What we can learn from the glibc security flaw and why you need to think about Continuous Security as part of your container strategy.
On February 18, 2016 a critical security announcement was made regarding glibc and how it affected the Linux operating system. One quick summary of what glibc does and how it relates to the security problem comes from Red Hat’s Knowledgebase:
The glibc package contains standard libraries which are used by multiple programs on the system. In order to save disk space and memory, as well as to make upgrading easier, common system code is kept in one place and shared between programs. This package contains the standard C library against which all GNU/Linux programs are linked. The libresolv library shipped with glibc provides functions which provide translation between host names and IP addresses. nss_dns is the glibc component which provides the Name Service Switch (NSS) service module which uses libresolv to perform DNS lookups.
It meant that someone could craft a DNS response that could result in arbitrary code being executed on a system. This is really bad stuff.
Since almost every program or service on Linux uses the glibc libraries, the problem affected potentially everything running on the operating system. Because of Docker’s packaging format and the way it encapsulates libraries, glibc is effectively included in every image. In a world with thousands of operating system instances / containers / hosts, the affected attack surface is quite large. While Red Hat provides fixes for critical issues like these quickly and efficiently, getting the fixes rolled out to all of your systems is, in many cases, neither quick nor efficient.
Companies spend tremendous amounts of time and effort reacting to these problems. They develop or purchase tools and implement processes to scan systems to find vulnerabilities and then, ultimately, address them. But why isn’t security a more automatic, integrated and continuous part of systems management? Fortunately, there’s a new way. Continuous Security with a container application platform like OpenShift can make rolling out these fixes painless and automated.
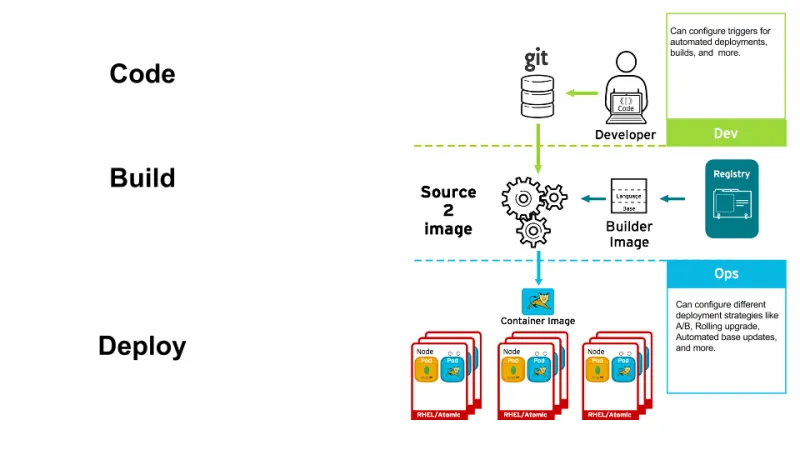
When Red Hat releases updates for the base operating system, it also rebuilds its Docker images and pushes them to its public registry. This is the first part of the magic of Continuous Security with OpenShift -- the updated source image is available.
OpenShift’s Source-to-Image (S2I) process combines a runtime (like Ruby or Python) with source code and produces an image that runs the code. These S2I base images are packaged, shipped and supported by Red Hat, and would be updated with the fixed glibc package in the Red Hat registry. The full list of shipped and supported technologies is here, but consider the example of the rhscl/ruby-22-rhel7 image.
On a regular basis, OpenShift can import metadata from source registries, and, during this import, would detect that the ruby-22-rhel7 image had changed. This would count as an “image change trigger”, and is critical to the concept of Continuous Security. For builds that are dependent on this image, and that have triggers defined, OpenShift would automatically rebuild the application image, thus incorporating the fixed glibc libraries.
Additionally, OpenShift provides powerful tooling for automated deployment. Once the build is complete, it is pushed to OpenShift’s internal registry. OpenShift can immediately detect changes to images in its internal registry, and, for applications where these same triggers are defined, would deploy the updated image.
For a customer with an external CI/CD system, it becomes even more interesting:
- The CI/CD system monitors for image metadata changes
- The CI system causes OpenShift to build a new image, incorporating binary artifacts
- OpenShift will automatically deploy this image to “Dev”
- The CI system performs in-situ integration tests
- The CI system then promotes the image and repeats this process, leveraging OpenShift’s automated deployment strategies at each step of the way
Ultimately, by leveraging CI/CD and OpenShift, the entire process of rebuilding the application to incorporate the latest fixes, testing, and ensuring that it is deployed everywhere within the environment could be 100% automated. Is your organization ready to embrace Continuous Security with OpenShift?
저자 소개
채널별 검색
오토메이션
기술, 팀, 인프라를 위한 IT 자동화 최신 동향
인공지능
고객이 어디서나 AI 워크로드를 실행할 수 있도록 지원하는 플랫폼 업데이트
오픈 하이브리드 클라우드
하이브리드 클라우드로 더욱 유연한 미래를 구축하는 방법을 알아보세요
보안
환경과 기술 전반에 걸쳐 리스크를 감소하는 방법에 대한 최신 정보
엣지 컴퓨팅
엣지에서의 운영을 단순화하는 플랫폼 업데이트
인프라
세계적으로 인정받은 기업용 Linux 플랫폼에 대한 최신 정보
애플리케이션
복잡한 애플리케이션에 대한 솔루션 더 보기
가상화
온프레미스와 클라우드 환경에서 워크로드를 유연하게 운영하기 위한 엔터프라이즈 가상화의 미래