Andres Martinez, Principal Developer, has been having a rough time lately. While the root cause analysis following the now-infamous two-day outage acquitted his team’s code of wrongdoing, Martinez has spent enough time around the codebase that he knows a major event caused by his team’s code is not a matter of “If,” but “When.”
His stress is growing every day - he knows that being the only one with extensive experience and knowledge of the codebase is a single point of failure. He is the single thread holding up the technical-debt-Sword of Damocles. He knows that the thread is at risk of breaking, and soon.
A New Hope?
In his conversations over the past few weeks around process improvement with Chief Architect Daniel Mitchell, he’s heard some great initial success stories from the adoption of Infoblox and F5 automation. He finds himself encouraged by their successes - if Ops can do it, so can we!
So he begins to craft a plan to modernize the DSE inventory application. Of course, revamping the entire application stack would take way more time and money than they had available. The increasing fragility of the application environments meant his team spends almost all of their time just keeping the lights on. During his discussions with Mitchell, he realizes that he doesn’t have to modernize everything at once, but he needs to start somewhere.
It’s a question with - for once - an easy answer: they need to modernize their version control in the same way the operations team has modernized its version control. Each development team had their own preferred repository, as well as their own preferred way of managing the roll-out of new features due to a lack of coordination during development. This led to three separate git repositories being used -- in addition to a subversion repository that had somehow managed to survive.
Martinez considers how he might be able to leverage Git to reduce the application’s technical debt - but it quickly becomes apparent to him that it’s not limited to his team’s code. He sees the same potential train wreck happening with the new infrastructure work, so whatever solution they implement needs to be scalable across all aspects of the company. After reviewing his options, he decides to launch a pilot program with GitLab on Red Hat OpenShift.
What is GitOps?
During a brainstorming session in the Dev Team Room, one of Martinez’s direct reports asks him, “What’s GitOps? Git-driven DevOps?”
“Yes, exactly - let me show you.” He pulls up a diagram on his laptop:
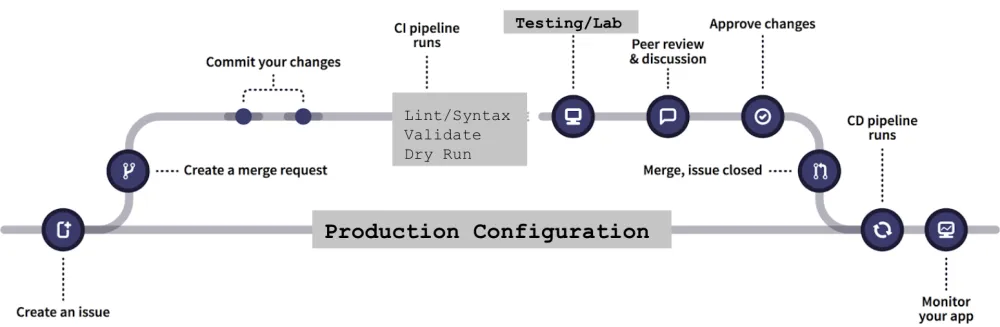 “GitOps is based on three principles: Infrastructure-as-Code (or IaC), merge requests, and CI/CD. Let’s start with IaC - although in reality, it’s more like ‘anything-as-code,’ since in an ideal world, anything that is a policy, config, or any other operations work would be stored in code. The great thing about IaC is that it declares the desired state of your infrastructure in a Git repository, which means you can integrate it into your existing git workflows easily. This in turn leads to way more visibility on changes to infrastructure. More eyes equal fewer chances of a flaw leaking into the system.”
“GitOps is based on three principles: Infrastructure-as-Code (or IaC), merge requests, and CI/CD. Let’s start with IaC - although in reality, it’s more like ‘anything-as-code,’ since in an ideal world, anything that is a policy, config, or any other operations work would be stored in code. The great thing about IaC is that it declares the desired state of your infrastructure in a Git repository, which means you can integrate it into your existing git workflows easily. This in turn leads to way more visibility on changes to infrastructure. More eyes equal fewer chances of a flaw leaking into the system.”Configuring Merge Request-based pipelines in GitLab
Martinez opens a local copy of the inventory application and creates a new branch. He then creates a new file in the root directory of the project called .gitlab-ci.yml. He adds this code to the file:
default: image: node:latest cache: paths: - node_modules stages: - prepare_env - build - package - deploy .openshift_job: image: daviestreetent/gitlab-ci-openshift before_script: - oc login $OC_URL --token=$OC_TOKEN --insecure-skip-tls-verify - oc project $OC_NAMESPACESLUG-dev "Prepare OpenShift Environment (Dev)": extends: .openshift_job stage: prepare_env script: - echo "===== ENFORCING INFRASTRUCTURE OBJECTS =======" - oc apply --filename=./.openshift/dev --recursive=true --wait=true -n $OC_NAMESPACESLUG-dev rules: - if: '$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME == "master"' when: always - when: never "Prepare OpenShift Environment (Staging)": extends: .openshift_job stage: prepare_env script: - echo "===== ENFORCING INFRASTRUCTURE OBJECTS =======" - oc login $OC_URL --token=$OC_TOKEN --insecure-skip-tls-verify - oc project $OC_NAMESPACESLUG-staging - oc apply --filename=./.openshift/staging --recursive=true --wait=true -n $OC_NAMESPACESLUG-staging rules: - if: '$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME == "staging"' when: always - when: never "Prepare OpenShift Environment (Production)": extends: .openshift_job stage: prepare_env script: - echo "===== ENFORCING INFRASTRUCTURE OBJECTS =======" - oc apply --filename=./.openshift/prod --recursive=true --wait=true -n $OC_NAMESPACESLUG-prod rules: - if: '$CI_COMMIT_REF_NAME == "prod"' when: always - when: never build: stage: build image: node:latest script: - npm install allow_failure: true artifacts: paths: - node_modules expire_in: 1 week "Package Image on OCP": extends: .openshift_job stage: package script: - oc start-build openshift-spring-custom --follow --from-dir . "Deploy Application on OCP": extends: .openshift_job stage: deploy when: manual script: - oc project $OC_NAMESPACESLUG-dev - oc rollout latest dc/openshift-test-app
“Ok, so that’s a big file - let’s break it down. What we’re doing is establishing some defaults, configuring the stages our pipeline will contain, specifying some global configurations, and then for each stage, we describe the job we want to run. You can see a few common elements from each of these jobs."
"First, they have a human-readable label. Then we see they extend the defaults stage we defined earlier, and define when in the pipeline the job is run. Now we specify our scripts to run for the job, and then optionally establish rules - as an example in the cases above, you can see that the job "Prepare OpenShift Environment (Production)": would only be run if the branch we’re merging into was labeled “prod” - this allows you to be more or less picky about what occurs on different environments."
"In the case of this pipeline, we’re taking the API objects described in the .openshift directory and the appropriate subdirectory and running an oc apply on them. If the apply succeeds, the job proceeds to the next stage, where we build and package a new iteration of the application. The final stage, deploy, is configured to require a manual action in order to roll out the new project.”
“So now that we’ve got that out of the way, let’s commit our pipeline code and see what it looks like on GitLab.”
He commits the code, and pulls up the repository on GitLab. It looks like this:
 “Looks like the job failed - that’s completely normal, because we haven’t installed or configured a runner for our project. Let’s do that now.”
“Looks like the job failed - that’s completely normal, because we haven’t installed or configured a runner for our project. Let’s do that now.”Installing the GitLab Runner Operator
“First, we need to install the Operator, which we do through the OpenShift Console.”

“After clicking on the Runner Operator, we’re asked to specify a few things for the installation. We’ll choose a specific namespace to install the operator for, so we can keep our workstreams clean.”

“After clicking on ‘Install,’ the Runner Operator should be online within a few minutes.”

“Now we need to tell GitLab about our runner, and establish a connection. To do this, we’ll need to head to the GitLab project’s Settings page, and click on ‘CI/CD.’ Next we expand the ‘Runners’ section. You can see that we have an option to ‘Set up a specific runner manually.’ We will need to copy the registration token and set up a secret in our OpenShift project.”
 “Using the OpenShift command line makes this pretty straightforward. We just log in to our project…”
“Using the OpenShift command line makes this pretty straightforward. We just log in to our project…”
oc project “PROJECT NAMESPACE”
“And then create a secret file with the token we just copied.”
cat > gitlab-runner-secret.yml <<< EOF apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: gitlab-runner-secret type: Opaque stringData: runner-registration-token: YOUR_TOKEN_HERE # your project runner secret EOF oc apply -f gitlab-runner-secret.yml
"Now let’s create the runner itself.”
cat > gitlab-runner.yml <<< EOF apiVersion: apps.gitlab.com/v1beta2 kind: Runner metadata: name: example spec: imagePullPolicy: Always gitlabUrl: ‘https://gitlab.com’ tags: ‘openshift, test’ token: gitlab-runner-secret EOF oc apply -f gitlab-runner.yml
oc get runners NAME AGE gitlab-runner 5m oc get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE gitlab-runner-bf9894bdb-wplxn 1/1 Running 0 5m
“Now that it’s reporting as running, we can check back with GitLab to see that the Runner has phoned home and is now available.”

Deploying a requested change using the GitLab Runner Operator
“Let’s test it out. I’ve modified the version number for NodeJS for our application - take a look at the following commit:”

“Looks good - let’s now create a merge request, and approve it. After a few minutes, we can start to see our pipeline jobs have all successfully passed, up to the final ‘deploy’ stage, which requires manual intervention:”

“Take a peek behind the scenes - this is what the Prepare_env job is reporting. You can see that the new configurations have been successfully applied, specifically in this case, the build config.”
 “All we need to do now is deploy - we’ll click on the ‘play’ button to kick it off... Looks like it’s running nicely!”
“All we need to do now is deploy - we’ll click on the ‘play’ button to kick it off... Looks like it’s running nicely!”
 “And now it’s finished. If we look in the logs for the build we can see that it did indeed rollout the new version of our application. Where’s my ‘Easy Button?’”
“And now it’s finished. If we look in the logs for the build we can see that it did indeed rollout the new version of our application. Where’s my ‘Easy Button?’”

Tune in next time…
A few days and several pizzas later, Martinez’s team steps away from their keyboards and joins him in a conference room. Already seated at the table is Zachary L. Tureaud, Director of Security Engineering. Martinez motions to his team to take a seat.
“I think we can all agree that we’ve had amazing success in improving our development pipeline. I have already seen an increase in velocity through some of the issues that have been worked on for the past couple of days. It seems evident that the new pipeline has taken a very large bite out of our workload, and freed us up to move faster and even have some time to brainstorm.”
“It’s because of this success that I’ve asked Zachary to take a look at what we’ve done to see if we might be able to leverage this system to increase our security as well. Our relationship with the security team has not been well-maintained over the past few years. We haven’t had the time to work with them on ensuring we maintain our security, and need to do a better job shifting that security burden left. I’ll let Zachary explain further.”
Tureaud stands up and grabs a whiteboard marker. “Alright, is everyone sitting comfortably? Then we’ll begin.”
To be continued
If you’d like to see a step-by-step demonstration of the methods described in this post, please take a look at the video on our YouTube channel.
Resources
- Install GitLab Runner on Red Hat OpenShift (GitLab Docs)
- GitLab CI/CD Pipelines documentation
- GitLab CI/CD Jobs documentation
- An example GitOps project on GitLab.com
Über den Autor
Ähnliche Einträge
Extend trust across the software supply chain with Red Hat trusted libraries
How DTCC uses GitOps to accelerate customer value and security
Command Line Heroes: Season 2: Bonus_Developer Advocacy Roundtable
Composable infrastructure & the CPU’s new groove | Technically Speaking
Nach Thema durchsuchen
Automatisierung
Das Neueste zum Thema IT-Automatisierung für Technologien, Teams und Umgebungen
Künstliche Intelligenz
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die es Kunden ermöglichen, KI-Workloads beliebig auszuführen
Open Hybrid Cloud
Erfahren Sie, wie wir eine flexiblere Zukunft mit Hybrid Clouds schaffen.
Sicherheit
Erfahren Sie, wie wir Risiken in verschiedenen Umgebungen und Technologien reduzieren
Edge Computing
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die die Operations am Edge vereinfachen
Infrastruktur
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von der weltweit führenden Linux-Plattform für Unternehmen
Anwendungen
Entdecken Sie unsere Lösungen für komplexe Herausforderungen bei Anwendungen
Virtualisierung
Erfahren Sie das Neueste über die Virtualisierung von Workloads in Cloud- oder On-Premise-Umgebungen
