Creating "golden images" of an operating system (OS) is a popular and recommended practice for deploying new systems to any environment, from the data center to the public cloud. They enable rapid deployments that are more maintainable and can better conform to your unique Standard Operating Environment (SOE) requirements. Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) provides two options to help you build customized RHEL OS images: RHEL image builder and Red Hat Insights image builder. An overview and list of latest articles about these can be found here: https://redhat.com/image-builder.
Insights image builder has recently added the first boot script configuration feature to embed scripts in the image that are run when an instance first starts up. This enables you to run your scripts to do any variety of custom tasks. This new pre-release feature is currently available by enabling Preview mode and will later transition to full production support status.
This article will focus on Insights image builder and demonstrate how to execute a simple shell script at first boot, as well as explain how it works. In later articles, we will demonstrate more advanced functionality, such as implementing RHEL system roles, registering to Red Hat Satellite and initiating callbacks to Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform.
Creating the image with Insights image builder
Insights image builder can be accessed under Inventory->Images in Insights for RHEL of the Hybrid Cloud Console. You can try the first boot script configuration by enabling Preview mode at the top of the screen. When this feature transitions out of preview status, this step will no longer be necessary.I’ll start by creating a new blueprint, and selecting the version of RHEL and target environments that I would like to use for the image.

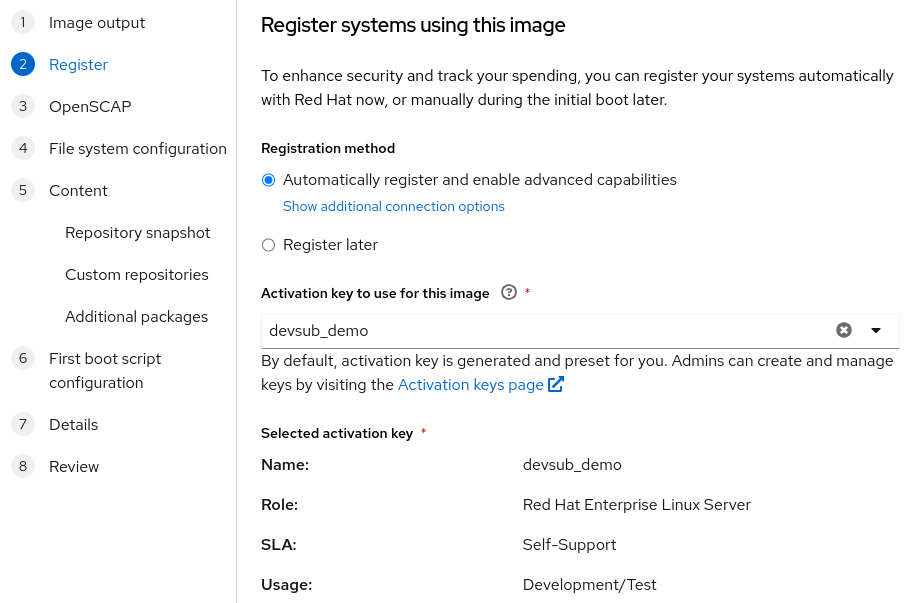
On the registration step of image builder, it is recommended that the system be registered with Red Hat. This will make sure that any script commands to install or update software will be able to download RHEL content, assuming network access to Red Hat is available.
Including a shell script for first boot automation
Insights image builder provides a text box, complete with syntax highlighting, for you to drag and drop, upload, or write your scripts from scratch. It will auto-detect both bash shell and python scripts.
Note that this feature supports regular shell (bash) and Python scripts that can run in a normal RHEL environment. This makes it easier to test script functionality in a normal environment. This is different from traditional RHEL installer kickstart, post-install scripting which are executed in a “chroot” environment and can be very challenging to test and debug.
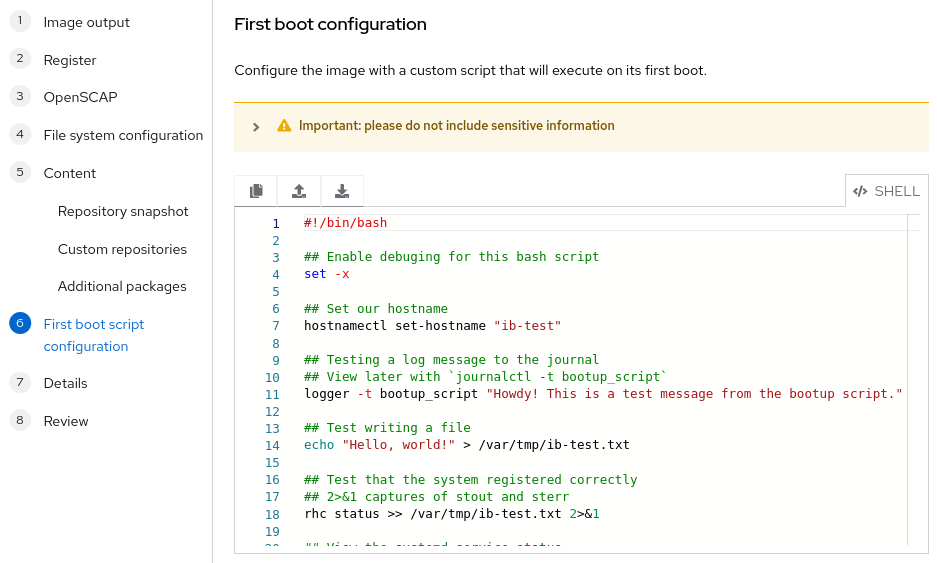
In this example, I used the following bash script. Note that it provides multiple examples of how to capture debugging output for later review.
#!/bin/bash
## Enable debugging for this bash script
set -x
## Test writing a file with a starting time stamp
date > /var/tmp/ib-test.txt
echo "Hello, world!" >> /var/tmp/ib-test.txt
## Set our hostname
hostnamectl set-hostname "ib-test"
## Testing a log message to the journal
## View later with `journalctl -t bootup_script`
logger -t bootup_script "Howdy! This is a test message from the bootup script."
## Test that the system registered correctly
## 2>&1 captures of stout and sterr
rhc status >> /var/tmp/ib-test.txt 2>&1
## View the systemd service status
systemctl status custom-first-boot >> /var/tmp/ib-test.txt 2>&1
## Final time stamp
date >> /var/tmp/ib-test.txtHow does it work?
The first boot script execution works by defining a systemd unit service with the oneshot option. This means the script will only run a single time. The shell script is renamed as /usr/local/sbin/custom-first-boot.done to ensure it is not run again while remaining available for future reference. The systemd unit file looks like this:
[root@ib-test ~# cat /etc/systemd/system/custom-first-boot.service
[Unit]
Description=Run first boot script
ConditionPathExists=/usr/local/sbin/custom-first-boot
Wants=network-online.target
After=network-online.target
After=osbuild-first-boot.service
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/usr/local/sbin/custom-first-boot
ExecStartPost=mv /usr/local/sbin/custom-first-boot /usr/local/sbin/custom-first-boot.done
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.targetValidation and debugging
The steps to provision a system from the image vary depending on the target platform. For more information, refer to the Insights image builder documentation.
Once a system is provisioned from the image, I logged in to the system to verify that the first boot script had properly run and to review the logging output.
Note that by using the set -x option at the beginning of the shell script, it captures all of the commands executed. This is good for debugging but may not be a recommended practice or conform to your organization’s security requirements as it could leak sensitive information.
First, I queried systemd about the service with the journalctl -u custom-first-boot.service command.

Next, I reviewed the output file that my script was writing to with the cat /var/tmp/ib-test.txt command.

Lastly, I reviewed the system’s primary messaging log to see where the service was run during startup using the less /var/log/messages command, and then searching for the custom-first-boot text.

Wrap up
The Insights image builder first boot script configuration functionality opens up many exciting possibilities that enable you to further customize your RHEL golden images. Check out the overview and list of latest articles here, then go over to Insights image builder to create your own custom blueprints and RHEL images.
Sobre el autor
Terry Bowling has been designing and administering UNIX and GNU/Linux environments since 1999. He brings this experience to the Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) and Insights Product Management teams to provide help streamline the assembling, deployment, and management of RHEL for our customers. Experience it today at redhat.com/image-builder.
Más como éste
Strategic momentum: The new era of Red Hat and HPE Juniper network automation
Redefining automation governance: From execution to observability at Bradesco
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
A composable industrial edge platform | Technically Speaking
Navegar por canal
Automatización
Las últimas novedades en la automatización de la TI para los equipos, la tecnología y los entornos
Inteligencia artificial
Descubra las actualizaciones en las plataformas que permiten a los clientes ejecutar cargas de trabajo de inteligecia artificial en cualquier lugar
Nube híbrida abierta
Vea como construimos un futuro flexible con la nube híbrida
Seguridad
Vea las últimas novedades sobre cómo reducimos los riesgos en entornos y tecnologías
Edge computing
Conozca las actualizaciones en las plataformas que simplifican las operaciones en el edge
Infraestructura
Vea las últimas novedades sobre la plataforma Linux empresarial líder en el mundo
Aplicaciones
Conozca nuestras soluciones para abordar los desafíos más complejos de las aplicaciones
Virtualización
El futuro de la virtualización empresarial para tus cargas de trabajo locales o en la nube
