This blog post covers a proof of concept, which shows how to monitor Apache Airflow using Prometheus and Grafana.
Airflow monitoring diagram
Let’s discuss the big picture first. Apache Airflow can send metrics using the statsd protocol. These metrics would normally be received by a statsd server and stored in a backend of choice. Our goal though, is to send the metrics to Prometheus. How can the statsd metrics be sent to Prometheus?
It turns out that the Prometheus project comes with a statsd_exporter that functions as a bridge between statsd and Prometheus. The statsd_exporter receives statsd metrics on one side and exposes them as Prometheus metrics on the other side. The Prometheus server can then scrape the metrics exposed by the statsd_exporter. Overall, the Airflow monitoring diagram looks as follows:
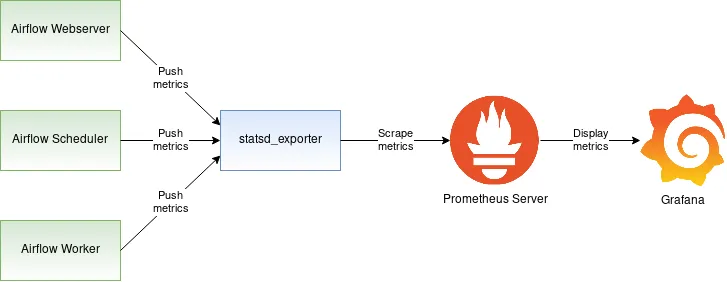
The diagram depicts three Airflow components: Webserver, Scheduler, and the Worker. The solid line starting at the Webserver, Scheduler, and Worker shows the metrics flowing from these three components to the statsd_exporter. The statsd_exporter aggregates the metrics, converts them to the Prometheus format, and exposes them as a Prometheus endpoint. This endpoint is periodically scraped by the Prometheus server, which persists the metrics in its database. Airflow metrics stored in Prometheus can then be viewed in the Grafana dashboard.
The remaining sections of this blog will create the setup depicted in the above diagram. We are going to:
Configure Airflow to publish the statsd metrics.
Convert the statsd metrics to Prometheus metrics using statsd_exporter.
Deploy the Prometheus server to collect the metrics and make them available to Grafana.
By the end of the blog, you should be able to watch the Airflow metrics in the Grafana dashboard. Follow me to the next section, where we are going to start by installing Apache Airflow.
 ¿Quiere lograr más con la imagen base universal (UBI) de Red Hat?
¿Quiere lograr más con la imagen base universal (UBI) de Red Hat?
 ¿Quiere lograr más con la imagen base universal (UBI) de Red Hat?
¿Quiere lograr más con la imagen base universal (UBI) de Red Hat?
Enabling statsd metrics on Airflow
In this tutorial, I am using Python 3 and Apache Airflow version 1.10.12. First, create a Python virtual environment where Airflow will be installed:
$ python -m venv airflow-venvActivate the virtual environment:
$ . airflow-venv/bin/activateInstall Apache Airflow along with the statsd client library:
$ pip install apache-airflow $ pip install statsd
Create the Airflow home directory in the default location:
$ mkdir ~/airflowCreate the Airflow database and the airflow.cfg configuration file:
$ airflow initdbOpen the Airflow configuration file airflow.cfg for editing:
$ vi ~/airflow/airflow.cfgTurn on the statsd metrics by setting statsd_on = True. Before saving your changes, the statsd configuration should look as follows:
statsd_on = True statsd_host = localhost statsd_port = 8125 statsd_prefix = airflow
Based on this configuration, Airflow is going to send the statsd metrics to the statsd server that will accept the metrics on localhost:8125. We are going to start that server up in the next section.
The last step in this section is to start the Airflow webserver and scheduler process. You may want to run these commands in two separate terminal windows. Make sure that you activate the Python virtual environment before issuing the commands:
$ airflow webserver $ airflow scheduler
At this point, the Airflow is running and sending statsd metrics to localhost:8125. In the next section, we will spin up statsd_exporter, which will collect statsd metrics and export them as Prometheus metrics.
Converting statsd metrics to Prometheus metrics
Let’s start this section by installing statsd_exporter. If you have the Golang environment properly set up on your machine, you can install statsd_exporter by issuing:
$ go get github.com/prometheus/statsd_exporterAlternatively, you can deploy statsd_exporter using the prometheus/statsd-exporter container image. The image documentation includes instructions on how to pull and run the image.
While Airflow is running, start the statsd_exporter on the same machine:
$ statsd_exporter --statsd.listen-udp localhost:8125 --log.level debug level=info ts=2020-09-18T15:26:51.283Z caller=main.go:302 msg="Starting StatsD -> Prometheus Exporter" version="(version=, branch=, revision=)" level=info ts=2020-09-18T15:26:51.283Z caller=main.go:303 msg="Build context" context="(go=go1.14.7, user=, date=)" level=info ts=2020-09-18T15:26:51.283Z caller=main.go:304 msg="Accepting StatsD Traffic" udp=localhost:8125 tcp=:9125 unixgram= level=info ts=2020-09-18T15:26:51.283Z caller=main.go:305 msg="Accepting Prometheus Requests" addr=:9102 level=debug ts=2020-09-18T15:26:52.534Z caller=listener.go:69 msg="Incoming line" proto=udp line=airflow.executor.open_slots:32|g level=debug ts=2020-09-18T15:26:52.534Z caller=listener.go:69 msg="Incoming line" proto=udp line=airflow.executor.queued_tasks:0|g level=debug ts=2020-09-18T15:26:52.534Z caller=listener.go:69 msg="Incoming line" proto=udp line=airflow.executor.running_tasks:0|g level=debug ts=2020-09-18T15:26:52.534Z caller=listener.go:69 msg="Incoming line" proto=udp line=airflow.dag_processing.processes:1|c level=debug ts=2020-09-18T15:26:52.637Z caller=listener.go:69 msg="Incoming line" proto=udp line=airflow.dag_processing.processes:-1|c level=debug ts=2020-09-18T15:26:52.684Z caller=exporter.go:114 msg="counter must be non-negative value" metric=airflow_dag_processing_processes event_value=-1 level=debug ts=2020-09-18T15:26:54.535Z caller=listener.go:69 msg="Incoming line" proto=udp line=airflow.executor.open_slots:32|g level=debug ts=2020-09-18T15:26:54.535Z caller=listener.go:69 msg="Incoming line" proto=udp line=airflow.executor.queued_tasks:0|g level=debug ts=2020-09-18T15:26:54.535Z caller=listener.go:69 msg="Incoming line" proto=udp line=airflow.executor.running_tasks:0|g level=debug ts=2020-09-18T15:26:54.535Z caller=listener.go:69 msg="Incoming line" proto=udp line=airflow.dag_processing.processes:1|c level=debug ts=2020-09-18T15:26:54.542Z caller=listener.go:69 msg="Incoming line" proto=udp line=airflow.dag.loading-duration.example_trigger_target_dag:0.004020|ms level=debug ts=2020-09-18T15:26:54.546Z caller=listener.go:69 msg="Incoming line" proto=udp line=airflow.scheduler_heartbeat:1|c level=debug ts=2020-09-18T15:26:54.637Z caller=listener.go:69 msg="Incoming line" proto=udp line=airflow.dag_processing.processes:-1|c ...
If everything went well, you should see the Airflow metrics rolling on the screen, as in the above example. You can also verify that the statsd_exporter is doing its job and exposing the metrics in the Prometheus format. The Prometheus metrics should be reachable at localhost:9102. You can use curl to obtain the Prometheus metrics:
$ curl localhost:9102/metrics # HELP airflow_collect_dags Metric autogenerated by statsd_exporter. # TYPE airflow_collect_dags gauge airflow_collect_dags 50.056391 # HELP airflow_dag_loading_duration_example_bash_operator Metric autogenerated by statsd_exporter. # TYPE airflow_dag_loading_duration_example_bash_operator summary airflow_dag_loading_duration_example_bash_operator{quantile="0.5"} 1.108e-06 airflow_dag_loading_duration_example_bash_operator{quantile="0.9"} 4.942e-06 airflow_dag_loading_duration_example_bash_operator{quantile="0.99"} 4.942e-06 airflow_dag_loading_duration_example_bash_operator_sum 1.8886000000000002e-05 airflow_dag_loading_duration_example_bash_operator_count 7 # HELP airflow_dag_loading_duration_example_branch_dop_operator_v3 Metric autogenerated by statsd_exporter. # TYPE airflow_dag_loading_duration_example_branch_dop_operator_v3 summary airflow_dag_loading_duration_example_branch_dop_operator_v3{quantile="0.5"} 1.61e-06 airflow_dag_loading_duration_example_branch_dop_operator_v3{quantile="0.9"} 5.776e-06 airflow_dag_loading_duration_example_branch_dop_operator_v3{quantile="0.99"} 5.776e-06 airflow_dag_loading_duration_example_branch_dop_operator_v3_sum 1.8076e-05 airflow_dag_loading_duration_example_branch_dop_operator_v3_count 6 ...
Collecting metrics using Prometheus
After completing the previous section, the Airflow metrics are now available in the Prometheus format. As a next step, we are going to deploy the Prometheus server that will collect these metrics. You can download the Prometheus precompiled binary from the project download page or from the GitHub release pages. Alternatively, you can leverage the existing Prometheus container image.
The minimum Prometheus configuration that will collect the Airflow metrics looks like this:
scrape_configs: - job_name: airflow static_configs: - targets: ['localhost:9102']
It instructs the Prometheus server to scrape the metrics from the endpoint localhost:9102 periodically. Save the above configuration as a file named prometheus.yml and start the Prometheus server by issuing the command:
$ prometheus --config.file prometheus.ymlYou can now use your browser to go to the Prometheus built-in dashboard at http://localhost:9090/graph and check out the Airflow metrics.
Displaying metrics in Grafana
Finally, we are going to display the Airflow metrics using Grafana. Interestingly enough, I was not able to find any pre-existing Grafana dashboard for Airflow monitoring. So, I created a basic dashboard that you can find on GitHub. The dashboard looks like this:

Conclusion
In this post, we deployed a proof of concept of Airflow monitoring using Prometheus. We deployed and configured Airflow to send metrics. We leveraged statsd_exporter to convert the metrics to the Prometheus format. We collected the metrics and saved them in Prometheus. Finally, we displayed the metrics on the Grafana dashboard. This proof of concept was spurred by my search for a way to monitor Apache Airflow, and it may be a good starting point for you. If you make further improvements to the dashboard that you’d like to share with the community, I would be happy to receive a pull request.
Sobre el autor
Más como éste
Why the future of AI depends on a portable, open PyTorch ecosystem
AI in telco – the catalyst for scaling digital business
Crack the Cloud_Open | Command Line Heroes
Open source for climate finance | Technically Speaking
Navegar por canal
Automatización
Las últimas novedades en la automatización de la TI para los equipos, la tecnología y los entornos
Inteligencia artificial
Descubra las actualizaciones en las plataformas que permiten a los clientes ejecutar cargas de trabajo de inteligecia artificial en cualquier lugar
Nube híbrida abierta
Vea como construimos un futuro flexible con la nube híbrida
Seguridad
Vea las últimas novedades sobre cómo reducimos los riesgos en entornos y tecnologías
Edge computing
Conozca las actualizaciones en las plataformas que simplifican las operaciones en el edge
Infraestructura
Vea las últimas novedades sobre la plataforma Linux empresarial líder en el mundo
Aplicaciones
Conozca nuestras soluciones para abordar los desafíos más complejos de las aplicaciones
Virtualización
El futuro de la virtualización empresarial para tus cargas de trabajo locales o en la nube
