We’re all familiar with top, a real-time system monitor which shows usage of your Linux hardware and network resources. As a top command alternative, atop also provides sysadmins with real-time system insight, and also allows for an anatomized view of which processes are using the most CPU, memory, storage, or network.
Let’s take a look at using atop for Linux server performance analysis.
Advantages of atop
Atop is an ASCII, full-screen performance monitor which can log and report the activity of all server processes. One feature I really like is that atop stays active in the background for long-term server analysis (up to 28 days by default). Other advantages include:
- Shows resource usage of all processes, even those that are closed or completed.
- Monitors threads within processes and ignores processes that are unused.
- Accumulates resource usage for all processes and users with the same name.
- Highlights critical resources using colors (red).
- Adds or removes columns as the size of the display window changes.
- Includes disk I/O and network utilization.
- Uses the
netatopkernel module to monitor TCP, UDP, and network bandwidth.
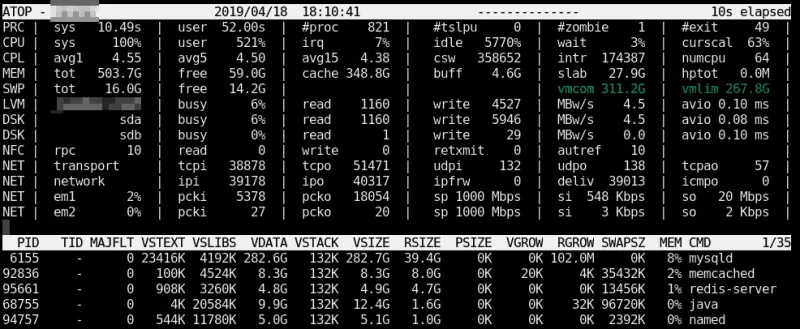
Once atop is launched, by default it shows system activity for CPU, memory, swap, disks, and network in 10-second intervals. In addition, for each process and thread, you can analyze CPU utilization, memory consumption, disk I/O, priority, username, state, and even exit codes:
Install atop on Red Hat Enterprise Linux/CentOS/Fedora Linux
[Want to try out Red Hat Enterprise Linux? Download it now for free.]
First, install and enable the Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) repo. See Red Hat solution #308983 if you’re not sure how to do this. Once that task is complete, you can install atop:
yum install atop
Launch it similar to top, using:
atop
Using atop
When it comes to using atop, a good place to start is to read the man pages:
man atop
Useful atop launch commands include:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
atop -1 |
Launch with average-per-second total values. |
atop -a |
Launch with active processes only. |
atop -c |
Launch with command-line per process. |
atop -d |
Launch with disk info. |
atop -m |
Launch with memory info. |
atop -n |
Launch with network info. |
atop -s |
Launch with scheduling info. |
atop -v |
Launch with various info (e.g., PPID, user, or time). |
atop -y |
Launch with individual threads. |
Once atop is running, press the following shortcut keys to sort processes:
| Shortcut key | Description |
|---|---|
a |
Sort in order of most active resources. |
c |
Revert to sorting by CPU consumption (default). |
d |
Sort in order of disk activity. |
m |
Sort in order of memory usage. |
n |
Sort in order of network activity. |
Reading atop reports and logs
By default, after installation, the atop daemon writes snapshots to a compressed log file (e.g., /var/log/atop/atop_20140813). These log files can be read using:
atop -r </full/path/to/atop/log/file>
Once you open a log file (e.g., atop -r /var/log/atop/atop_20140813), then use t to go forward in 10-minute intervals, and T to go back. You can analyze specific times by pressing b and then entering the time. The above shortcut keys also work in this mode: a, c, d, m, and n.
You can use shortcuts with atopsar. For example, using the flag -c 30 5 with atopsar generates a report for current CPU utilization for five minutes (10 times with intervals of 30 seconds):
atopsar -c 30 5
Using the flag -A with return all available reports.
atopsar -A
But, you can limit this output to a specific time window using beginning (-b) and end (-e) flags:
atopsar -A -b 11:00 -e 11:15
Wrapping Up
There are some good advantages and unique features of atop, as listed above. Personally, I like how atop allows you to isolate and analyze CPU usage, memory consumption, storage I/O, etc., for each process and thread.
Still, some of us will continue to prefer top or htop, and they are both great tools. After reading this article, I hope more people will also add or continue to use atop as one of their go-to Linux analysis and troubleshooting tools.
Über den Autor
Hayden James is a Linux Systems Analyst and Internet Entrepreneur from the Caribbean. He relocated to the US ten years ago, where he maintained Linux servers and sold small startups. Today, he supports clients remotely from his island home while also managing a niche web hosting venture. His web blog features Linux Sysadmin related articles: haydenjames.io.
Ähnliche Einträge
More than meets the eye: Behind the scenes of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 10 (Part 4)
Why should your organization standardize on Red Hat Enterprise Linux today?
The Overlooked Operating System | Compiler: Stack/Unstuck
Linux, Shadowman, And Open Source Spirit | Compiler
Nach Thema durchsuchen
Automatisierung
Das Neueste zum Thema IT-Automatisierung für Technologien, Teams und Umgebungen
Künstliche Intelligenz
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die es Kunden ermöglichen, KI-Workloads beliebig auszuführen
Open Hybrid Cloud
Erfahren Sie, wie wir eine flexiblere Zukunft mit Hybrid Clouds schaffen.
Sicherheit
Erfahren Sie, wie wir Risiken in verschiedenen Umgebungen und Technologien reduzieren
Edge Computing
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die die Operations am Edge vereinfachen
Infrastruktur
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von der weltweit führenden Linux-Plattform für Unternehmen
Anwendungen
Entdecken Sie unsere Lösungen für komplexe Herausforderungen bei Anwendungen
Virtualisierung
Erfahren Sie das Neueste über die Virtualisierung von Workloads in Cloud- oder On-Premise-Umgebungen
