Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA) provides customers a single pane of glass to view and manage their virtual machines (VMs) and containers in the same environment along with common tooling for observability, governance, and infrastructure as code. The initial release of OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA gave [HT1] customers a unified way to manage their VMs alongside their containerized workloads, but lacked the ability for customers to be compliant with Windows licenses and to pay AWS and Microsoft for those licenses.
We are pleased to be announcing the public preview of Windows Server license included support for OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA. With license included support, the cost of the Windows license is bundled with the Amazon bare metal EC2 instance cost and billed per vCPU. This allows customers running Windows VMs on ROSA a convenient way to manage their licensing costs with their compute usage. For any additional questions on Windows licensing please refer to the AWS and Microsoft FAQ.
The public preview of Windows Server license included is only available in us-west-2 and can be enabled by following this documentation. The public preview is fully supported and the customer will be charged Windows license fees by AWS for the number of cores in their bare metal instance. This feature is expected to be generally available in all regions by the end of Q1 2025.
OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA relies on EC2 bare metal instances as the worker nodes that our VMs are deployed to. The Windows bare metal instance will be billed a Windows license fee based on the total vCPU of the EC2 instance. This means that the instance is billed as if it’s full of Windows VMs, even if it’s only partially full or running a mix of Windows and Linux. Due to this, customers will want to take some steps to ensure they are not mixing workloads on their Windows nodes. At this point we’ll assume that you’re already familiar with running OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA, but if you’re not, refer to this previous blog to get started.
There are different ways to segment workloads within our ROSA cluster, but for this example we’ll be using the Kubernetes concept of Taints and Tolerations. This means that the worker node will have a taint in the form of a key value pair, and only VMs with a matching toleration will be able to deploy on the node.
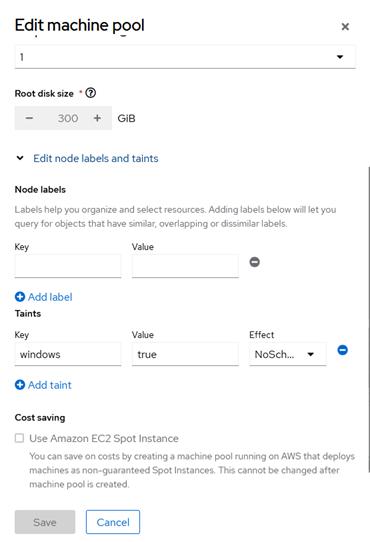
First, using the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console we’ll add a new machine pool to house our Windows EC2 bare metal instances. In the below example, we’ve created a new machine pool with a single EC2 bare metal instance. Now we want to add a taint to this machine pool to ensure only Windows VMs will deploy there. To do this, expand the node labels and taints section then add the following taint with a Key=windows and Value=true, and the Effect=NoSchedule and then save.
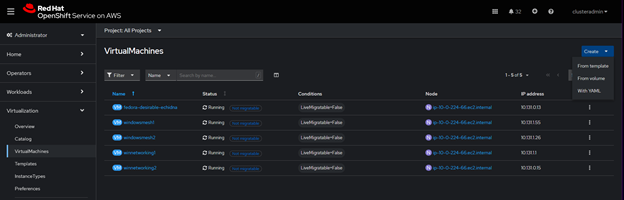
To test this, we’ll navigate directly to our ROSA cluster and try to add a Linux VM to the newly created Windows worker node. We’ll select Virtual Machines and then Create from the template and choose a Linux distro.
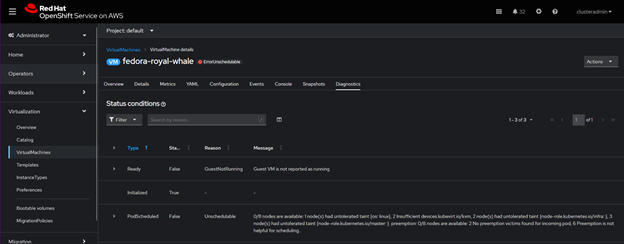
Then select Quick Create Virtual Machine, and we immediately see an ErrorUnschedulable due to the taint on the machine pool, if we select the error and View Diagnostic, we can see the full error. Telling us that there are no nodes available due to our previously applied taint.
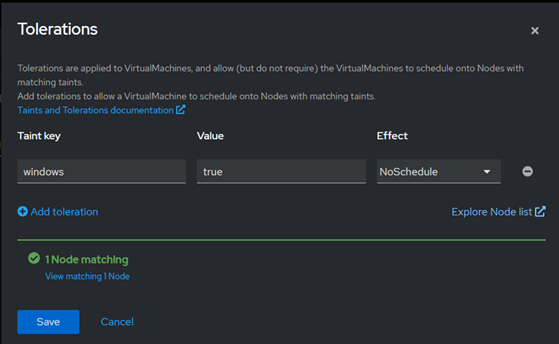
Let’s add a new VM with the correct toleration, for this example we’ll select Fedora again and this time select Customize VirtualMachine, followed by Customize VirtualMachine Parameters.

From this page we’ll select the Scheduling tab and then Tolerations to add the corresponding key value pair. The GUI lets us know that we entered the key value pair correctly as the toleration matches a node in our cluster. Once we select Save, we can create the VM.
Since the VM’s toleration matches the node’s taint it schedules as normal, and in a few minutes we have a running VM on our node.
In this example we walked through creating a new Windows VM on a Windows BareMetal machine pool in ROSA, but what if we’re migrating VMs into the cluster with the Migration Toolkit for Virtualization Operator (MTV)? At the time of writing this the MTV Operator does not allow adding a toleration or Node Label as part of a migration plan for the migrating VMs. To achieve separation we can apply the taints and tolerations after the fact but use NoExecute instead of NoSchedule. NoExecute will evict running pods on the node that do not have a matching toleration, where NoSchedule will leave running pods without a matching toleration on the node, but will not schedule any new pods to the node unless they have the toleration. Additionally we could apply a taint to the Linux machine pools hosting our Linux based VMs and then the MTV Operator will only schedule the Windows VMs on the un-tainted Windows machine pools.
If you’d like more information about Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA or to discuss how you can migrate your VMs to ROSA please reach out to your AWS account team or Red Hat account team to get started.
To get started with ROSA, check out our hands-on experience here.
Walk through the learning path to learn more about OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA. Read the 15 reasons to adopt OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA ebook.
If you are at AWS ReInvent, make sure to stop by booth #844 to get hands-on with OpenShift Virtualization and listen to a few mini-theatre sessions about migrating your VMs to ROSA.
Sugli autori
Altri risultati simili a questo
PNC’s infrastructure modernization journey with Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization
Shadow-Soft shares top challenges holding organizations back from virtualization modernization
SREs on a plane | Technically Speaking
Ricerca per canale
Automazione
Novità sull'automazione IT di tecnologie, team e ambienti
Intelligenza artificiale
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che consentono alle aziende di eseguire carichi di lavoro IA ovunque
Hybrid cloud open source
Scopri come affrontare il futuro in modo più agile grazie al cloud ibrido
Sicurezza
Le ultime novità sulle nostre soluzioni per ridurre i rischi nelle tecnologie e negli ambienti
Edge computing
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che semplificano l'operatività edge
Infrastruttura
Le ultime novità sulla piattaforma Linux aziendale leader a livello mondiale
Applicazioni
Approfondimenti sulle nostre soluzioni alle sfide applicative più difficili
Virtualizzazione
Il futuro della virtualizzazione negli ambienti aziendali per i carichi di lavoro on premise o nel cloud
