Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly moving from a theoretical concept to a central engine of enterprise value, transforming sectors from healthcare to finance. The capacity of AI to analyze, predict, and automate makes it an indispensable asset for modern innovation. Yet, this widespread adoption introduces a significant security imperative: as AI workloads scale, so does the risk of unauthorized access to proprietary AI models and the sensitive data they handle.
These AI models are significant assets for organizations, representing substantial investments in research, training, and inferencing. Protecting them requires a robust security strategy that goes beyond traditional measures for data at rest (in storage) and in transit (over networks). The most vulnerable state is data in use, the moment it's actively being processed in memory.
This is where confidential computing emerges as a game-changer. By providing a trusted execution environment (TEE), it strengthens application security through isolation, encryption, and attestation, protecting data and code as they are being used. This approach enables a comprehensive defense-in-depth strategy, which is crucial for regulated industries handling sensitive information. By integrating these security features with a scalable, high-performance AI and machine learning (ML) ecosystem, companies can leverage AI with confidence, without sacrificing security for speed.
In this blog, we will explore the usage of Red Hat OpenShift confidential containers along with NVIDIA confidential GPUs to protect AI workloads, focusing on Red Hat AI Inference Server as the workload.
Confidential containers on bare metal
Confidential containers (CoCo) are a cloud-native implementation of confidential computing that brings the security of a TEE to a standard containerized workload (such as Intel TDX or AMD SEV-SNP). While this technology is often discussed in the context of public cloud security, its value on bare metal deployments is equally compelling and will be the focus of this blog.
The core value of confidential containers on bare metal lies in their ability to protect data in use from threats that exist within your own data center. Traditionally, data is vulnerable when decrypted in memory, especially to attacks from privileged software such as the host operating system or a malicious insider with administrative access. CoCo addresses this by running container workloads inside encrypted virtual machines (VMs) residing within the hardware's TEE called confidential VMs (CVMs). CoCo relies on the Trustee attestation solution to prove to the workload’s owner that it is running on genuine, untampered-with hardware, providing organizations with the confidence to handle their most sensitive workloads in their own data centers.
Red Hat OpenShift is the industry's leading hybrid cloud application platform powered by Kubernetes, providing a robust and scalable foundation for orchestrating containerized applications, including complex AI workloads. Building on this, OpenShift confidential containers bring the power of confidential computing directly to your containerized applications.
CoCo simplifies the adoption of confidential computing by abstracting away the complexity of the underlying hardware, allowing consumers to deploy secure workloads using familiar container images and Kubernetes manifests. When a confidential container workload is initiated, CoCo creates a CVM within the CPU's TEE in the background and performs the necessary attestation operations using Trustee.
The following diagram shows the overall OpenShift confidential containers deployed for a typical use case of secrets retrieval by the workload:

For additional information on this solution, including explanations of each of the components, we recommend reading our previous blog: Introducing confidential containers on bare metal.
In the context of securing AI workloads, NVIDIA confidential GPUs provide the key differentiation, in addition to the TEEs. CoCo is developing support for deployments of confidential containers with NVIDIA confidential GPUs, including end-to-end attestation solutions (CPUs and GPUs).
Unlocking enterprise AI with NVIDIA's Blackwell GPUs and confidential containers
The widespread adoption of AI in the enterprise hinges on a fundamental challenge of securing sensitive data and proprietary models in an increasingly complex and distributed environment. While confidential computing has long been a goal, the convergence of NVIDIA’s cutting-edge GPU technology with cloud-native practices is finally making it a reality. The combination of NVIDIA’s Blackwell architecture and confidential containers presents a monumental opportunity to leap forward, providing a complete, end-to-end security solution for AI workloads on Kubernetes.
For years, the power of confidential computing was primarily confined to the CPU with data-in-use protected within a CPU's TEE. As AI workloads are becoming increasingly dependent on GPU acceleration, a significant security gap has emerged—data moved to an unprotected GPU, leaving it vulnerable to threats from a compromised host or malicious administrators.
NVIDIA's Hopper architecture in the H100 and H200 GPUs changed this, introducing the first GPU-based confidential computing capabilities. This innovation extended the TEE to the GPU, protecting data and models even while they were being processed. Now, the new Blackwell architecture further enhances this capability, providing robust hardware-level security that is a prerequisite for any enterprise-grade AI deployment. It’s no longer just about protecting data at rest or in transit, it's about securing it where it matters most—while it's actively being used.
Confidential containers: Securing the cloud-native AI stack
While GPU confidential computing secures the hardware, CoCo provides the crucial software layer that makes confidential AI practical and scalable for modern enterprise deployments. Built on open source projects like Kata Containers, CoCo allows you to deploy AI workloads in a hardened, isolated environment.
In a Kubernetes cluster, a confidential container runs within its own lightweight CVM. This CVM provides a hardware-backed TEE that protects the container's contents from the host operating system, the hypervisor, and any privileged users or malicious actors. For enterprises, this is a game-changer because it allows them to:
- Protect intellectual property: Proprietary AI models, like large language models (LLMs) such as Nemotron, can be containerized and “lifted and shifted” into a confidential container. The model weights and logic are encrypted and protected from being stolen or tampered with.
- Protect sensitive data: Data such as PII/PHI can be processed within the confidential container, so it remains private and compliant with regulations, even when running on a shared public cloud infrastructure.
- Enable multi-tenancy: A single Kubernetes cluster can host and protect AI workloads from different business units or even multiple organizations, with each workload isolated within its own TEE.
End-to-end attestation: Building a chain of trust
Security is not just about isolation, it's about verifiable trust. You must be able to verify the integrity of the entire computing stack—from the hardware and firmware to the confidential container and its contents. This process is known as composite attestation. It creates a cryptographically provable chain of trust that an enterprise can verify before a workload is ever allowed to run.
NVIDIA's confidential GPUs, when combined with CoCo, enable this end-to-end attestation. The system can cryptographically prove that the AI workload is running on a genuine NVIDIA GPU with confidential computing enabled, and that the container and its contents have not been tampered with. This attestation capability provides a high degree of assurance that the entire environment is secure and trusted, which is a requirement for many regulated industries and a critical factor for wider enterprise adoption.
By combining the unparalleled processing power of NVIDIA's GPUs with the scalable and protected isolation provided by confidential containers, enterprises can finally deploy their most sensitive AI workloads with confidence. This new paradigm of "confidential AI" is not just a security feature, it’s an enabler for innovation, helping companies fully leverage AI without compromising on privacy, security, or compliance.
When adding confidential GPUs, our previous use case is transformed to the following diagram:

The Trustee attestation flow covers both the CPU and GPU, connecting both the TEE and the secure enclave inside the confidential GPU to the workload running in a pod (confidential container).
For additional details on this solution and the different building blocks, we recommend reading our previous blogs: AI meets security: POC to run workloads in confidential containers using NVIDIA accelerated computing and Secure AI inferencing: POC with NVIDIA NIM on CoCo with OpenShift AI.
Red Hat AI Inference Server
Red Hat AI Inference Server is a specialized, open source software solution designed to optimize the process of running AI models in production. At its core, it is the main piece of the puzzle that allows an AI application to communicate with a pre-trained model, especially LLMs and other generative AI models, and generate a response. This process, known as AI inference, is where the business value of an AI model is finally realized.
Built on the open source vLLM project, Red Hat AI Inference Server is engineered to overcome the everyday challenges of deploying complex AI models at scale, which include high costs, latency issues, and infrastructure complexity. It provides capabilities such as high performance and efficient inferencing (optimized memory management, continuous batching, model parallelism), hybrid cloud and multi-accelerator support, model optimization, enterprise-ready solution and more.
In essence, Red Hat AI Inference Server serves as the engine for enterprise AI, turning complex models into fast, cost-effective, and scalable services that can be deployed anywhere across a hybrid cloud infrastructure.
For AI workloads, running Red Hat AI Inference Server with confidential containers on bare metal provides two key benefits. First, it protects the intellectual property of the AI model, which is a significant business asset. The model's logic and weights are shielded from theft or tampering by preventing access even from an administrator with physical access to the server. Second, it helps protect the confidentiality of the input data, which is important for industries that handle sensitive information, such as financial or medical records. This allows a business to maintain complete control over its data and hardware while still achieving the security and isolation typically associated with public cloud solutions. As mentioned in previous sections, this solution relies heavily on the Trustee's attestation to verify the TEE and confidential GPUs aren’t tampered with.
The following diagram extends the previous one to show how an AI workload runs inside CoCo:
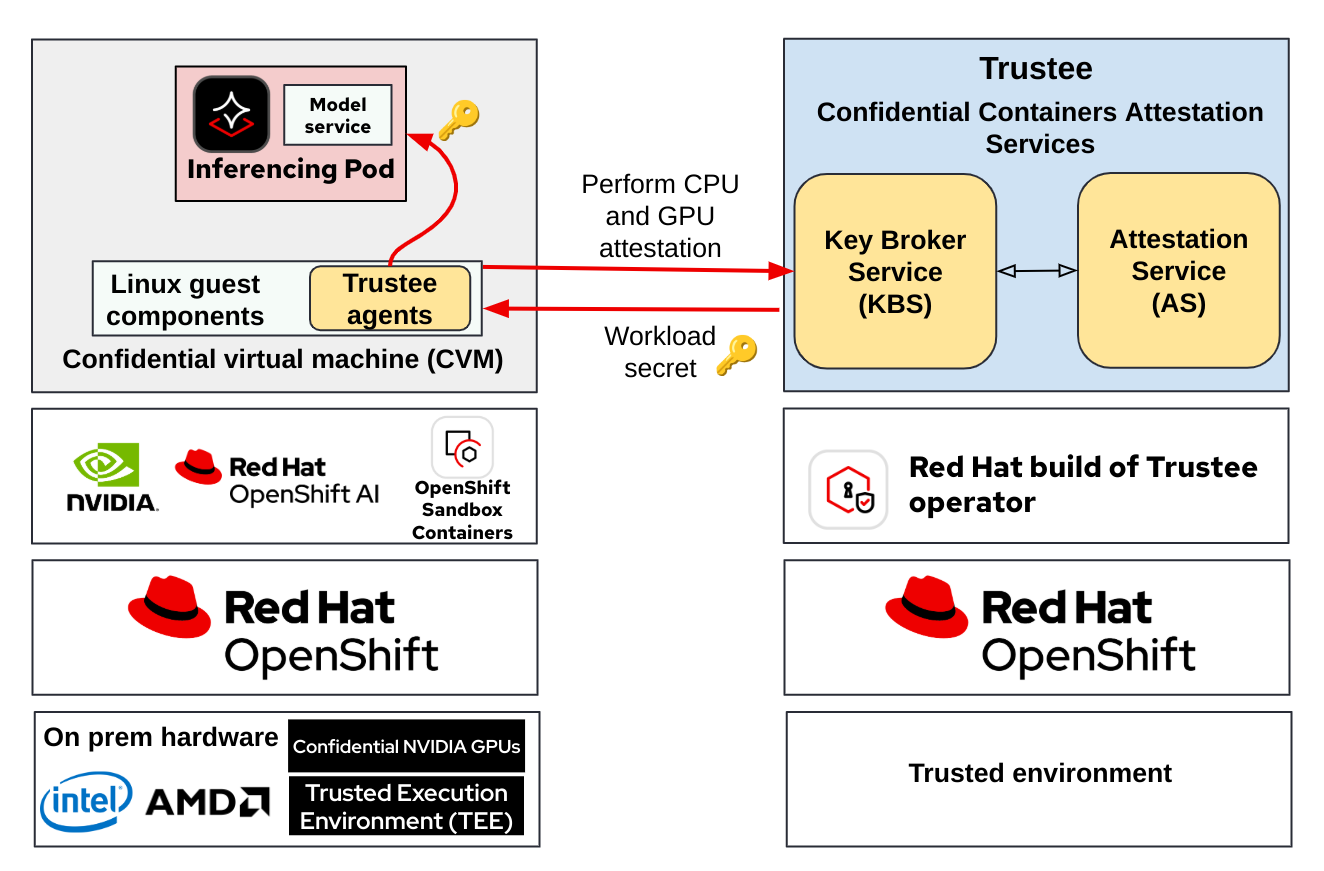
We are now shifting from a generic confidential container workload (running in the pod) to a specific inferencing pod. In this case, the workload secret can be the key to decrypt the model before being executed.
Demo: AI inferencing with CoCo bare metal and confidential GPUs
We will next present a demo of Red Hat AI Inference Server as a workload running inside CoCo, leveraging confidential GPUs for inferencing work.
The following demo uses an Intel TDX processor to ensure memory encryption:
And the same capability is also offered by AMD with SEV-SNP:
While Red Hat AI Inference Server provides a solid platform for performance and efficiency, a growing number of AI use cases require more than just speed, they require absolute security. This is particularly true when dealing with sensitive data, proprietary models, and highly regulated industries. Running Red Hat AI Inference Server with confidential containers and confidential GPUs creates a powerful combination that addresses these critical security needs.
The value of this approach can be broken down into 3key areas:
- Protecting data in use: By running Red Hat AI Inference Server inside a confidential container, the entire workload, including the AI model, the sensitive input data (such as financial records or patient information), and the inference results, is protected by TEEs and confidential GPUs. This creates an isolated "vault" that is protected against malicious or even privileged software on the host system, including the administrator. It’s also critical for regulated industries to meet the required strict data privacy regulations.
- Safeguarding intellectual property: Your proprietary AI model is a significant business asset. It represents years of research, development, and investment. Without proper protection, this "secret sauce" is vulnerable to theft or reverse engineering. This includes both model integrity and enabling secure collaboration between organizations.
- Protecting the full AI pipeline with confidential GPUs: AI inference workloads are heavily reliant on powerful GPUs, and this is where NVIDIA confidential GPUs come into play. They extend the TEE from the CPU to the GPU itself and also provide secure hardware mechanisms so all data and command transfers between the confidential container CPU and confidential GPU are encrypted.
Final thoughts
As AI continues to integrate itself more deeply into our digital infrastructure, the demand for robust security will only intensify. Confidential computing, powered by NVIDIA confidential GPUs and orchestrated by Red Hat OpenShift with confidential containers, represents a holistic solution to this challenge.
Recurso
A empresa adaptável: da prontidão para a IA à disrupção
Sobre os autores
Mengmei Ye is a Staff Research Scientist in Hybrid Cloud department at IBM T.J. Watson Research Center. She received her Ph.D. degree in Electrical and Computer Engineering from Rutgers University in 2021. Her research work has been recognized with a Distinguished Paper with Artifacts Award at ACSAC 2023, a Best Paper Award at IEEE ICCD 2016, and a Best Paper Nomination at IEEE HOST 2018.
Claudio is a software engineer at IBM Research and he has collaborated with open source communities for many years enabling confidential computing in multiple computer architectures. Currently, he is collaborating with upstream and downstream communities to enable NVIDIA GPUs in Confidential Containers for secure AI workloads.
Niteesh has worked for almost 22 years in various roles to enable various virtualization, filesystem and security features in AIX on IBM POWER systems. For last 5 years, he has been working on strengthening security for hardware based virtualized execution environments in Linux on x86 systems.
Pradipta is working in the area of confidential containers to enhance the privacy and security of container workloads running in the public cloud. He is one of the project maintainers of the CNCF confidential containers project.
Jens Freimann is a Software Engineering Manager at Red Hat with a focus on OpenShift sandboxed containers and Confidential Containers. He has been with Red Hat for more than six years, during which he has made contributions to low-level virtualization features in QEMU, KVM and virtio(-net). Freimann is passionate about Confidential Computing and has a keen interest in helping organizations implement the technology. Freimann has over 15 years of experience in the tech industry and has held various technical roles throughout his career.
Emanuele Giuseppe Esposito is a Software Engineer at Red Hat, with focus on Confidential Computing, QEMU and KVM. He joined Red Hat in 2021, right after getting a Master Degree in CS at ETH Zürich. Emanuele is passionate about the whole virtualization stack, ranging from Openshift Sandboxed Containers to low-level features in QEMU and KVM.
Mais como este
Innovation is a team sport: Top 10 stories from across the Red Hat ecosystem
Production-ready: Red Hat’s blueprint for 2026
Technically Speaking | Build a production-ready AI toolbox
Technically Speaking | Platform engineering for AI agents
Navegue por canal
Automação
Últimas novidades em automação de TI para empresas de tecnologia, equipes e ambientes
Inteligência artificial
Descubra as atualizações nas plataformas que proporcionam aos clientes executar suas cargas de trabalho de IA em qualquer ambiente
Nuvem híbrida aberta
Veja como construímos um futuro mais flexível com a nuvem híbrida
Segurança
Veja as últimas novidades sobre como reduzimos riscos em ambientes e tecnologias
Edge computing
Saiba quais são as atualizações nas plataformas que simplificam as operações na borda
Infraestrutura
Saiba o que há de mais recente na plataforma Linux empresarial líder mundial
Aplicações
Conheça nossas soluções desenvolvidas para ajudar você a superar os desafios mais complexos de aplicações
Virtualização
O futuro da virtualização empresarial para suas cargas de trabalho on-premise ou na nuvem




