The ls command is a basic, useful, and obvious utility that Linux users have been putting to work for decades. Originally debuted in an AT&T build of UNIX, the ls command we know today is a part of the GNU Coreutils packages of our favorite distributions; unless you are using macOS (then its BSD). The utility on offer here is rather simple. The ls command allows us to list files in a directory. It doesn't do anything special or crazy, but it does do something very necessary. I want to take a look at what options we have available when using ls and how to make those options work for you.
ls with no options

This lists all of the non-hidden files and directories in your working directory. Simple! Although, in my opinion, not the most useful.
ls -l

The -l option signifies the long list format. This shows a lot more information presented to the user than the standard command. You will see the file permissions, the number of links, owner name, owner group, file size, time of last modification, and the file or directory name. This option is used in conjunction with many other options on a regular basis.
[ Free download: Advanced Linux commands cheat sheet. ]
ls -lh
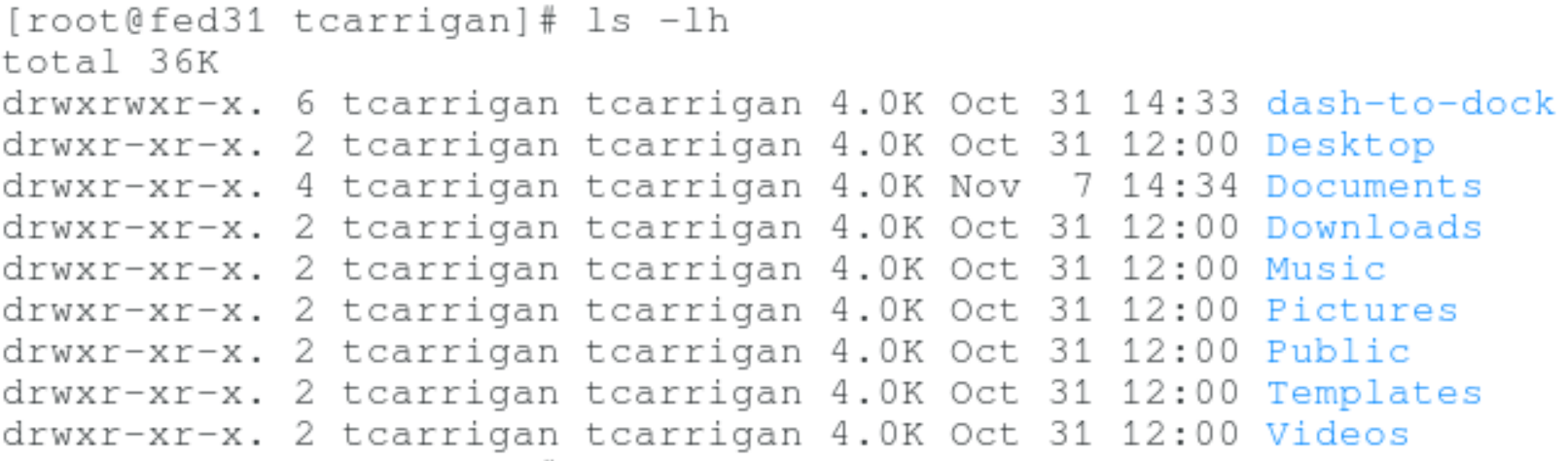
The -lh flag is the same long list format command as above, however, the file size is displayed in a human-readable format. Notice the difference between the file size outputs in the previous two screens.
ls -r

This option, like the standard ls command, lists all non-hidden files and directories. However, this command lists them in reverse order.
ls -a

The -a option displays all files, hidden or otherwise. Some files begin with . or .. and those files are hidden from the user by default.
ls -ltr

This combination of options will show the latest modification to a file or directory in reverse order.
ls -F
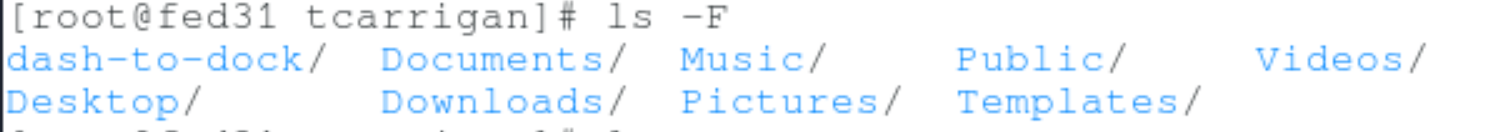
This will show the / character at the end of all directories.
ls -lS
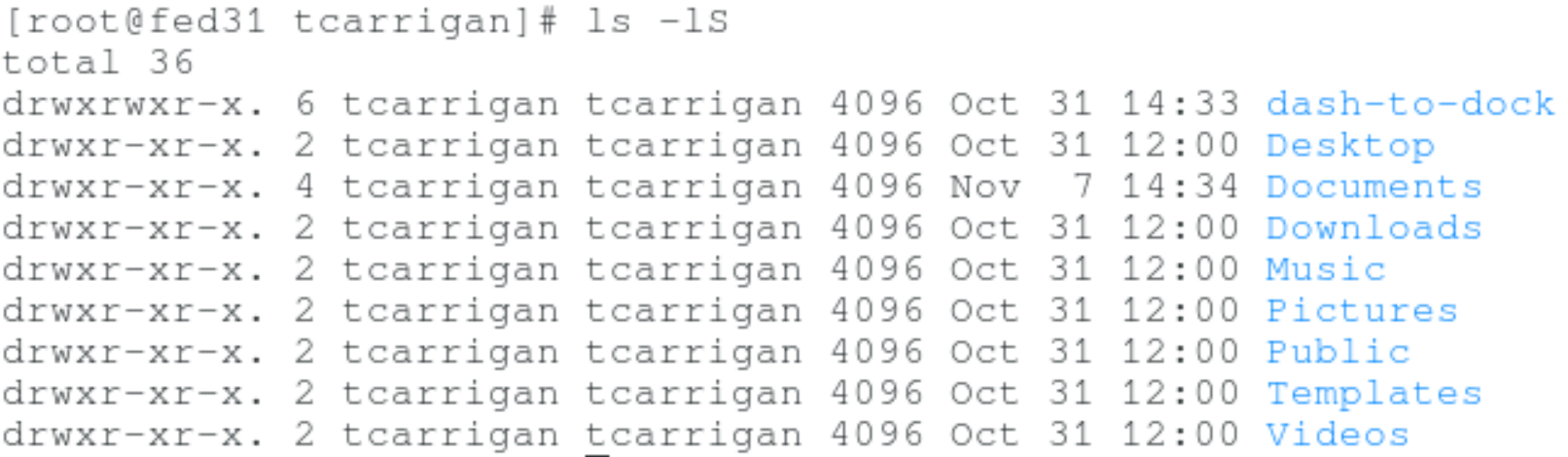
Displays the files in order of size from largest to smallest.
ls -R
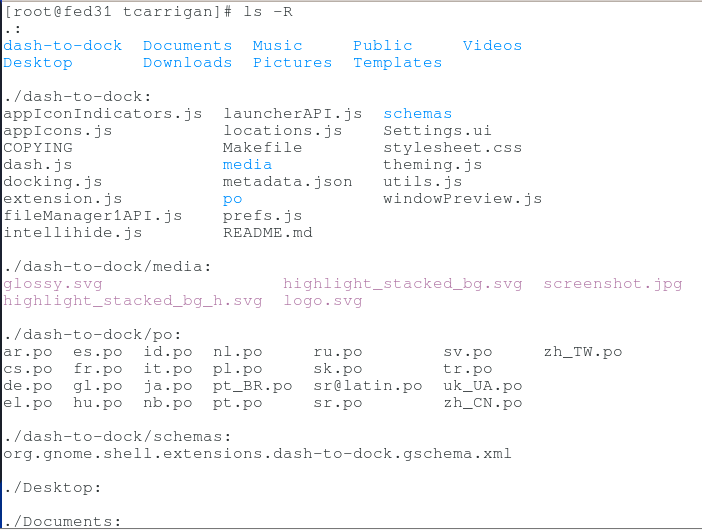
This option will list directory trees in a long format.
ls -i
This option will display the inode number beside each file or directory. An inode is the index node that identifies a specific file. Some files have multiple hard links, however if the hard links of multiple files share an inode, they are equivalent.
ls --version

This command will show you the version of the ls command that you are using.
man ls

This will allow you to access the man page for the ls command and see all of the information that this article doesn't cover.
The ls command is used by people everyday at a subconscious level. We all know the basics, but there are some great options that are under-utilized. I challenge you to make a point to use some of these lesser-known options in your daily work. You may be surprised at the utility that is available to you.
BONUS: To really become efficient, set up an alias for your favorite flavor of ls. For more information on creating aliases in Linux, see my previous article here.
Want to try out Red Hat Enterprise Linux? Download it now for free.
Sull'autore
Tyler is the Sr. Community Manager at Enable Sysadmin, a submarine veteran, and an all-round tech enthusiast! He was first introduced to Red Hat in 2012 by way of a Red Hat Enterprise Linux-based combat system inside the USS Georgia Missile Control Center. Now that he has surfaced, he lives with his wife and son near Raleigh, where he worked as a data storage engineer before finding his way to the Red Hat team. He has written numerous technical documents, from military procedures to knowledgebase articles and even some training curricula. In his free time, he blends a passion for hiking, climbing, and bushcraft with video games and computer building. He is loves to read and enjoy a scotch or bourbon. Find him on Twitter or on LinkedIn.
Altri risultati simili a questo
Why should your organization standardize on Red Hat Enterprise Linux today?
RPM and DNF features and enhancements in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 10.1
The Overlooked Operating System | Compiler: Stack/Unstuck
Linux, Shadowman, And Open Source Spirit | Compiler
Ricerca per canale
Automazione
Novità sull'automazione IT di tecnologie, team e ambienti
Intelligenza artificiale
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che consentono alle aziende di eseguire carichi di lavoro IA ovunque
Hybrid cloud open source
Scopri come affrontare il futuro in modo più agile grazie al cloud ibrido
Sicurezza
Le ultime novità sulle nostre soluzioni per ridurre i rischi nelle tecnologie e negli ambienti
Edge computing
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che semplificano l'operatività edge
Infrastruttura
Le ultime novità sulla piattaforma Linux aziendale leader a livello mondiale
Applicazioni
Approfondimenti sulle nostre soluzioni alle sfide applicative più difficili
Virtualizzazione
Il futuro della virtualizzazione negli ambienti aziendali per i carichi di lavoro on premise o nel cloud
