To make your way in the IT industry, a fundamental understanding of cryptography concepts is vital. However, many still struggle when it comes to handling TLS certificates, certificate requests, and all sorts of keys. Before I start with those, let's talk about the basic concepts of encryption in cryptography. In this article, I explain the basics of symmetric and public key cryptography to lay a strong foundation to build on. I focus on the key concepts and leave the math to the experts.
Our protagonists throughout this article are Alice, who wants to communicate with Bob over a public channel. We also have Eve and Trudy. The following techniques should make eavesdropping impossible. Messing up the content of a message shouldn't go unnoticed.
[ You might also enjoy reading: Passwordless SSH using public-private key pairs ]
Symmetric key cryptography
It's called symmetric key cryptography because the same key is used to encrypt a message as to decrypt it. You could think of it as an actual key for a lock that secures your message so neither Eve nor Trudy would be able to read it or mess with it on its way to Bob.
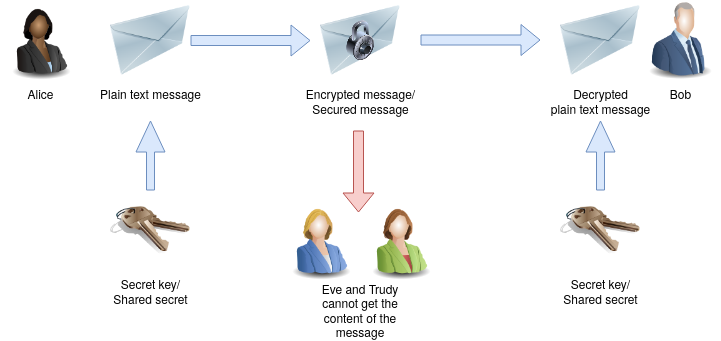
Of course, Bob could use the same secret key/shared secret to send an encrypted message to Alice. Eve and Trudy don't have a chance to get the plaintext from the intercepted message.
Symmetric key algorithms have the advantage of being pretty fast. On the downside, it's difficult to distribute the shared secret to the communication partners. To send the key over a public (and unsecured) channel is not an option because Eve could intercept it and would be able to decrypt all future communications between Alice and Bob. The best way is for Alice and Bob to exchange the key personally face to face. Think of your teammate who is located in another country. You can guess how hard it could be to exchange the shared secret securely.
Now think of a situation where Alice and Bob are not the only participants in communication but Jason, Tyler, and Nate, too. You would have to meet them all in person for a secure key exchange.
The communication between Alice and Bob is secure as long as the shared secret stays private. If the secret key gets lost, or there is a chance that it is compromised, e.g., Eve got knowledge of it, you have to create a new key and distribute it to all communication partners again.
Think of the key to your office building, which you use for several doors in your office. When you lose it, all the locks have to be replaced, and you and your colleagues need new keys. It's a mess. That's the same mess when you have to renew a secret key in symmetric key cryptography.
Asymmetric cryptography
Asymmetric cryptography, or public key cryptography, solves the key distribution problem of symmetric key cryptography. It does so by using a pair of keys instead of a single one.
An asymmetric key algorithm is used to generate a pair of keys: A private key and a public key. As the name suggests, you should keep the private key safe and secure and share it with no one. Think of it as the key to your home. I bet you keep your eyes on this. The public key, on the other hand, is meant to be distributed publicly. You don't have to keep it a secret and can share it with anybody. But why is that?
While the public key can encrypt a message, it is not able to decrypt it again. Only the corresponding private key can do that. If Eve and Trudy know Bob's public key, they can use it to send an encrypted message to him. However, they cannot decrypt a message that Alice sends to Bob encrypted using the same public key. The message can only be decrypted using Bob's corresponding private key.
When Alice and Bob want to use public key cryptography to communicate, they have to exchange their public keys and are good to go.

But what happens when Trudy uses Bob's public key to send him a message in the name of Alice? How could Bob check if this message really came from Alice and wasn't changed on the way to him? Well, Alice can use her private key to sign the message, and Bob can use Alice's public key to check and verify the signature.

The security of public key cryptography depends on the privacy of the private key. If the private key gets compromised, you would have to generate a new pair of keys and revoke the old ones. However, it's much easier to distribute the public key than a shared secret as you could simply send it via email.
So the distribution problem is solved. You have a way to encrypt/decrypt messages, verify the sender, and confirm a message's integrity. Any downsides? Yes, public key algorithms are pretty slow compared to symmetric key algorithms. That's the reason why there are some forms of hybrid techniques that use public key cryptography to exchange a symmetric session key and continue the communication using the faster symmetric key algorithm.
[ Thinking about security? Check out this free guide to boosting hybrid cloud security and protecting your business. ]
Wrap up
The symmetric key algorithms work pretty fast, but the distribution of the shared secret could be difficult. The security of this technique requires that every participant keeps the shared secret private. Public key algorithms are slower, but it's much easier to distribute and exchange public keys. Remember to keep your private key safe and secure all the time.
Sull'autore
Jörg has been a Sysadmin for over ten years now. His fields of operation include Virtualization (VMware), Linux System Administration and Automation (RHEL), Firewalling (Forcepoint), and Loadbalancing (F5). He is a member of the Red Hat Accelerators Community and author of his personal blog at https://www.my-it-brain.de.
Altri risultati simili a questo
Chasing the holy grail: Why Red Hat’s Hummingbird project aims for "near zero" CVEs
Elevate your vulnerabiFrom challenge to champion: Elevate your vulnerability management strategy lity management strategy with Red Hat
Data Security And AI | Compiler
Data Security 101 | Compiler
Ricerca per canale
Automazione
Novità sull'automazione IT di tecnologie, team e ambienti
Intelligenza artificiale
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che consentono alle aziende di eseguire carichi di lavoro IA ovunque
Hybrid cloud open source
Scopri come affrontare il futuro in modo più agile grazie al cloud ibrido
Sicurezza
Le ultime novità sulle nostre soluzioni per ridurre i rischi nelle tecnologie e negli ambienti
Edge computing
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che semplificano l'operatività edge
Infrastruttura
Le ultime novità sulla piattaforma Linux aziendale leader a livello mondiale
Applicazioni
Approfondimenti sulle nostre soluzioni alle sfide applicative più difficili
Virtualizzazione
Il futuro della virtualizzazione negli ambienti aziendali per i carichi di lavoro on premise o nel cloud
