In a previous article, How to measure and use network latency data to improve 5G user experience, we demonstrated the importance of latency for network service performance and user experience and its impact on business and the economy.

This article presents the engineering development for latency-driven service and application orchestration. The goal is to address the challenges with a well-crafted technical solution and harvest its benefits. It leverages the partnership between Red Hat and Ddosify.
[ Read Hybrid cloud and Kubernetes: A guide to successful architecture ]
Background
Kubernetes is the standard application platform used across industries. Using Kubernetes in a cloud-native way (reasonably sized, distributed, up-to-date ephemeral clusters) requires extensive cluster management capabilities to perform tasks, including:
- Lifecycle management (LCM) of Kubernetes cluster(s) on different infrastructure types with end-to-end visibility and control.
- Distribution, placement, and management of workloads (wherever, whenever, and however needed) from a single-pane view with the lifecycle, security, and compliance information required by legal and industry specifications.
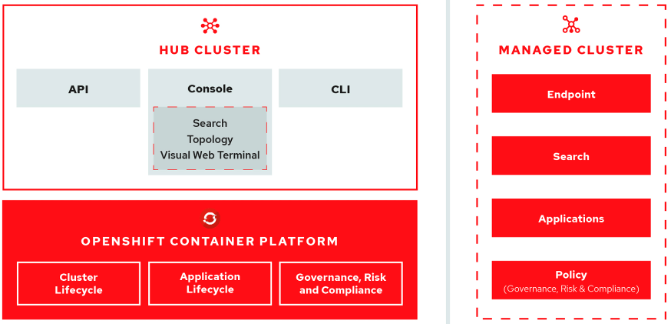
The open-cluster-management project addresses the challenges above with the following capabilities:
- Works across various application environments, including multiple data centers, private clouds, and public clouds that run Kubernetes clusters.
- Simplifies creating Kubernetes clusters and offering lifecycle management using a single pane.
- Enforces policies at the managed clusters using Kubernetes-supported custom resource definitions (CRD).
- Deploys and maintains Day 2 operations of applications distributed or placed across a fleet of clusters.
Red Hat develops and maintains these capabilities with an open source mindset and methodology. It also packages and hardens them for enterprise needs under the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management (RH-ACM) product umbrella.
Solution and testing
Our solution blueprint leverages RH-ACM and basic Kubernetes constructs (such as label selectors) to implement latency-driven workload lifecycle management (scheduling, placement, continuous monitoring, and auto-migration) across multiple managed Kubernetes clusters.
[ Learn the basics; download the Kubernetes cheat sheet. ]
We created a new latency application placement operator to work with RH-ACM that performs three tasks:
- Integrates with the Ddosify latency API
- Automates latency measurement operations seamlessly
- Uses collected latency data for application scheduling
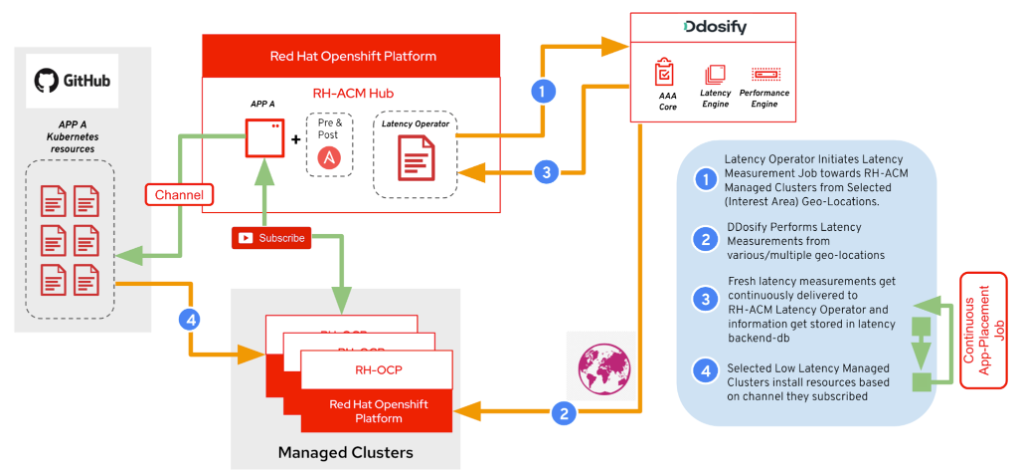
Breaking down the latency operator workflow depicted above:
- Install the latency operator on the RH-ACM Hub cluster and configure it with the desired point of origin per workload using location labels. The latency operator creates a latency measurement job on the Ddosify cloud (using the Ddosify Latency API).
- Ddosify cloud performs latency measurements from marked-down geolocation granularity (global, continent, country, state, city).
- Collected fresh latency data gets pushed or pulled from the Ddosify cloud to RH-ACM, and Latency Operator and Placement Rule lifecycle management run as depicted in the figure below.
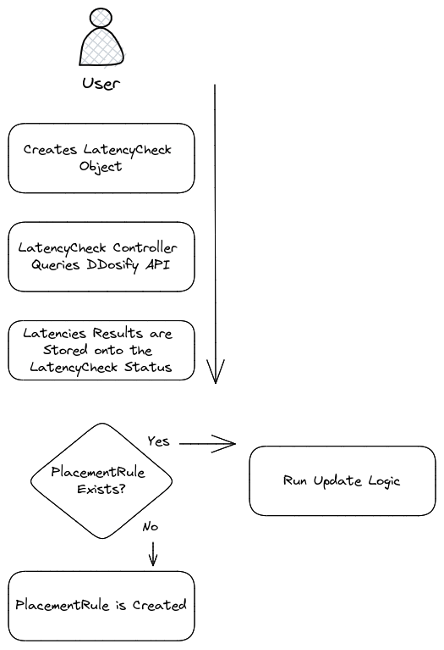
- Suppose the Placement Rule gets updated and the new destination is another cluster. RH-ACM schedules the application on the new low-latency cluster and removes the workload from the previously selected cluster.
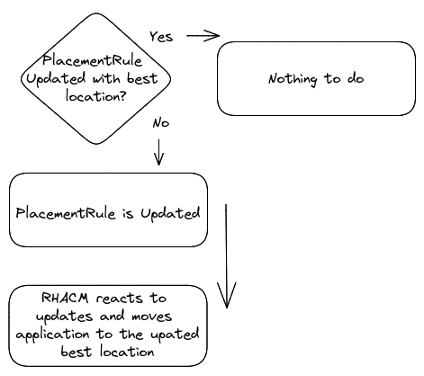
The solution blueprint covers continuous auto-application migration based on current latency metrics collected on interest origin locations where an application or service and users or consumers reside.
Testbed and demonstration
We recorded a demo in our testbed consisting of a hub cluster (name:local-cluster) and a managed cluster (name:sandbox01). These clusters are labeled (label:ddosify) with geolocation values (EU.ES.MA, EU.ES.BCN) on RH-ACM. The test bed allows you to experience:
- A latency comparison: At the demo application's initial orchestration time (first deployment), the cluster in EU.ES.BCN was observed with the lowest latency (41ms) versus EU.ES.MA with higher latency (43ms), and hence the application was deployed and tagged with EU.ES.BCN label -> sandbox01.
- A latency-based adjustment: We enforced (added fake latency overhead) an override on latency measurements on the external latency API integration side. The EU.ES.BCN (cluster:sandbox01) climbed to 45ms latency and the EU.ES.MA (cluster:local-cluster) stayed at 43ms. Hence, the local-cluster became the lowest latency cluster available for nearby service consumers.
- An application migration: RH-ACM autonomously initiated an application migration from sandbox01 (EU.ES.BCN) to the local-cluster (EU.ES.MA) cluster.
Wrapping up
Using an overseeing platform and service orchestrator (RH-ACM) with programmable capabilities (Kubernetes Operator framework) allows us to implement dynamic application management that leverages continuously measured latency (with user experience the key factor).

Per an agreement with the CNCF's Open Cluster Management (OCM) Working Group (WG), we will be working closely with the OCM WG to revise this custom latency operator to be part of the scoring framework.
This originally appeared on Medium and is republished with permission.
저자 소개
Fatih, known as "The Cloudified Turk," is a seasoned Linux, Openstack, and Kubernetes specialist with significant contributions to the telecommunications, media, and entertainment (TME) sectors over multiple geos with many service providers.
Before joining Red Hat, he held noteworthy positions at Google, Verizon Wireless, Canonical Ubuntu, and Ericsson, honing his expertise in TME-centric solutions across various business and technology challenges.
With a robust educational background, holding an MSc in Information Technology and a BSc in Electronics Engineering, Fatih excels in creating synergies with major hyperscaler and cloud providers to develop industry-leading business solutions.
Fatih's thought leadership is evident through his widely appreciated technology articles (https://fnar.medium.com/) on Medium, where he consistently collaborates with subject matter experts and tech-enthusiasts globally.
유사한 검색 결과
Simplify Red Hat Enterprise Linux provisioning in image builder with new Red Hat Lightspeed security and management integrations
F5 BIG-IP Virtual Edition is now validated for Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization
Can Kubernetes Help People Find Love? | Compiler
Scaling For Complexity With Container Adoption | Code Comments
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래

