Railway systems have been around for centuries and serve as a highly cost-effective method for freight delivery and rail is growing in popularity among passengers. Rail systems with a significant legacy operational technology (OT) footprint are just embarking on the digital transformation journey.
Bringing edge technology and operational intelligence to rail transportation can drive additional efficiencies while improving safety. Sensors provide data required to build a comprehensive view of operations represented through a digital twin of the rail network. Intelligence gained from the data can automatically and optimally orchestrate the movement of rolling stock. This blog post reviews Alstom’s use of Red Hat edge technologies to transform railway operations.
Alstom is a global leader that develops and markets mobility solutions to provide sustainable foundations for the future of transportation, from high-speed trains, metros, monorails and trams to turnkey systems, services, infrastructure, signaling and digital mobility. The company is headquartered in France with operations in seventy countries.
Climate variations make it challenging to deliver reliable solutions in locations like Kazakhstan, requiring components to undergo significant testing. Alstom’s signaling solutions provide improved safety with better capacity and reliability using data acquired from sensors combined with edge processing.
With an increased demand for faster, climate-friendly transportation options and the unpredictability of gasoline prices making personal transportation more expensive, rail companies' need for edge solutions is likely to increase over the next decade. Red Hat technologies delivered the capability required by Alstom’s rail network solutions to overcome the following challenges:
Hardened cybersecurity: With transportation being a critical resource, security is an essential requirement, as a hacker taking control of OT systems can have severe consequences. Railway systems vendors require complete control of hardware and software with in-depth testing.
High-availability devices: With rolling stock and railway lines located in areas with climates varying from sub-zero weather to desert conditions, an end-to-end Internet of Things (IoT) solution requires resilient built-for-purpose devices.
Limited connectivity: Tracks in remote areas with little to no connectivity require devices to operate independently. Edge solutions are ideally suited to deliver essential functionality in these environments.
Integration: Integrating existing legacy OT systems with the modern container technology of IT systems needs a reliable messaging service with guaranteed delivery and built-in security.
The components used by the Alstom solution are illustrated here:
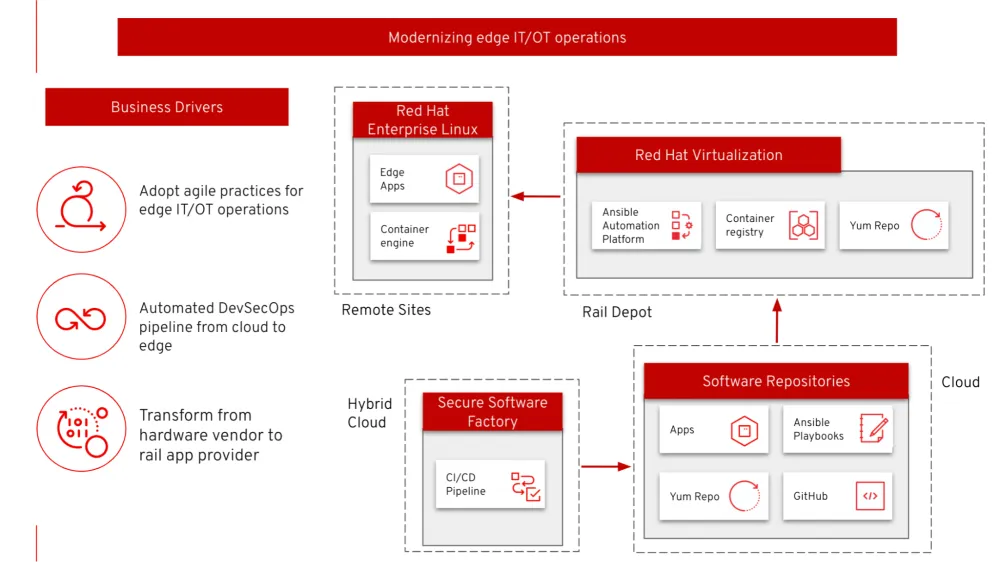
You can learn more about each component — such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) and Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform — on the Red Hat website. Here we'll articulate the following benefits of open source components in an edge solution implementation:
Agility: Depending on the size of the rail network, there may be thousands of devices running software. The patching of these applications and the underlying operating system software must be automated in an edge architecture.
Security: Hackers are frequently attacking soft targets like the IT environments of small businesses. There is a high attraction to hacking a nation’s infrastructure, requiring complete control of end-to-end hardware and software in a railway network. In-house management and ownership of the software supply chain pipeline reduce the risk of bad actors taking control of the hardware and software stack.
Response time: With thousands of wayside devices in a rail network, the speed of responding to events is essential for handling continuous communications from rolling stock. Cloud-native technology utilizing containers running software on bare metal enables an environment delivering low latency requirements of an edge solution.
The business value of an edge solution applied in rail networks contributes to the bottom line, and includes:
Energy efficiency: Railroad operators use fixed rail network information to plan passenger and freight schedules. Data from sensors can be used to optimize the energy use of rolling stock by continuously adjusting schedules in real-time.
Increased usage of infrastructure: Automation using discrete data from the rail network can enable trains to travel with a shorter distance between trains. The increased capacity speeds freight transportation and improves passenger experience by reducing wait times without added capital expenditure on infrastructure. Reliability and punctuality increase the adoption of railways for transport, resulting in a lower carbon footprint.
Security and safety: Combining IT and OT potentially allows bad actors to interfere with critical functions, which can result in severe consequences. Enforcing stronger IT security involves getting updates to the edge to close known vulnerabilities and utilizing an operating system resistant to adding additional software outside of the image-creating procedure. Using fewer vendors and a continuously updated open source software stack protects the infrastructure from cybersecurity threats.
Customer safety and experience: Real-time adjustments to schedules improves overall punctuality. Collecting detailed information about a rail network helps proactively inform customers of delays.
Predictive maintenance: Data from sensors that help detect changes in vibration and sound is used to detect upcoming failures, further improving uptime while reducing rolling stock maintenance costs. Better reliability and uptime of equipment can reduce unforeseen delays.
Other industries that combine IT and OT at the edge
Alstom’s implementation of an edge solution is an innovative implementation of open source container technology that combines IT and OT to deliver business value. Several other industries that are listed below can apply such solutions:
Local governments: Optimize transport systems by rerouting traffic in real-time using in-vehicle data and sensor data across a municipality. Integrating data with neighboring cities can improve traffic efficiencies. Metro bus networks can use sensors for predictive maintenance, enhancing customer experience with fewer vehicle breakdowns. Crowd management at stadiums could use data from gate sensors and surveillance cameras.
Shipping services: Trucking can use vehicle data to plan and optimize crew scheduling, and optimize trip routing with information from sensors to lower the carbon footprint.
Manufacturing plants: Predictive maintenance can increase production efficiencies while reducing the machine operating budget. They can also optimize operations using data from sensors represented in a digital twin of a manufacturing plant.
Public utilities: Using 5G technology, data from sensors can detect water leaks and direct repair crews to the most appropriate locations proactively.
Commercial buildings: Optimize air conditioning systems to deliver a consistent climate experience throughout a building by combining natural air with artificial heating or cooling systems. Enhance energy efficiency with intelligence from data collected from sensors inside and outside the building.
Modernization of edge environments promises significantly improved efficiencies. Combining OT with IT puts enterprises on a path to becoming fully digital businesses. Alstom's implementation of an edge solution is an example of a collection of open source software contributing to the core-to-cloud-to-edge innovation.
The Alstom solution delivers a better experience for passengers and improves freight efficiencies without adding expensive physical infrastructure. The solution meets the security and high availability requirements of critical infrastructure. Enterprises should use proven architectural frameworks like Alstom has to accelerate the digital transformation journey for next-generation edge innovation.
저자 소개
RobustCloud LLC provides strategy and insight into adopting modern cloud technologies to improve business outcomes. The company offers advisory services and works closely with end-user companies, ISVs and SI’s, and vendors to help all parts of the ecosystem understand cloud computing, map business goals, and objectives, review and fine-tune strategies, and identify benefits and returns on investment, and more. RobustCloud brings extensive and diverse experience crafting and delivering innovative solutions to the enterprise market. Principal Consultant, Larry Carvalho, is frequently quoted in the press and available to conduct webinars, moderate panel discussions, and advise on message content.
Most recently, Larry worked as an industry analyst at IDC, covering overall cloud technologies while specializing in cloud platforms. Larry has progressive and broad experience in business and information technology, assisting global enterprise customers to gain competitive advantage with diverse experience in building new service initiatives, business development, consulting, and systems integration in software professional services organizations in multiple industries. Prior roles include project executive, solutions facilitator, architect, systems analyst, database designer, trainer, and programmer.
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래
