Windows Machine Config Operator (WMCO) 6.0.0 available on OpenShift 4.11 will move from Windows Server configured with Docker runtime to Windows Server configured with containerd runtime. You can read more about Dockershim deprecation here. Switching from Docker to containerd runtime is relatively easy, and will have better performance and lower overhead. Because the Docker runtime is deprecated in Kubernetes 1.24, containerd is now the default runtime for WMCO-supported Windows nodes. Upon the installation of or an upgrade to WMCO 6.0.0, containerd is installed as a Windows service. The kubelet will now uses containerd for image pulls and as the container runtime instead of the Docker runtime.
Steps to configure containerd for Running Windows Container Workloads on OpenShift.
Install OpenShift 4.11
Follow these steps to install OpenShift Container Platform. Be sure the following pre-requisites documented here are followed.
Prerequisites
- You have access to an OpenShift Container Platform cluster using an account with
cluster-adminpermissions. - You have installed the OpenShift CLI (
oc). - You have installed your cluster on a supported platform using installer-provisioned infrastructure, or using user-provisioned infrastructure with the
platform: nonefield set in yourinstall-config.yamlfile. - You have configured hybrid networking with OVN-Kubernetes for your cluster. This must be completed during the installation of your cluster. For more information, see Configuring hybrid networking.
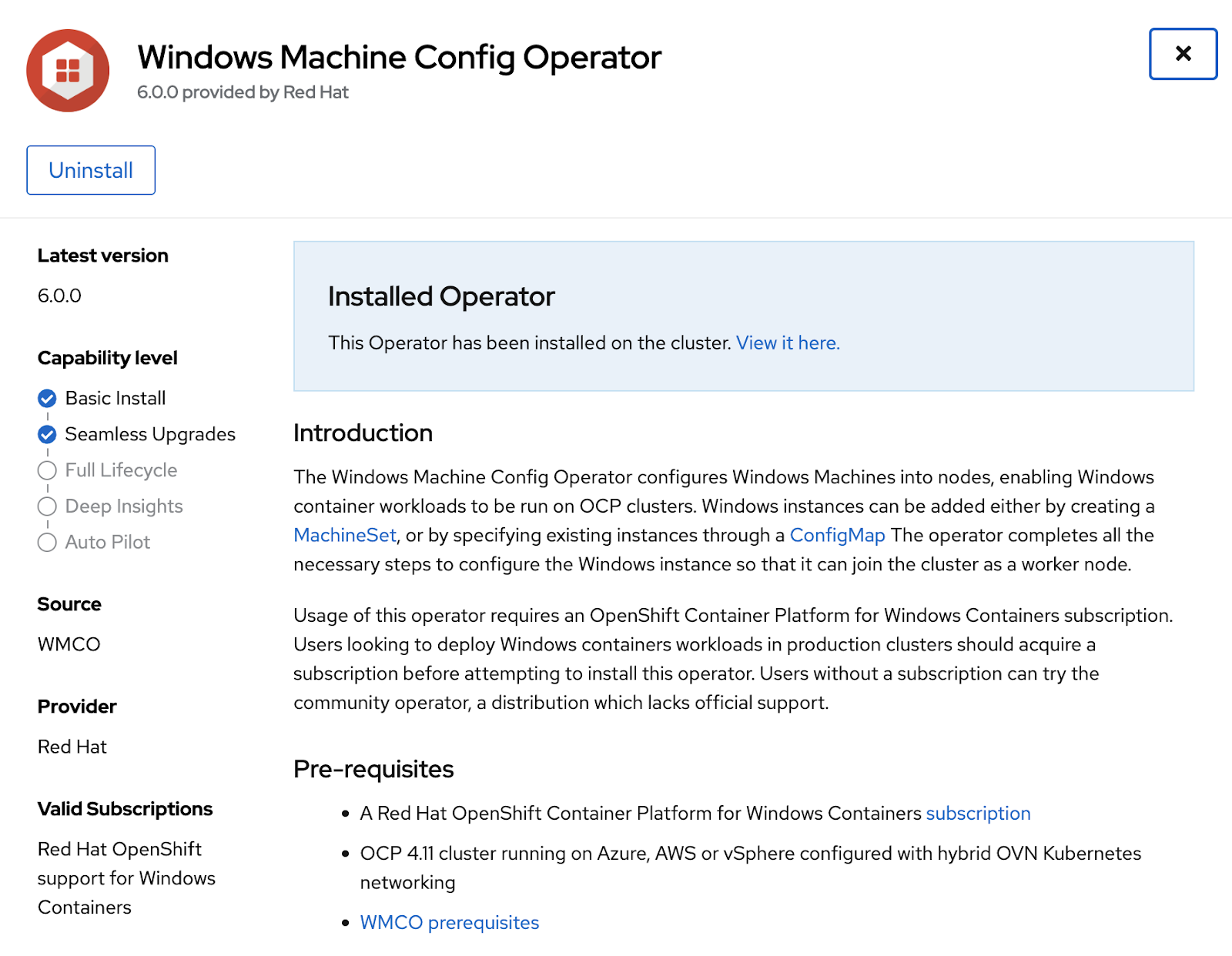
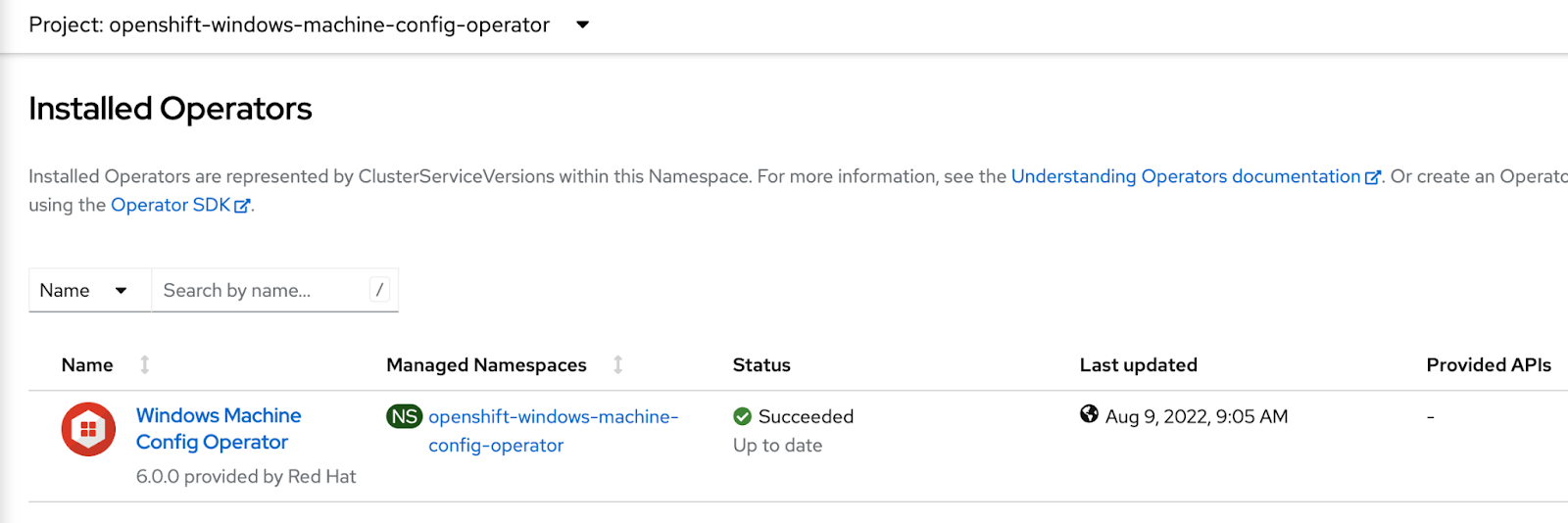
Install Windows Machine Config Operator 6.0.0
You can install the Windows Machine Config Operator using either the web console or OpenShift CLI (oc). Refer to product documentation for steps on how to install WMCO from the inCluster Operator Hub.
Be sure that the Windows Machine Config Operator is installed under Installed Operators.
Configure an instance using Windows MachineSets
You can create a Windows MachineSet object to serve a specific purpose in your OpenShift Container Platform cluster. For example, you might create infrastructure Windows machine sets and related machines so that you can move supporting Windows workloads to the new Windows machines. Here is a sample YAML that defines a Windows MachineSet object running on Microsoft Azure that the Windows Machine Config Operator (WMCO) can react upon. Please refer to the product documentation for the exact steps for configuring a Windows instance for your platform.
apiVersion: machine.openshift.io/v1beta1
kind: MachineSet
metadata:
labels:
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-cluster: <infrastructure_id>
name: <windows_machine_set_name>
namespace: openshift-machine-api
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-cluster: <infrastructure_id>
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-machineset: <windows_machine_set_name>
template:
metadata:
labels:
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-cluster: <infrastructure_id>
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-machine-role: worker
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-machine-type: worker
machine.openshift.io/cluster-api-machineset: <windows_machine_set_name>
machine.openshift.io/os-id: Windows
spec:
metadata:
labels:
node-role.kubernetes.io/worker: ""
providerSpec:
value:
apiVersion: azureproviderconfig.openshift.io/v1beta1
credentialsSecret:
name: azure-cloud-credentials
namespace: openshift-machine-api
image:
offer: WindowsServer
publisher: MicrosoftWindowsServer
resourceID: ""
sku: 2022-datacenter
version: latest
kind: AzureMachineProviderSpec
location: <location>
managedIdentity: <infrastructure_id>-identity
networkResourceGroup: <infrastructure_id>-rg
osDisk:
diskSizeGB: 128
managedDisk:
storageAccountType: Premium_LRS
osType: Windows
publicIP: false
resourceGroup: <infrastructure_id>-rg
subnet: <infrastructure_id>-worker-subnet
userDataSecret:
name: windows-user-data
namespace: openshift-machine-api
vmSize: Standard_D2s_v3
vnet: <infrastructure_id>-vnet
zone: "<zone>"
Examine installed configured container runtime
From the command line, type oc get nodes -o widecode> and observe the output. You should be able to see that containerd is configured as the container runtime for the Windows node.
Upgrading from earlier versions of OpenShift and WMCO
The procedure for an upgrade that includes migration to containerd follows the regular upgrade process.
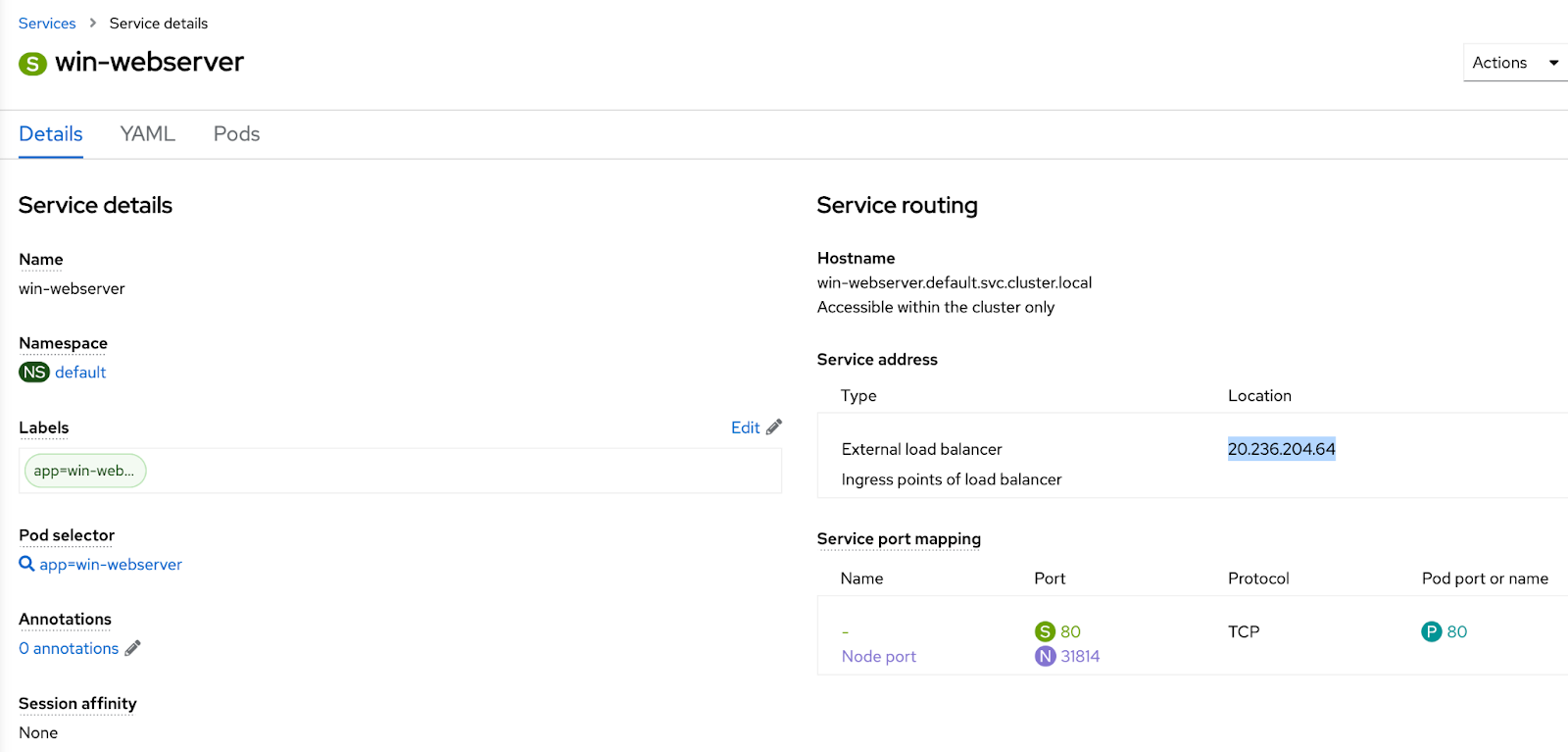
Run a sample workload
Deploy a sample application to the cluster and be surethe pod is running. Expose the application as a service.
Expand Networking->Services->Name of your service to note the external load balancer location as highlighted below.
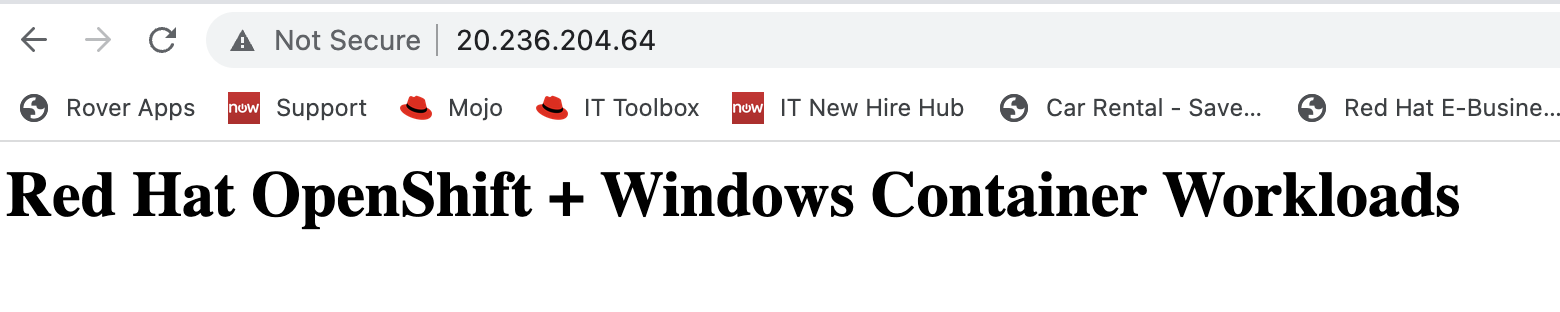
Hit that endpoint from a browser to be sure you can access the application.
Über die Autoren
Ähnliche Einträge
GitOps-Promotions endlich beherrschbar machen
AI in telco – the catalyst for scaling digital business
Get into GitOps | Technically Speaking
Composable infrastructure & the CPU’s new groove | Technically Speaking
Nach Thema durchsuchen
Automatisierung
Das Neueste zum Thema IT-Automatisierung für Technologien, Teams und Umgebungen
Künstliche Intelligenz
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die es Kunden ermöglichen, KI-Workloads beliebig auszuführen
Open Hybrid Cloud
Erfahren Sie, wie wir eine flexiblere Zukunft mit Hybrid Clouds schaffen.
Sicherheit
Erfahren Sie, wie wir Risiken in verschiedenen Umgebungen und Technologien reduzieren
Edge Computing
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die die Operations am Edge vereinfachen
Infrastruktur
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von der weltweit führenden Linux-Plattform für Unternehmen
Anwendungen
Entdecken Sie unsere Lösungen für komplexe Herausforderungen bei Anwendungen
Virtualisierung
Erfahren Sie das Neueste über die Virtualisierung von Workloads in Cloud- oder On-Premise-Umgebungen