The response to Stan’s Robot Shop, Instana's sample containerized microservice application, has been fantastic – and when we wrote a primer on deploying Instana’s sample microservice application on Kubernetes, users ate it up.
So let’s talk OpenShift. If you didn’t catch our blog about managing OpenShift application performance with Instana, it’s worth a read.
As a Prime Red Hat partner, Instana has published several informational blog posts, including a discussion on Red Hat OpenShift basics and publishing a sample microservices application called Stan’s Robot Shop. This article outlines the steps for deploying the Robot Shop sample microservice application on OpenShift.
OpenShift Prerequisites for Microservices
Red Hat offers OpenShift as a managed container service, but this exercise uses minishift, which allows you to run a small OpenShift cluster on your laptop. I run minishift with Virtualbox, but other options are available. To see the performance results, you will also need an Instana account (if you don’t have one, you can sign up for a free Instana trial).
Installing Your Sample Microservices Application on OpenShift
To start you will need Stan’s Robot Shop code:
$ git clone https://github.com/instana/robot-shop
If you don’t have git installed, simply go to the Stan’s Robot Shop repository and select the download link on the top right of the page to get a zip file of the code.
Fire up minishift and open its console so you can see what is going on.
$ minishift start --vm-driver virtualbox
$ minishift console
This will start a small OpenShift cluster with 2 CPU and 2GB of memory, which is plenty to run Stan’s Robot Shop. Login to the console with the account “developer” using anything except blank for the password – no check is performed. In a different browser tab, open your Instana dashboard Infrastructure Map.
Since OpenShift is built on Kubernetes, we could just use the regular kubectl commands, but this would miss out on the extra automation features of OpenShift. The OpenShift equivalent of kubectl is oc, set this up:
$ eval $(minishift oc-env)
Next, we install the Instana agent on the cluster. You will find helper scripts under the OpenShift directory of the code you previously downloaded. Before running the script, edit the instana-agent-os.yaml file and set secret key to base64 encoded agent key. You will find the agent key under Management Portal, accessible from the drop down menu at the top right of your Instana dashboard. The Agent Key is displayed after selecting Agent Key on the Management Portal home page.
$ echo -n "your agent key" | base64
$ cd OpenShift
$ ./agent-deploy.sh
The “instana-agent” project is created on the OpenShift dashboard and after a minute or two you will see your OpenShift cluster appear on the Instana dashboard.

The Instana agent has already discovered some containers running on the minishift virtual host, these are OpenShift, Docker registry and HA-Proxy. Congratulations you now have a running OpenShift environment fully monitored by Instana, you are on your way to microservice nirvana.
OpenShift has its own Docker registry that is used to stage images before they are deployed as applications. A Docker image is imported into this registry then a deployment or application is made from this image. By linking the two together updating the image in the local OpenShift registry automatically updates the deployment or application. The script used to deploy Stan’s Robot Shop uses this method of automation.
$ ./deploy.sh
After running this script, the robot-shop project will appear in the OpenShift dashboard. Drill into this project, Applications -> Pods, here you will be able to watch the Pods being created and started, it will take a few minutes to complete.
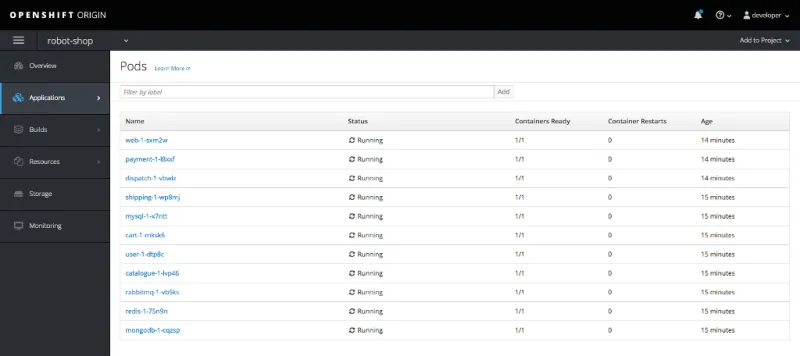
Once all the Pods are running, goto Applications -> Services and select the web service. To make this service externally available change the type from ClusterIP to NodePort and define the port as 30080. Select Actions drop down at the top right then select Edit YAML.

Stan’s Robot Shop is now available on port 30080 of the minishift IP address
$ minishift ip
Navigate to http://
Now you can click about and generate some load. Meanwhile over on the Instana dashboard, the agent will have automatically discovered all those new containers and started monitoring them.
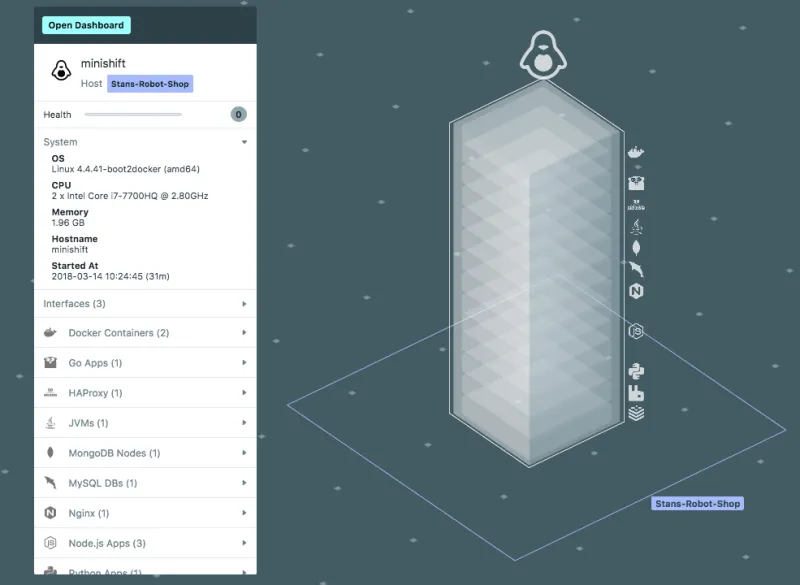
As you generate some load every request is traced end to end and the service map is automatically built.

Monitoring Your Sample Microservice Application on OpenShift
Monitoring OpenShift with Instana is very easy.
You have reached microservice monitoring Guru status and achieved a Zen like inner peace not having to worry about how your application is performing. What are you going to do with all the time you have just got back?
In future posts I will cover End User Monitoring, application troubleshooting and other container orchestration systems. Stay tuned.
저자 소개
유사한 검색 결과
Key considerations for 2026 planning: Insights from IDC
Red Hat and Sylva unify the future for telco cloud
Edge computing covered and diced | Technically Speaking
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래
