Red Hat OpenShift 4.21, based on Kubernetes 1.34 and CRI-O 1.34, is now generally available. Together with Red Hat OpenShift Platform Plus, this release demonstrates our continued commitment to delivering the trusted, comprehensive, and consistent application platform that enterprises rely on for production workloads across the hybrid cloud without compromising on security.
This release emphasizes running AI training jobs, containerized microservices, and virtualized applications on the same infrastructure with the same operational model. With OpenShift 4.21, you can simultaneously modernize existing IT infrastructure and accelerate AI innovation on a single, cost-efficient platform that scales automatically based on real-time business demand.
Imagine a large financial institution that needs to maintain legacy virtual machines (VMs) for core banking while also training new AI models for fraud detection. Previously, these two worlds lived in different systems, creating "silos" and wasted costs.
But with OpenShift 4.21, this firm can run both on the same infrastructure. Using the new Dynamic Resource Allocation (DRA) operator, they can even prioritize high-end GPUs for AI training during the day, but automatically shift those resources or scale them to zero at night to save money. Additionally, they can move active VMs between data centers with zero downtime, helping to ensure banking services stay online even during hardware maintenance.
Whether you deploy OpenShift as a self-managed platform, or consume it as a fully managed cloud service, you get a complete set of integrated tools and services for cloud-native, AI, virtual and traditional workloads alike. This blog covers key innovations in OpenShift 4.21 across AI, core platform capabilities, and virtualization. For complete details, see the OpenShift 4.21 release notes.
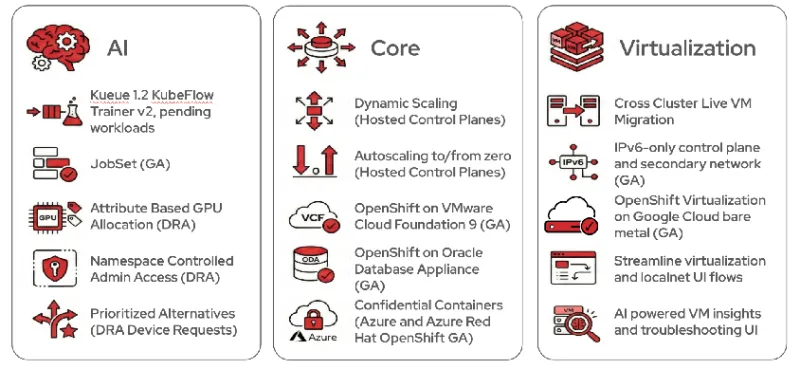
AI
Artificial intelligence has become a cornerstone of modern industry, driving breakthroughs in everything from personalized healthcare to autonomous systems. However, as AI models grow in complexity, the underlying infrastructure must evolve to handle massive computational demands efficiently. In this release of OpenShift, we continue to add AI features into the platform to support production AI workloads at scale.
Streamline AI workloads with Red Hat build of Kueue v1.2
With OpenShift 4.21, Red Hat build of Kueue v1.2 delivers two capabilities that matter for AI teams at scale:
- Support for KubeFlow Trainer v2 in Red Hat OpenShift AI 3.2: Instead of managing separate resources for each machine learning (ML) framework, data scientists now work with a single TrainJob API. They focus on model code while platform teams define infrastructure through training runtimes.
- Visibility API for pending workloads: Before this, batch jobs sat in queues with no insight into position or wait time. Users couldn't tell whether they were first or hundredth in line. Administrators had no way to spot resource bottlenecks. Now both sides see what's happening. Users get estimated start times. Administrators identify where specific resources, like GPU types, are oversubscribed. The queue isn't a black box anymore.
Manage distributed workloads with JobSet
The JobSet Operator reaches general availability in this release. Teams can orchestrate distributed workloads using their existing GitOps workflows, role-based access control (RBAC) policies, and monitoring tools. JobSet delivers flexible scheduling and fault tolerance for complex, interdependent jobs, which enable organizations to run demanding machine learning and distributed computing workloads at scale with operational consistency.
Match workloads to GPU hardware with precision and flexibility
As AI workloads scale across the enterprise, the traditional approach to GPU allocation of counting devices and hoping they match your needs breaks down fast. OpenShift 4.21 introduces three capabilities in DRA that fundamentally change how organizations request and consume GPU resources.

Attribute-based GPU allocation with DRA driver
Instead of requesting a GPU, you now specify what you actually need (for example, "a GPU with at least 40GB of VRAM"). The scheduler queries hardware attributes directly using common expression language (CEL), eliminating manual node labeling, so there's no more maintaining gpu-type=h100 labels across your cluster. The system reads hardware capabilities and matches them to workload requirements automatically. To use this feature, you need to use the vendor-provided operator or driver with DRA capability enabled.
Namespace controlled admin access in DRA
Standard DRA locks a GPU to its assigned pods, so even monitoring tools and debuggers cannot touch them. Admin access creates privileged exceptions for infrastructure workloads without disrupting user allocations. This is particularly useful for cluster wide monitoring and live debugging.
Prioritized alternatives in device requests
Define fallback strategies directly in your resource requests. Instead of "H100 or fail", you specify an ordered list: H100 first, then A100, then V100. The scheduler attempts each option in sequence until it finds available capacity.
Core
OpenShift's core infrastructure remains the industry standard for hybrid cloud resilience by continuously evolving to meet modern performance and cost requirements. In this latest release, we've optimized resource efficiency through innovations like autoscaling for hosted control planes to dynamically adjust memory, or scale to zero to eliminate idle infrastructure costs.
Furthermore, OpenShift continues to expand its ecosystem through validated integrations with platforms like VMware Cloud Foundation 9 and Oracle Database Appliance, ensuring customers can deploy OpenShift across the hybrid cloud.
Right-Sizing in hosted control planes
In OpenShift 4.21, hosted control planes for Red Hat OpenShift now include native VerticalPodAutoscaler (VPA) integration. Your control plane components scale automatically based on real-time memory consumption, and not static estimates or node counts. The system monitors actual usage and adjusts resources dynamically, without manual intervention, shifting from capacity planning to demand response. Instead of predicting what you'll need six months out, the platform observes what's happening now and responds. Your control planes stay precisely sized for current workload. That means no performance degradation from under-provisioning, no wasted spend from over-provisioning.
Autoscale from/to zero on hosted control planes
Hosted control planes now scale to zero during inactivity. Control planes hibernate while preserving configuration and state, then resume automatically when needed, thus eliminating costs for idle infrastructure. NodePools follow the same pattern, scaling down to zero nodes in development, test, and ephemeral environments. This makes Hosted Control Planes the most cost-effective way to run OpenShift. This feature ensures that the hosted control plane remains operative in a standby state, providing a perfect balance between quick availability and aggressive cost optimization.
Run OpenShift on VMware Cloud Foundation 9
OpenShift adds support for VMware vSphere Foundation 9 (VVF9) and VMware Cloud Foundation 9 (VCF9) beginning with OpenShift 4.18. This provides compatibility with VMware NSX for infrastructure networking and OVN-Kubernetes for the overlay network. Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes 2.15.1+ extends fleet management capabilities across these platforms, while Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation 4.19.7 and 4.20 are available as Technology Preview, with general availability planned in early 2026. Migration guidance from vSphere 8 and VCF 5 to VCF9 will follow in 2026, ensuring customers can modernize their VMware infrastructure with full OpenShift support.
Learn more at GA support for Red Hat OpenShift on VMware vSphere Foundation 9 and VMware Cloud Foundation 9.
Bring OpenShift to your Oracle Database Appliance
The Oracle Database Appliance is a pre-configured, integrated bundle of hardware, storage, networking, and software designed specifically to run Oracle databases. It is often described as a "database in a box" because it eliminates the complexity of building a custom server stack from scratch. You can now deploy OpenShift on Oracle Database Appliance and benefit from operational simplicity, security, and compliance.
Deploy zero-trust workloads in Microsoft Azure and Microsoft Azure Red Hat OpenShift with Confidential Containers
With OpenShift 4.21, we add support for Confidential Containers on customer-managed clusters in Microsoft Azure or as a managed service with Microsoft Azure Red Hat OpenShift. Confidential Containers provide a hardware-based security layer that protects data while data is processed in memory. This helps ensure that your code and data are isolated from the cloud provider, host operating system, and even hypervisors, making it a critical choice for highly regulated industries like finance and healthcare.
With Confidential Containers in Microsoft Azure, you effectively remove the cloud operator from your trusted computing base (TCB). This means even if an attacker gains root access to the physical host or the Microsoft Azure control plane, they cannot read the cleartext data sitting in your container's memory.
Virtualization
Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization runs VMs and containers on the same platform, enabling one team to work with one set of tools on a single infrastructure. This matters because most companies still rely on VMs for critical workloads, and moving everything to containers overnight isn't realistic or necessary. OpenShift Virtualization lets you modernize at your own pace by using OpenShift to manage both containerized and virtualized workloads through the same networking, storage, and security layer.
Migrate virtual machines across clusters with zero downtime
Cross-cluster live migration with OpenShift Virtualization lets administrators move running VMs between different OpenShift clusters with zero downtime. Administrators can now perform cluster maintenance, rebalance resources across regions, or migrate workloads to newer hardware without service interruption while managing multi-cluster environments under strict service level agreements.
IPv6-only control plane and secondary network support
IPv6-only control plane and secondary network support is now generally available. This is a major step forward for organizations running out of IPv4 addresses. It allows you to deploy OpenShift clusters and virtualized workloads in modern, IPv6-native environments, simplifying network architectures by removing the need for complex Network Address Translation (NAT) workarounds.
By supporting IPv6 across both the cluster's core management layer and its secondary interfaces, OpenShift Virtualization ensures that high-density deployments can scale indefinitely while meeting strict government and telecommunications compliance mandates. This transition not only streamlines network routing and improves end-to-end security but also future-proofs infrastructure for the next generation of globally connected services.
OpenShift Virtualization on Google Cloud
OpenShift Virtualization on Google Cloud bare metal allows organizations to run VMs directly on dedicated hardware, bypassing the overhead of traditional nested virtualization. This deployment model is critical for performance-sensitive workloads requiring direct access to physical CPU features and hardware acceleration, such as low-latency databases or specialized telecommunications applications. By running on bare metal, you gain the flexibility of the cloud while maintaining the raw performance and predictable latency of an on-premises server. This integration streamlines the migration of legacy VM-based applications to Google Cloud, enabling a unified management experience for both containers and virtual machines within a single OpenShift control plane.
Learn more at Bringing Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization to Google Cloud.
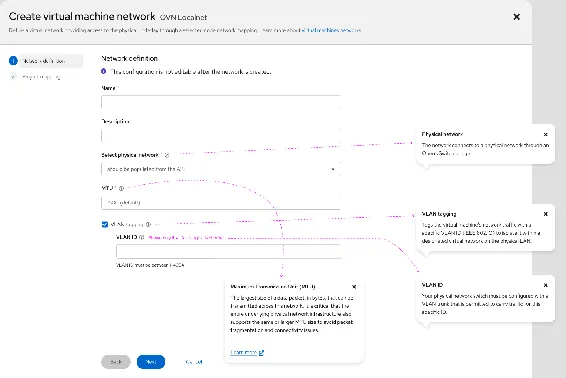
Configure virtual networks with enhanced Virtualization UI
OpenShift Virtualization's enhanced UI guides administrators to the right network configurations while preserving advanced control. Administrators can now create secondary ClusterUserDefinedNetworks using localnet topology with built-in guardrails that prevent accidental deletion of UDN-derived NetworkAttachmentDefinitions. The enhanced host network flow surfaces common configuration paths first, accelerating setup from intent to working configuration. Physical network abstraction organizes NodeNetworkConfigurationPolicies into logical units, enabling teams to manage host connectivity cohesively while retaining deep customization as needed.
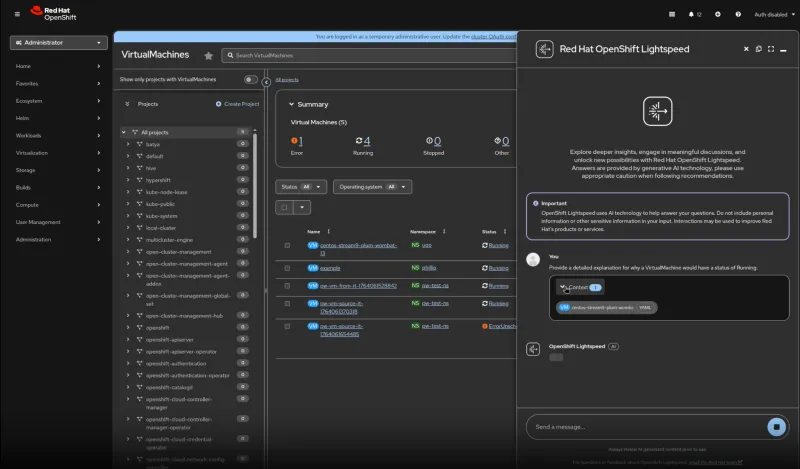
Troubleshoot VMs with Red Hat OpenShift Lightspeed
We've integrated the Red Hat OpenShift Lightspeed virtual AI assistant with the OpenShift Virtualization user interface, so virtualization administrators no longer need to switch interfaces or manually upload files. Instead, virtualization administrators can now get in-context, AI-powered insights for tasks, such as troubleshooting virtual machine errors.
Try Red Hat OpenShift 4.21 today
Get started today with the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console and take advantage of the latest features and enhancements in OpenShift. To find out what's next, check out the following resources:
- What's new and what's next in Red Hat OpenShift
- Red Hat interactive experiences
- In the clouds
- OpenShift YouTube channel
- OpenShift blogs
- OpenShift commons
- Red Hat Developer blogs
- Red Hat Portfolio Architecture Center
- Validated patterns
The complete list of the Red Hat OpenShift 4.21 updates are in the OpenShift 4.21 release notes. Send us feedback through your Red Hat contacts, or create an issue on GitHub.
Prueba del producto
Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform | Versión de prueba del producto
Sobre los autores
Ju Lim works on the core Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform for hybrid and multi-cloud environments to enable customers to run Red Hat OpenShift anywhere. Ju leads the product management teams responsible for installation, updates, provider integration, and cloud infrastructure.
Más como éste
Shadow-Soft shares top challenges holding organizations back from virtualization modernization
Manage clusters and applications at scale with Argo CD Agent on Red Hat OpenShift GitOps
Navegar por canal
Automatización
Las últimas novedades en la automatización de la TI para los equipos, la tecnología y los entornos
Inteligencia artificial
Descubra las actualizaciones en las plataformas que permiten a los clientes ejecutar cargas de trabajo de inteligecia artificial en cualquier lugar
Nube híbrida abierta
Vea como construimos un futuro flexible con la nube híbrida
Seguridad
Vea las últimas novedades sobre cómo reducimos los riesgos en entornos y tecnologías
Edge computing
Conozca las actualizaciones en las plataformas que simplifican las operaciones en el edge
Infraestructura
Vea las últimas novedades sobre la plataforma Linux empresarial líder en el mundo
Aplicaciones
Conozca nuestras soluciones para abordar los desafíos más complejos de las aplicaciones
Virtualización
El futuro de la virtualización empresarial para tus cargas de trabajo locales o en la nube

