Since the launch of MLCommons, Red Hat has been an active participant in the MLCube project hosted by the Best Practices Working Group. Red Hat employees are contributing to the design and development of this exciting project which aims to reduce friction around creating and consuming machine learning (ML) models.
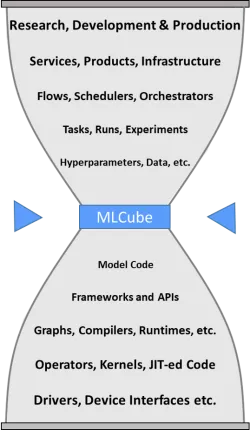
MLCube is designed to make it easier for researchers to share innovative ML models, developers to experiment with different models, and software companies to create infrastructure for models. MLCube provides a thin interface for creating "plug and play" ML models that can be shared across the artificial intelligence (AI) industry and acts as a shipping container for these models.
MLCube aims to address several key issues. Let's look at some of the most pressing issues we would like to solve.
Integrating ML models wastes time and slows deployments to production
When using a model you didn't author yourself, you need to do substantial manual work to enable the model to run on a new system. This slows down R&D and hinders the user experience for AI platforms. MLCube offers a standard mechanism for packaging models in a standard way to avoid this manual work.
Non-standard interfaces and custom configurations hinder broad adoption of ML
MLCube helps enable “plug and play” models with a simple, clean and thin interface. It is presented as a directory that contains:
An OCI-compliant container image (e.g., a Podman image)
The metadata to run the image
The metadata for one or more supported ML tasks
Today, the ML tasks are essentially file system-level function calls. The work is ongoing to extend this concept to work with inferencing (model serving). Here is an example of MLCube executing a training task:

No standardized way of packaging ML models
Model creators use unique and disparate methods for packaging their models with custom scripts and configuration settings. Due to lack of standardization of model packaging many hours are spent simply trying to get models run on a new system.
MLCube provides a way to create and specify the information needed to run the model. An MLCube can be constructed by any model creator who follows a simple checklist for packaging the model into a shareable container with the standardized interface common to all MLCubes. MLCommons provides tools to help validate and run these packages.
Difficulties in sharing models at both the training and inference steps of the model lifecycle
MLCube is not a siloed solution, it is designed as an ecosystem enabler that helps remove friction and share models broadly. MLCubes can be used for training or inference across multiple platforms: Linux, Kubernetes, and public clouds.
The Best Practices Working Group provides reference runners - simple software to help with executing MLCubes, but it also encourages third parties to adopt MLCube for use with more powerful infrastructure.
Red Hat is working with a number of MLCommons members to further develop the MLCube concept. Specifically, we rely on Podman and Red Hat Universal Base Image (UBI) as foundational OCI-compliant components that are used to create an MLCube.
Podman is designed to run, build, share and deploy applications using OCI container images. A great advantage of Podman vs. other container runtimes, such as Docker, is it does not require root privileges to run containers, making it a safer and less error-prone tool.
UBI is based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) and allows you to build, share and collaborate on your containerized application where you want. Model creators can choose to use freely distributable UBI as the base layer of their OCI containers and use Podman to run them, making these enterprise-grade software technologies available to the users of their MLCubes.
Red Hat has a history of contributing and shaping open source solutions that benefit the entire industry. Through our involvement in the best practices working group in general, and in the development of the MLCube concept in particular, Red Hat is aiming to provide a complete and effective solution that could greatly improve the adoption of many ML applications.
Stay tuned for future updates on the progress MLCommons is making in democratizing access to AI and machine learning for everyone.
Sugli autori
Diane Feddema is a Principal Software Engineer at Red Hat Inc in the Performance and Scale Team with a focus on AI/ML applications. She has submitted official results in multiple rounds of MLCommons MLPerf Inference and Training, dating back to the initial MLPerf rounds. Diane Leads performance analysis and visualization for MLPerf benchmark submissions and collaborates with Red Hat Hardware Partners in creating joint MLPerf benchmark submissions.
Diane has a BS and MS in Computer Science and is presently co-chair of the Best Practices group of the MLPerf consortium.
Yan Fisher is a Global evangelist at Red Hat where he extends his expertise in enterprise computing to emerging areas that Red Hat is exploring.
Fisher has a deep background in systems design and architecture. He has spent the past 20 years of his career working in the computer and telecommunication industries where he tackled as diverse areas as sales and operations to systems performance and benchmarking.
Having an eye for innovative approaches, Fisher is closely tracking partners' emerging technology strategies as well as customer perspectives on several nascent topics such as performance-sensitive workloads and accelerators, hardware innovation and alternative architectures, and, exascale and edge computing.
Altri risultati simili a questo
AI in telco – the catalyst for scaling digital business
The nervous system gets a soul: why sovereign cloud is telco’s real second act
Technically Speaking | Build a production-ready AI toolbox
Technically Speaking | Platform engineering for AI agents
Ricerca per canale
Automazione
Novità sull'automazione IT di tecnologie, team e ambienti
Intelligenza artificiale
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che consentono alle aziende di eseguire carichi di lavoro IA ovunque
Hybrid cloud open source
Scopri come affrontare il futuro in modo più agile grazie al cloud ibrido
Sicurezza
Le ultime novità sulle nostre soluzioni per ridurre i rischi nelle tecnologie e negli ambienti
Edge computing
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che semplificano l'operatività edge
Infrastruttura
Le ultime novità sulla piattaforma Linux aziendale leader a livello mondiale
Applicazioni
Approfondimenti sulle nostre soluzioni alle sfide applicative più difficili
Virtualizzazione
Il futuro della virtualizzazione negli ambienti aziendali per i carichi di lavoro on premise o nel cloud
