The very act of modernizing means not only is there an application feedback loop to improve, there will be a similar loop running around infrastructure and security compliance that allows the application to operate in its current state in a production environment. Let’s talk a bit about what this might look like and some challenges to keep in mind when modernizing.
Importance of the operations feedback loop
In most legacy environments, a separate operations team is responsible for the operations feedback loop. In spite of movements such as the site reliability engineering movement (SRE) and/or DevOps, many legacy applications are still deployed and monitored in a ticket driven/manual process approach.
Here is what a legacy application’s operations cycle might look like.

When something goes wrong, emergency meetings that consume evenings and weekends occur. This can result in an operations team that is resistant to changing a running application (especially if it has been running for a while). This can work against our previously established product feedback loop. If this is not flushed out at the beginning of the modernization project, a lot of time can be wasted.
I have seen modernization efforts succeed with their application goals only to fail to get to production because their operational requirements could not be achieved because the existing operations processes or the legacy infrastructure are unable to handle the new load. This is very bad for the modernization team and their executive champion.
Operations feedback loop
Let’s return to our diagram of what an operational feedback loop might look like for a legacy application. This loop begins with the provisioning of necessary hardware (there might be tickets and manual process here as well, but we will skip over that). For today’s discussion we jump to the deployment of the application on that hardware (potentially manually) and then switch to focus on the stability of the application running in its environment(s). The security compliance of that environment is constantly being addressed as threats arise.

Just like the product loop, the Process step requires the operations team to come to an agreement on how to move forward. Some of the required understanding to reach this sort of agreement includes:
- current enterprise limitations,
- security policies and standards, and
- the application being operated and its functionality.
As mentioned previously, SRE practices and principles and a DevOps culture can be very valuable here. However, it should not be assumed that these are in place when dealing with legacy applications, or that it would be easy to add them. Much of the required knowledge to make all this work might rest with certain individuals. These individuals might not be very available or easy to work with due to too many requests for their time. Again, we will not go into fixing such issues in this article, but be aware they might exist when planning the modernization, and some time and effort should be put into understanding the operations process and culture.
Building successful operations teams
Ideally, from an enterprise point of view, the operations team making decisions will be a small team—similar to the product team—with the right mix of enterprise knowledge and innovation, so that they can come to a high quality and timely decision. I would argue that the same rules for building a product team we discussed previously should also apply to the operations team. To achieve outcomes as a small team in infrastructure, automation tools like Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform and DevOps tooling like Tekton and Argo CD can provide a ton of repeatable value with little manual effort required. Modernizing an operations team to use such tools is something Red Hat has many blogs, training and consulting packages to address. But returning to the previous point, the modernization team needs to be aware that working with/adding/enhancing the operations side of a legacy application needs to be part of the modernization, but might take more time than expected. Perhaps even more than the application side of the house. Plan accordingly.
The complete picture
For a legacy application to be safely changed or successfully built in the environment we are describing, we could see our new software feedback loop cycles integrating with the existing operation loops. If both feedback loops are aligned and functional, it is possible to successfully move code from its current state to the desired future state.
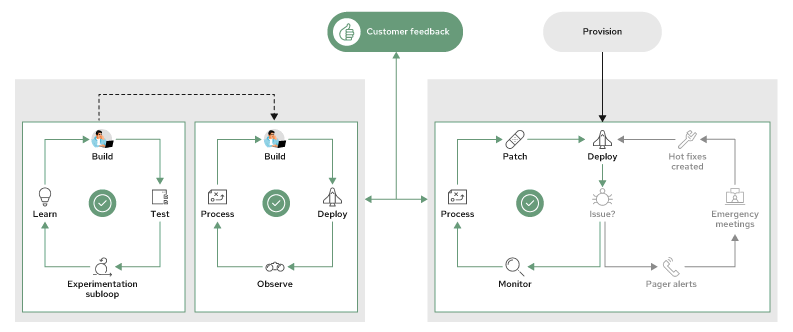
Enterprise alignment challenges
As you may have guessed, or have even experienced, aligning the loops can be challenging.

Sadly this might be the current everyday reality of many legacy applications, even after they have modernized the application code. Someone running a legacy application might look at this and, like the famous meme states: "This is fine."
But to successfully modernize an application, we will need to improve the operations feedback loop. As stated, fully changing a culture like this could be time consuming, but there are things that can be done to help the application team produce better outcomes that are less likely to trigger the Issues/Emergency Meeting side of the diagram.
In my next article, I will discuss how an opinionated workflow can help operations teams empower the developers building and deploying code to produce those outcomes that result in fewer fire drills.
Sull'autore
Luke Shannon has 20+ years of experience of getting software running in enterprise environments. He started his IT career creating virtual agents for companies such as Ford Motor Company and Coca-Cola. He has also worked in a variety of software environments - particularly financial enterprises - and has experience that ranges from creating ETL jobs for custom reports with Jaspersoft to advancing PCF and Spring Framework adoption in Pivotal. In 2018, Shannon co-founded Phlyt, a cloud-native software consulting company with the goal of helping enterprises better use cloud platforms. In 2021, Shannon and team Phlyt joined Red Hat.
Altri risultati simili a questo
Metrics that matter: How to prove the business value of DevEx
Red Hat OpenShift 4.21 brings Kubernetes to Oracle Database Appliance
Becoming a Coder | Command Line Heroes
Rolling with the Punches | Compiler: Tales From The Database
Ricerca per canale
Automazione
Novità sull'automazione IT di tecnologie, team e ambienti
Intelligenza artificiale
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che consentono alle aziende di eseguire carichi di lavoro IA ovunque
Hybrid cloud open source
Scopri come affrontare il futuro in modo più agile grazie al cloud ibrido
Sicurezza
Le ultime novità sulle nostre soluzioni per ridurre i rischi nelle tecnologie e negli ambienti
Edge computing
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che semplificano l'operatività edge
Infrastruttura
Le ultime novità sulla piattaforma Linux aziendale leader a livello mondiale
Applicazioni
Approfondimenti sulle nostre soluzioni alle sfide applicative più difficili
Virtualizzazione
Il futuro della virtualizzazione negli ambienti aziendali per i carichi di lavoro on premise o nel cloud
