This post was co-authored by Hemant Bhanawat, Director of Engineering at Yugabyte
Introduction
In this installment of this series on geographically distributed stateful workloads, we are going to take a look at YugabyteDB. YugabyteDB is a distributed SQL database designed around the CAP theorem and is just one of several options now available in the market of this new generation of distributed SQL databases. One of the reasons for featuring YugabyteDB is to not only illustrate that there are choices, but to be able to talk about different design decisions when using distributed SQL databases.
YugabyteDB Architecture
YugabyteDB is an open source distributed SQL database exposing the PostgreSQL API. It is compatible with PostgreSQL, so you should be able to connect any application that was previously developed to work with PostgreSQL.
YugabyteDB uses replicas for high availability and supports synchronization through the use of the Raft protocol. Additional features include partitions (called tablets) for scalability, and in case of a cross tablet transaction, the two-phase commit protocol is also implemented
YugabyteDB automatically partitions SQL tables into tablets without user intervention. It also automatically distributes tablet replicas to the configured failure domains ensuring, as much as possible, no data loss. This behavior can be influenced by the user by configuring the failure domains, replication factor, and database affinity to failure domains.
A YugabyteDB deployment consists of two components: the tablet server, which is the actual distributed database, and the master, which contains the database metadata (SQL databases, SQL tables, tablets definition, and their location in the various tablet server instances).
Separating the metadata from the data is a choice that some other distributed stateful workloads make. For example, Kafka stores metadata in ZooKeeper, and work is underway to move the metadata into special brokers called controllers. Separating the metadata makes sense given that it is generally much smaller in size and can be managed differently than the data itself. However, by doing so, it complicates the overall architecture. In particular, one must make sure that instances of the metadata server are properly distributed across the failure domain so as to not lose the entire database in the event of failure.
Geographical Deployment Design
From an architectural standpoint, the design for a geographically distributed YugabyteDB instance does not differ from the designs used in the previous installments of this series (part 2 and part 4). The following is a diagram depicting this architecture:

Starting from the top, we have a global load balancer directing connections to the YugabyteDB UI. Then, there are three OpenShift clusters with YugabyteDB instances deployed to each cluster. These instances can communicate with each other via a network tunnel implemented with Submariner.
Finally, at the bottom of the diagram, Red Hat Advanced Cluster Manager (RHACM) has been installed within a control cluster which we used to create the other clusters along with the global load balancer operator which facilitates configuring the global load balancer at the top of the diagram.
Each cluster is in a different region of a public cloud provider.
Zooming in on the YugabyteDB deployment, we have three tablet servers and a master (metadata server) in each cluster. Together, they form a logical YugabyteDB instance.

Step-by-step deployment instructuctions can be found at this repository.
Load Tests
We wanted to run the TPC-C standard OLTP benchmark to test both the performance and stability of the previously described deployment of YugabyteDB.
We executed this test in Google Cloud with the following configurations:
- Regions: us-east4, us-central1, us-west4
- Networking: Each cluster runs in its VPC, VPCs were peered, Submariner was configured with no NAT and VXLAN as the cable driver.
- Compute: Each tserver runs in a separate c2-standard-16 VM.
- Storage: standard pd-ssd disks.
We ran the TPC-C 1000 test with one client in each region for one hour; these were the results:
================RESULTS================
TPM-C | 4177.77
Efficiency | 97.27%
Throughput (req/s) | 148.52
================RESULTS================
TPM-C | 4164.43
Efficiency | 97.25%
Throughput (req/s) | 148.96
================RESULTS================
TPM-C | 4077.55
Efficiency | 95.22%
Throughput (req/s) | 144.00
Because of the way the tests are executed, the average efficiency must be taken as the final results of the test: 96.58. Efficiency is a metric derived from TPM-C (transactions per minute) and illustrates how close the tested database gets to the theoretical upper bound of transactions per minute given by the size of the test (the reason why there is an upper bound to the transaction per minute is that TPC-C incorporates thinking time for the emulated users).
This result is a pass, and it shows that this kind of deployment is usable in a production scenario.
Disaster Simulation
As usual, we wanted to also test how YugabyteDB behaved in a disaster situation. To do so, we isolated the network of one of the regions by preventing any inbound or outbound traffic while the TPC-C test was running:
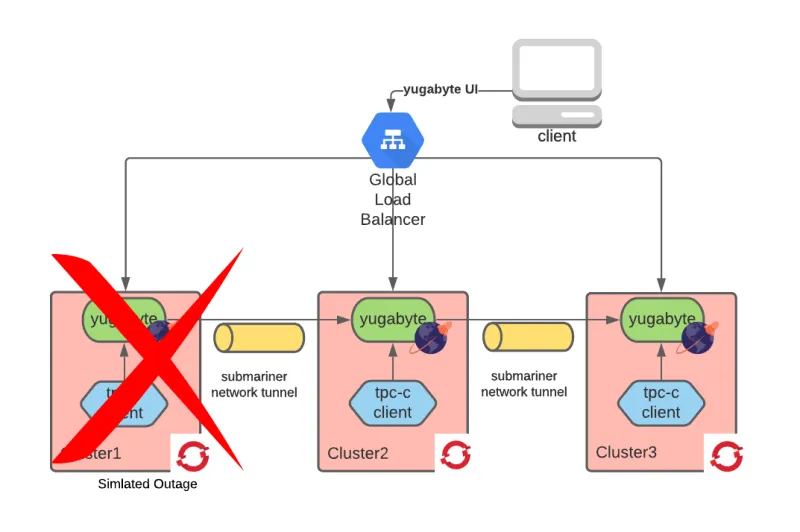
When we simulated the disaster, we observed a few errors in the surviving TPC-C clients; essentially, some in-flight transactions were rejected or failed to complete. We also noticed that YugabyteDB moved all of the tablet leaders to the healthy instances.
The system managed the disaster situation without the need for any human intervention.
When we restored connectivity to the isolated region, we did not notice any issues within the ongoing TPC-C clients. We also observed how YugabyteDB started rebalancing the database by moving the tablet leaders back to the newly available tablet servers.
Again, no human intervention was needed.
During the entire disaster simulation, the system experienced zero data loss (RPO 0) and very little unavailability (RTO measured in seconds).
Conclusion
In this article, we described how to deploy YugabyteDB in a geographically distributed fashion. We saw that, notwithstanding the inter-region latencies, a deployment of this kind can satisfy the TPC-C test, and therefore, could be potentially used for some real case scenarios. We also observed how, when a disaster occurs (in our case, the loss of a region), the database reacts autonomously, reorganizing itself and guaranteeing zero data loss and very short unavailability (measured in seconds).
À propos de l'auteur
Raffaele is a full-stack enterprise architect with 20+ years of experience. Raffaele started his career in Italy as a Java Architect then gradually moved to Integration Architect and then Enterprise Architect. Later he moved to the United States to eventually become an OpenShift Architect for Red Hat consulting services, acquiring, in the process, knowledge of the infrastructure side of IT.
Currently Raffaele covers a consulting position of cross-portfolio application architect with a focus on OpenShift. Most of his career Raffaele worked with large financial institutions allowing him to acquire an understanding of enterprise processes and security and compliance requirements of large enterprise customers.
Raffaele has become part of the CNCF TAG Storage and contributed to the Cloud Native Disaster Recovery whitepaper.
Recently Raffaele has been focusing on how to improve the developer experience by implementing internal development platforms (IDP).
Plus de résultats similaires
Key considerations for 2026 planning: Insights from IDC
Enhance workload security with confidential containers on Azure Red Hat OpenShift
When Should Data Die? | Compiler
Data-baeses | Compiler: Stack/Unstuck
Parcourir par canal
Automatisation
Les dernières nouveautés en matière d'automatisation informatique pour les technologies, les équipes et les environnements
Intelligence artificielle
Actualité sur les plateformes qui permettent aux clients d'exécuter des charges de travail d'IA sur tout type d'environnement
Cloud hybride ouvert
Découvrez comment créer un avenir flexible grâce au cloud hybride
Sécurité
Les dernières actualités sur la façon dont nous réduisons les risques dans tous les environnements et technologies
Edge computing
Actualité sur les plateformes qui simplifient les opérations en périphérie
Infrastructure
Les dernières nouveautés sur la plateforme Linux d'entreprise leader au monde
Applications
À l’intérieur de nos solutions aux défis d’application les plus difficiles
Virtualisation
L'avenir de la virtualisation d'entreprise pour vos charges de travail sur site ou sur le cloud
