With Portworx and Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization running on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA), users can reliably migrate their virtual machines to the cloud, and still get access to all the enterprise-grade storage features they need to run their applications in production.
What is ROSA?
Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA) is a managed implementation of Red Hat OpenShift on AWS with a 99.95% service level agreement (SLA) and a dedicated Red Hat site reliability engineering (SRE) team to manage the environment for you. The Red Hat SRE team assists with bringing up clusters using automation, confirms that your ROSA cluster is deployed using best practices, and that it stays up with 24/7 global coverage. This removes the burden of maintaining, integrating, and upgrading Kubernetes off your Cloud Architects and DevOps team while remaining in compliance with a fully supported open source stack.
ROSA is a fully supported version of OpenShift that, with version 4.14, supports the OpenShift Virtualization operator. While the Red Hat SRE team manages and maintains the ROSA cluster for you, the OpenShift Virtualization operator is customer managed with full Red Hat support.
OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA
Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization is a production-ready virtualization technology based on KVM and Kubevirt. OpenShift Virtualization allows you to run a traditional, full VM image of an operating system inside a container on the OpenShift application platform. The actual image runs on a pod in a worker node, but it's managed as if it were a container with a shared network and a YAML configuration file. Both Windows and Linux images are supported. The service is installed using the OpenShift operator marketplace (OperatorHub) and it requires dedicated hardware-based workers to run (AWS *.metal instances). As of OpenShift 4.14, it supports OCP-Virt operator deployment on ROSA when using dedicated hardware nodes in your worker pool.
For more details on the benefits of OpenShift Virtualization with a managed OpenShift service like AWS, read Managing Virtual Machines and Containers as code with OpenShift Virtualization on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
Enterprise-grade data management for OpenShift Virtualization with Portworx
With ROSA now supporting OpenShift Virtualization on metal instances, organizations expect the same enterprise-grade features and services they were used to when running virtual machines on-premises. This is where Portworx can help deliver abest in class storage and data management platform for OpenShift Virtualization. In this section, we will talk about how Portworx provides that common storage layer for both VMs and pods running on ROSA clusters, while delivering all the enterprise-grade features users expect from their virtualization infrastructure.
To deploy Portworx on ROSA clusters, you need an existing VPC.
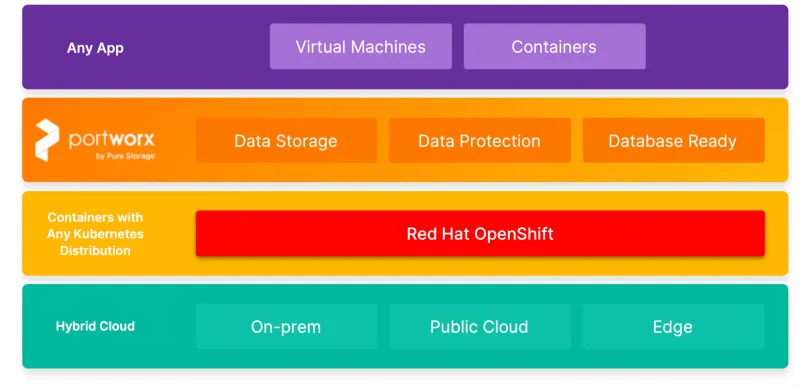
Portworx provides several significant features for OpenShift Virtualization running on ROSA clusters:
- Live Migration: This is an important feature for administrators to move workloads between worker nodes. Portworx provides a storage pool that stretches across AWS Availability zones, enabling administrators to migrate VMs or applications across zones to protect from a datacenter outage. Portworx enables users to Live Migrate their VMs across different worker nodes in their ROSA cluster, regardless of whether they are running these worker nodes in the same availability zone or across different availability zones in the same AWS region.

- High Availability: Users expect virtual machines to restart and be available on a different worker node during a node failure or an Availability Zone failure scenario. With Portworx and the native high availability it provides, VMs that are restarted across worker nodes or availability zones can mount the replica of the persistent volume running on the surviving node/AZ, without user intervention, and continue serving user traffic.

- Automated Storage Capacity Management: If you're modernizing your virtualization stack, you may be migrating hundreds, if not thousands, of virtual machines to OpenShift Virtualization. Monitoring VM disk utilization and expanding those disks manually across all the VMs can become a fulltime job. Portworx Autopilot is a rule-based engine that configures Autopilot rules for your VM disks. Portworx monitors disk utilization across all your VMs. As soon as a disk meets a configured condition, Portwork Autopilot performs an action defined in your Autopilot rule. This allows you to offload VM disk management to Portworx and focus on higher level tasks that actually add value to your organization.
- Disaster Recovery: When you run applications in production, you obviously have a disaster recovery plan. With Portworx Disaster Recovery (DR), you can build a synchronous disaster recovery solution, with zero Recovery Point Objective (RPO) or data loss, across two different ROSA clusters running in the same AWS region.

Alternatively, you can create an asynchronous disaster recovery (15 minute RPO) solution across two different ROSA clusters running across different AWS regions. Portworx DR allows you to build DR architectures and plan for failure scenarios when running virtual machines on ROSA in AWS.
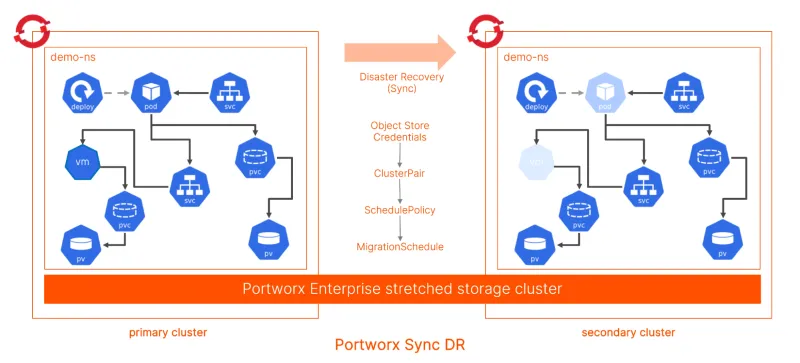
- Data Protection: In addition to disaster recovery, you also need the ability to backup and restore a VM running on ROSA, to handle non-failure scenarios like accidental deletion, data corruption, or ransomware attacks. Portworx Backup allows you to connect your ROSA cluster to the either self-managed or Backup-as-a-Service backup instance. You can use Portworx Backup to protect your virtual machines, and to restore them on either the same ROSA cluster or a different OpenShift or ROSA cluster with OpenShift Virtualization enabled.
Summary
If you want to see a few of these scenarios in action, we've published demonstrations that show you how Portworx can help you make OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA your next best business decision:
Über den Autor
Mayur Shetty is a Principal Solution Architect with Red Hat’s Global Partners and Alliances (GPA) organization, working closely with cloud and system partners. He has been with Red Hat for more than five years and was part of the OpenStack Tiger Team.
Ähnliche Einträge
Ford's keyless strategy for managing 200+ Red Hat OpenShift clusters
F5 BIG-IP Virtual Edition is now validated for Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization
Challenges In Solutions Engineering | Code Comments
Transforming Your Secrets Management | Code Comments
Nach Thema durchsuchen
Automatisierung
Das Neueste zum Thema IT-Automatisierung für Technologien, Teams und Umgebungen
Künstliche Intelligenz
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die es Kunden ermöglichen, KI-Workloads beliebig auszuführen
Open Hybrid Cloud
Erfahren Sie, wie wir eine flexiblere Zukunft mit Hybrid Clouds schaffen.
Sicherheit
Erfahren Sie, wie wir Risiken in verschiedenen Umgebungen und Technologien reduzieren
Edge Computing
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die die Operations am Edge vereinfachen
Infrastruktur
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von der weltweit führenden Linux-Plattform für Unternehmen
Anwendungen
Entdecken Sie unsere Lösungen für komplexe Herausforderungen bei Anwendungen
Virtualisierung
Erfahren Sie das Neueste über die Virtualisierung von Workloads in Cloud- oder On-Premise-Umgebungen
