Ansible Automation Platform (AAP) is an enterprise solution by Red Hat to make Ansible easier to use. It comes bundled with a lot of components to help you automate your processes across the entire Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). It provides you with various features such as Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), workflows, third-party integration via an API, notifications, shared SSH key credentials, and more. It also integrates well with LDAP and comes with pre-configured logging.
[ You might also like: Using Ansible Automation Webhooks for GitOps ]
Understanding the problem
The process looks like this: The development team changes the code and pushes the code to the Git repository used by the product. Once the code has been updated, the DevOps team pulls the latest code and then pushes it to the required servers via a playbook. The problem? The latest code must be downloaded manually every time and then pushed to the required servers. I'm going to show you how to automate that process.
Bringing in the solution
AAP supports integration with GitHub and GitLab. This integration is accomplished using a webhook. A webhook is a user-defined HTTP callback action that is triggered by an event such as updating a piece of code and pushing it to a repository. The action triggered, in this case, is the execution of a playbook on the desired managed hosts.

In the above diagram, the user pushes the latest code to the GitLab repository, triggering an event. The event is the code being pushed to the repository. This event further triggers an HTTP-based webhook that communicates with AAP via its API. This informs AAP to run the desired template on the selected inventory.
Configure an AAP webhook with GitLab:
So how does this process work? I've broken it down into six steps to make it easier to understand.
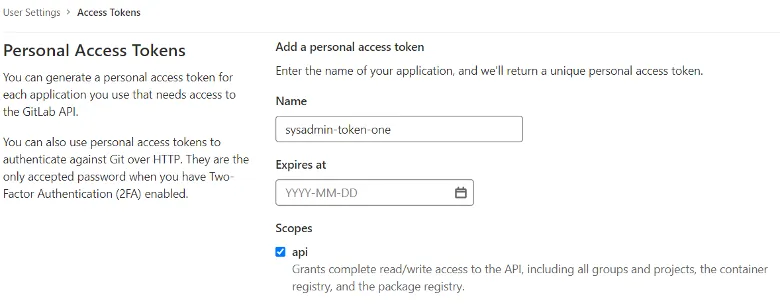
Step 1: Create a GitLab personal access token
Navigate to User Settings in your GitLab account and create a personal access token. This credential is used to establish an API connection to GitLab for use with webhook listener jobs to post status updates.
Step 2: Configure the GitLab personal access token
Create a new credential in AAP with the type, GitLab Personal Access Token. Provide a relevant name and organization, and then input your token.

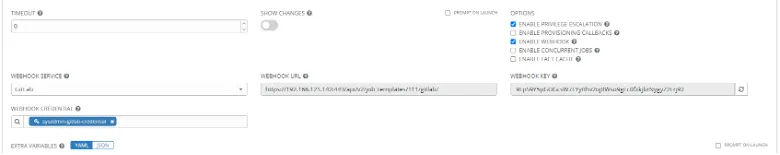
Step 3: Enable webhooks in AAP Template
Go to your AAP Template and check the Webhook button. This will require you to enter the webhook service, which is GitLab. Choose your previously created credential in the Webhook Credential option. Copy the Webhook URL and Webhook Key you were given and save the settings.
Step 4: Enable the webhook in the GitLab project
Navigate to the Webhook Settings of your GitLab project. Input the Webhook URL and Webhook Key you copied from the AAP Template. Choose Push events as the trigger because we wish to execute the template when the latest code is pushed. Disable SSL verification if your AAP does not have a valid SSL certificate.

Step 5: Make changes to your code and push to the repository
Push your changes to the GitLab repository via the GitLab interface or the Git CLI.

Step 6: Verify the Template execution
Navigate to Jobs in AAP. Your template should be in the process of execution or successfully executed. Notice the Launched By and the Extra Variables field. You will see the user as webhook and the extra variables employed by the webhook to complete the execution successfully.

[ Looking for more on system automation? Get started with The Automated Enterprise, a free book from Red Hat. ]
Wrap up
Automation has become a necessity in any organization’s management of its infrastructure. Using technologies like webhooks will make it easier for a system administrator to automatically deploy the latest changes on their managed hosts via an enterprise solution such as Ansible Automation Platform.
Sull'autore
Technological consultant and instructor for a Red Hat training partner based in India. Works on Ansible Tower, Red Hat Satellite, Python, and Ethical Hacking. Experience in delivering security and automation solutions as per business needs.
Altri risultati simili a questo
More than meets the eye: Behind the scenes of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 10 (Part 5)
AI insights with actionable automation accelerate the journey to autonomous networks
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
You Can’t Automate The Difficult Decisions | Code Comments
Ricerca per canale
Automazione
Novità sull'automazione IT di tecnologie, team e ambienti
Intelligenza artificiale
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che consentono alle aziende di eseguire carichi di lavoro IA ovunque
Hybrid cloud open source
Scopri come affrontare il futuro in modo più agile grazie al cloud ibrido
Sicurezza
Le ultime novità sulle nostre soluzioni per ridurre i rischi nelle tecnologie e negli ambienti
Edge computing
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che semplificano l'operatività edge
Infrastruttura
Le ultime novità sulla piattaforma Linux aziendale leader a livello mondiale
Applicazioni
Approfondimenti sulle nostre soluzioni alle sfide applicative più difficili
Virtualizzazione
Il futuro della virtualizzazione negli ambienti aziendali per i carichi di lavoro on premise o nel cloud
