Creating virtual machines (VMs) from golden images is a common practice. It minimizes the deployment time for new VMs and provides a familiar environment for the VM's owner. The admin benefits from creating golden images in an automated manner because it reflects the current configuration.
This blog post will show how to deploy KubeVirt Tekton tasks with example pipelines and how to run the windows-bios-installer pipeline. Prerequisites for this post are OpenShift (version 4.13), OpenShift Pipelines, and OpenShift Virtualization (version 4.13).
OpenShift Pipelines provides automation to create golden images for Windows VMs in OpenShift Virtualization.
Since this integration of OpenShift Virtualization with OpenShift Pipelines is still in tech preview, the OpenShift cluster administrator must enable it. Here's the command:
oc edit hco -n openshift-cnv kubevirt-hyperconverged
Set the spec.featureGates.deployTektonTaskResources field to true:
apiVersion: hco.kubevirt.io/v1beta1
kind: HyperConverged
metadata:
name: kubevirt-hyperconverged
spec:
featureGates:
deployTektonTaskResources: true

After the deployment succeeds, three example pipelines exist.
The example pipelines can be found through OpenShift administration under the Pipelines tab in the openshift-cnv namespace. Each pipeline can be triggered by clicking on the Options menu on the right side of the screen and then selecting the Start button. This starts the pipeline window, where the user must insert a URL to the Windows 10 ISO file.
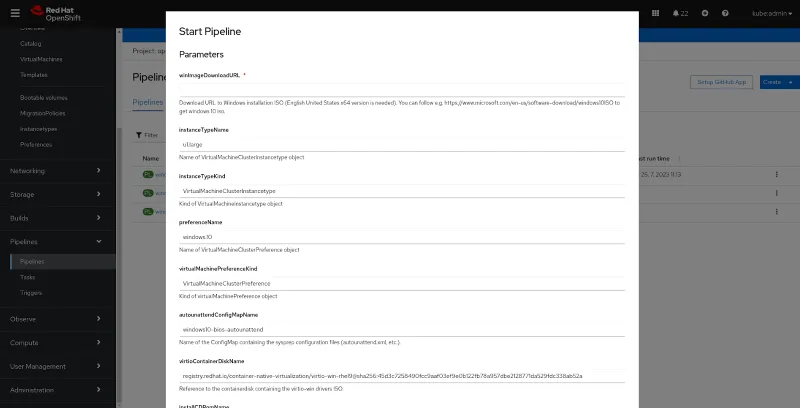
Other pipelines will be described in a follow-up blog post. The windows-bios-installer pipeline shows how to create your own Windows 10 golden image with VirtIO drivers installed in the OpenShift cluster. The pipeline's only required parameter is a URL to a Windows 10 ISO file; all other parameters have default values, which can be changed.
In addition to the pipeline, an example sysprep answer file named autounattend.xml is deployed in a config map. This answer file works with Microsoft's Windows installation multi-edition ISO for English United States and x64. Users can apply their own customizations to the Windows image with the sysprep answer file, as seen here.
The pipeline consists of multiple steps:
- Downloading the Windows ISO into a PVC
- Creating a virtual machine that uses the sysprep answer file to install Windows
- Copying the resulting disk image into the default Windows 10 boot source of the cluster
The result of this pipeline is a DataVolume in the openshift-virtualization-os-images namespace. When a user wants a new Windows 10 VM, the VM will be created from this DataVolume without any additional configuration required.
Wrap up
You have seen how to use a sample pipeline to automatically deploy golden VM images in an OpenShift environment. Golden images are a critical part of deploying consistent and current VMs. Automating this process helps maintain that consistency.
À propos des auteurs
Plus de résultats similaires
Red Hat to acquire Chatterbox Labs: Frequently Asked Questions
Key considerations for 2026 planning: Insights from IDC
Edge computing covered and diced | Technically Speaking
Parcourir par canal
Automatisation
Les dernières nouveautés en matière d'automatisation informatique pour les technologies, les équipes et les environnements
Intelligence artificielle
Actualité sur les plateformes qui permettent aux clients d'exécuter des charges de travail d'IA sur tout type d'environnement
Cloud hybride ouvert
Découvrez comment créer un avenir flexible grâce au cloud hybride
Sécurité
Les dernières actualités sur la façon dont nous réduisons les risques dans tous les environnements et technologies
Edge computing
Actualité sur les plateformes qui simplifient les opérations en périphérie
Infrastructure
Les dernières nouveautés sur la plateforme Linux d'entreprise leader au monde
Applications
À l’intérieur de nos solutions aux défis d’application les plus difficiles
Virtualisation
L'avenir de la virtualisation d'entreprise pour vos charges de travail sur site ou sur le cloud
