What is a load balancer? A load balancer is an efficient way to distribute the network traffic among various backend servers. It is also known as a server farm or server pool. It distributes client requests or network load to target web servers. Load balancers work on the round-robin concept, which ensures high reliability and availability.

One scenario
You have a web server that can manage 100 clients at a time. Suddenly the requests to that particular server increase by 100 percent. It's likely that the website will crash or be terminated. To avoid this situation, set up a target web server. In this scenario, the client never goes to the target web server. Instead, their request goes to the master server, and the master server sends the request to the target web server. When the target web server replies to the master web server, which is known as a reverse proxy.
[ You might also like: Turn a Kubernetes deployment into a Knative service ]
Using HAProxy as a proxy
The port on the main web server is called the frontend port. HAProxy is an HTTP load balancer that can be configured as a reverse proxy. Here we'll look at how I configured HAProxy by using an Ansible playbook.
Check the system where you need to configure HAProxy
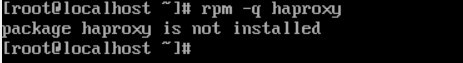
HAProxy is not installed on this system. You can confirm that with the following command:
rpm -q haproxy
Steps to configure HAProxy
Step 1 - Install HAProxy
To install HAProxy, you have to use a package module where you give the name of the service you want to install:
- name: "Configure Load balancer"
package:
name: haproxy
Step 2 - Copy the configuration file for the reverse proxy
Copy the configuration file so that you can modify it:
cp /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg /root/ws1/haproxy.cfg

Step 3 - Change frontend port and assign backend IPs
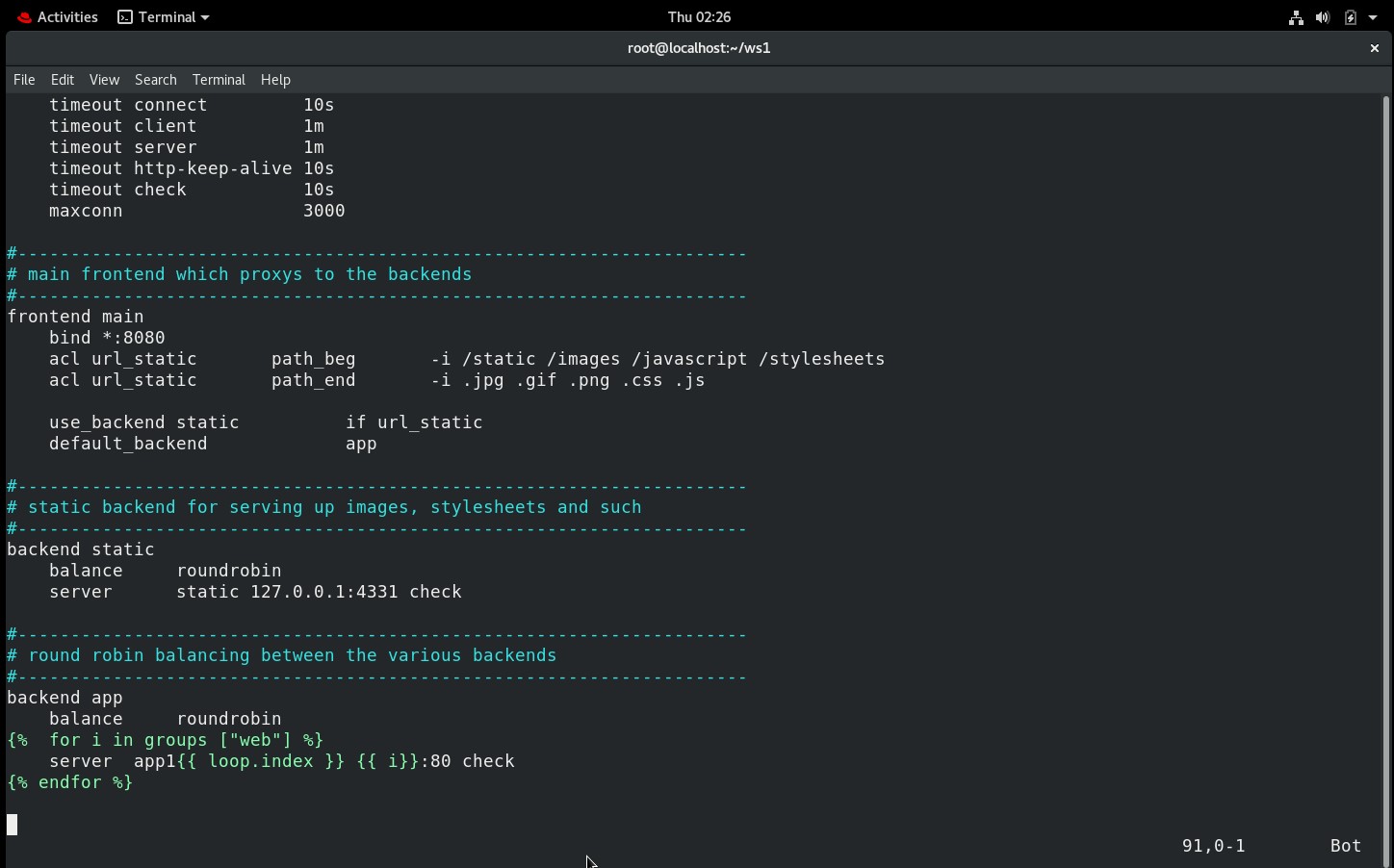
By default, the frontend is bound to port 5000. I changed the port number to 8080. I also applied a for loop to configure the backend IP. Now you can launch as many web servers as you need, and there is no need to manually configure the IP inside the /etc/httpd/httpd.conf. It will automatically fetch the IP from inventory.
backend app
balance roundrobin
{% for i in groups ["web"] %}
server app1{{ loop.index }} {{ i}}:80 check
{% endfor %}
Step 4 - Copy haproxy.cfg to the managed node
Using template mode, copy the config file for HAProxy from the controller node to the managed node:
- template:
dest: "/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg"
src: "/root/ws1/haproxy.cfg"
Step 5 - Start the service
Use the service module to start the HAProxy service:
- service:
name: "haproxy"
state: restarted
Check the system where you need to install httpd webserver
For testing the HAProxy configuration, you will also configure httpd on your target node with the help of Ansible. To check that you don't already have httpd on your system, use the following command:
rpm -q httpd

Step 1 - Install httpd
The package module is used to install httpd on the managed node:
- name: "HTTPD CONFIGURE"
package:
name: httpd
Step 2 - Copy the webpage
The template module is used to copy your webpage from the source to the destination:
- template:
dest: "/var/www/html/index.html"
src: "/root/ws1/haproxy.html"
Step 3 - Start the service
The service module is used to start the httpd service:
- service:
name: "haproxy"
state: restarted
Complete the playbook to configure the reverse proxy
In this playbook, you have two different hosts with two different groups. One group is for the web server, and another is for the load balancer:
---
- hosts: web
tasks:
- name: "HTTPD CONFIGURE"
package:
name: httpd
- template:
dest: "/var/www/html/index.html"
src: "/root/ws1/haproxy.html"
- service:
name: "httpd"
state: restarted
- hosts: lb
tasks:
- name: "Configure Load balancer"
package:
name: haproxy
- template:
dest: "/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg"
src: "/root/ws1/haproxy.cfg"
- service:
name: "haproxy"
state: restarted
Run the playbook
ansible-playbook haproxy.yml

Output
The playbook runs successfully, and the two target web servers can be accessed by the main web server using a load balancer.


[ Looking for more on system automation? Get started with The Automated Enterprise, a free book from Red Hat. ]
Conclusion
The load balancer and reverse proxy have now been configured by Ansible. You can add a layer of protection and availability to your web services by adding HAProxy to your infrastructure. Be sure to check out the documentation for your specific target to learn more.
Sull'autore
Sarthak Jain is a Pre-Final Year Computer Science undergraduate from the University of Petroleum and Energy Studies (UPES). He is a cloud and DevOps enthusiast, knowing various tools and methodologies of DevOps. Sarthak also Mentored more than 2,000 students Regarding the Latest Tech trends through their community Dot Questionmark.
Altri risultati simili a questo
Redefining automation governance: From execution to observability at Bradesco
How Banco do Brasil uses hyperautomation and platform engineering to drive efficiency
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
You Can't Automate The Fire | Code Comments
Ricerca per canale
Automazione
Novità sull'automazione IT di tecnologie, team e ambienti
Intelligenza artificiale
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che consentono alle aziende di eseguire carichi di lavoro IA ovunque
Hybrid cloud open source
Scopri come affrontare il futuro in modo più agile grazie al cloud ibrido
Sicurezza
Le ultime novità sulle nostre soluzioni per ridurre i rischi nelle tecnologie e negli ambienti
Edge computing
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che semplificano l'operatività edge
Infrastruttura
Le ultime novità sulla piattaforma Linux aziendale leader a livello mondiale
Applicazioni
Approfondimenti sulle nostre soluzioni alle sfide applicative più difficili
Virtualizzazione
Il futuro della virtualizzazione negli ambienti aziendali per i carichi di lavoro on premise o nel cloud
