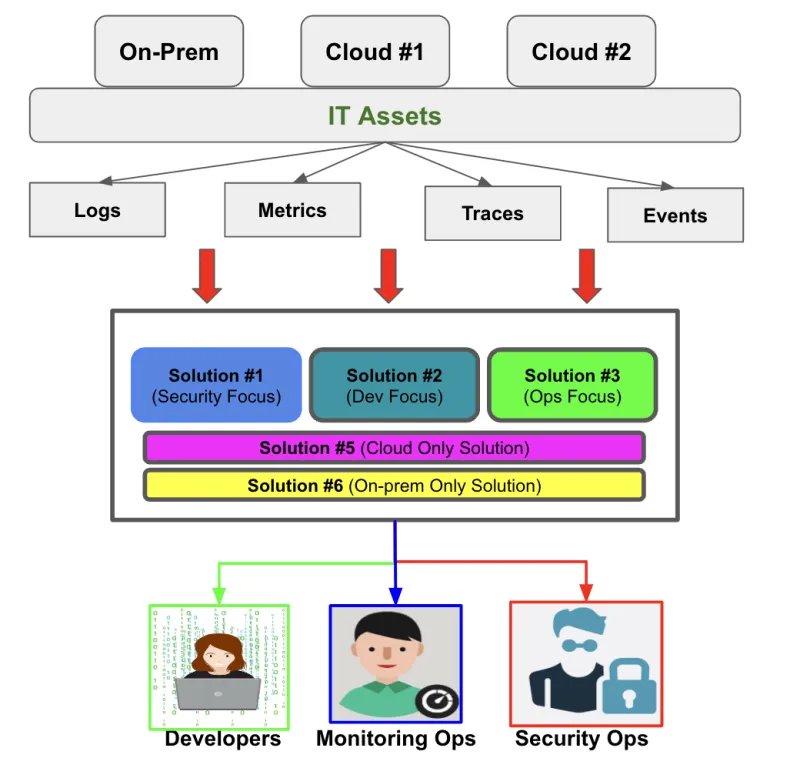
Benefits of heterogeneous observability:
- Better visibility: Heterogeneous observability allows organizations to get a more thorough view of their applications and infrastructure. By using multiple specialized tools, teams can monitor and analyze different layers of the system in detail to create a comprehensive picture of what's happening.
- More precise insights: Different components of an application or system require different monitoring and analysis tools. By using specialized tools for each component, teams can get more precise insights into the performance and behavior of each one.
- Greater flexibility: Heterogeneous observability gives teams greater flexibility to choose the right tools for the job. Different teams have different needs, and specialized tools allow them to select the best ones for their purposes.
- No vendor lock-in: Organizations can avoid being tied to a single vendor for their observability needs by using multiple tools from different vendors. Preventing vendor lock-in may provide more flexibility in the long run.
Unified observability
Unified observability involves consolidating monitoring data from various sources into a single unified view. This is more often the approach taken by a mature enterprise that has explored and realized the value of observability solutions.
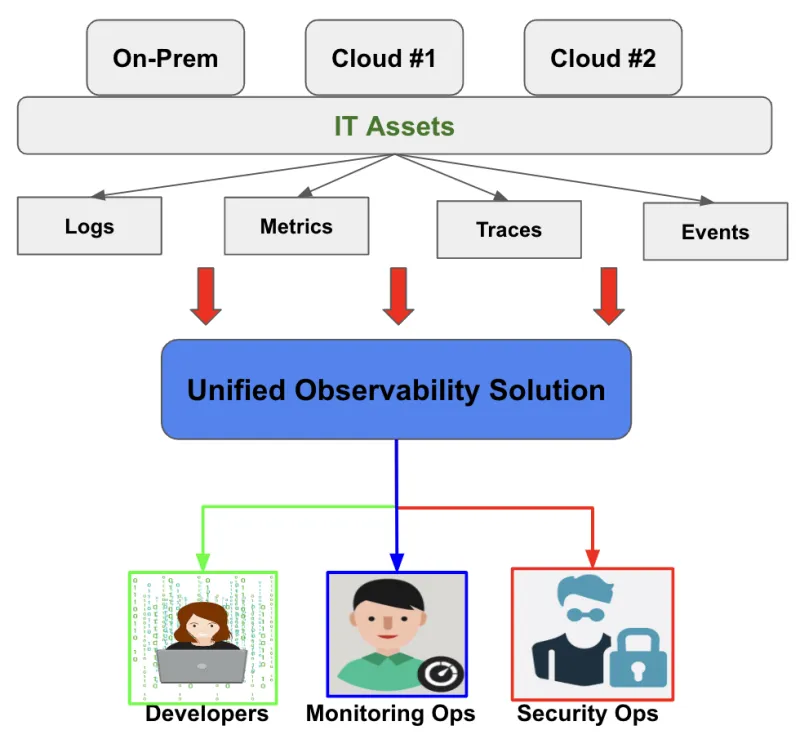
Benefits of unified observability:
- Simplicity: Teams can simplify monitoring and analysis workflows by consolidating monitoring data from various sources into a single view. This approach helps reduce the time and effort required to manage applications and infrastructure and troubleshoot problems.
- Holistic view: Unified observability provides a holistic view of the system, making it easier to identify and diagnose issues that span multiple components or layers.
- Better collaboration: A unified observability platform helps teams collaborate more easily and share insights more effectively, improving communication and coordination between different teams.
- Reduced costs: Consolidating data monitoring into a single view may reduce the costs associated with managing multiple tools and systems.
Making a choice
The choice between heterogeneous and unified observability is yours and really depends on your organization's specific needs and goals. Both approaches have their advantages, and the right choice will depend on factors such as the complexity of the system, the size of the organization, and the available resources.
Sobre el autor
Mike Calizo is a Principal Customer Service Manager at Elastic. Before Elastic, he was an Associate Principal Solution Architect based in New Zealand. His technology focuses are OpenShift, RHEL, Satellite, and Ansible. Mike is also a very active member of the open source community and enjoys organizing and presenting at Ansible and OpenShift Meetups in New Zealand several times a year.
Más como éste
AI insights with actionable automation accelerate the journey to autonomous networks
IT automation with agentic AI: Introducing the MCP server for Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
Adventures In Automation | Compiler
Navegar por canal
Automatización
Las últimas novedades en la automatización de la TI para los equipos, la tecnología y los entornos
Inteligencia artificial
Descubra las actualizaciones en las plataformas que permiten a los clientes ejecutar cargas de trabajo de inteligecia artificial en cualquier lugar
Nube híbrida abierta
Vea como construimos un futuro flexible con la nube híbrida
Seguridad
Vea las últimas novedades sobre cómo reducimos los riesgos en entornos y tecnologías
Edge computing
Conozca las actualizaciones en las plataformas que simplifican las operaciones en el edge
Infraestructura
Vea las últimas novedades sobre la plataforma Linux empresarial líder en el mundo
Aplicaciones
Conozca nuestras soluciones para abordar los desafíos más complejos de las aplicaciones
Virtualización
El futuro de la virtualización empresarial para tus cargas de trabajo locales o en la nube
