Tools like sed (stream editor) and grep (global regular expression print) are powerful ways to save time and make your work faster. Before diving deep into the use cases, I would like to briefly explain regular expressions (regexes), which are necessary for the text manipulation that we will do later.
What are regular expressions? When we deal with log files, text files, or a piece of code, we
need to understand that all of these consist of characters. When the length of the file is large, it becomes a necessity to filter out certain patterns in order to make your debugging easier. You will find examples of regular expressions throughout these use cases.
Group 1: Server data
Let’s say you have a file that has an occurrence of a string:

Now, how do you filter out site1’s details (the above file is a simple example), so that you can only grab the necessary info and manipulate the entries?
Clearly, we can see there is a common pattern ("Cloud deployment") throughout the file. So, now we can use filtering techniques to grab info from the file using grep. I remember this as "get regex n print."
Use case 1
If I want the servers from different regions, I can use grep as follows:

Use case 2
Now, say that you know want to filter out the servers on the basis of IP. You can do the same using:

Use case 3
Now, take a look at the first grep command image. Even though you knew your system’s subnet range, the command printed the occurrence of 10.1 throughout the file.
How can you solve this type of use case? We can handle this issue using regex-based advanced filtering, like this:
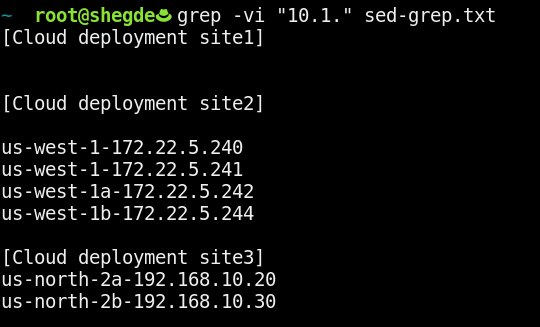
This example is just a possible usage of grep. Again, as this is a relatively small file, you can get what you want using what’s shown above. The -v switch reverses the search criteria, meaning that grep searches the file sed-grep.txt and prints out all of the details, excluding the <search-pattern> (10.1. in this case).
Use case 4
Say that you want to replace the IP addresses and move all of the servers in those regions to a different subnet. You can use sed for this use case.
From the man page, sed uses the format:
sed [options] commands [file-to-edit]
Our command for this use case might look like this:
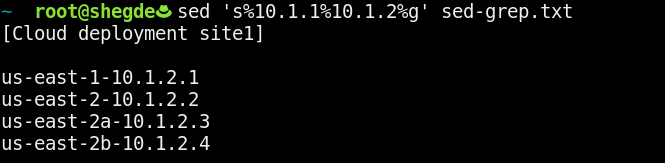
This command breaks down as follows:
- The
sstands for substitute. - The
%is a delimiter (we can use any characters here). - The
<search pattern>appears after the first%. - The
<replace pattern>appears after the second%. - The
gstands for global replace (meaning throughout the file).
Or:
s%<search-pattern>%<replace-pattern>%g
Use case 5
You can even change the servers’ regions in the file:

Use case 6
This use case is more advanced. We’ll only remove comments (#) from a file using sed:
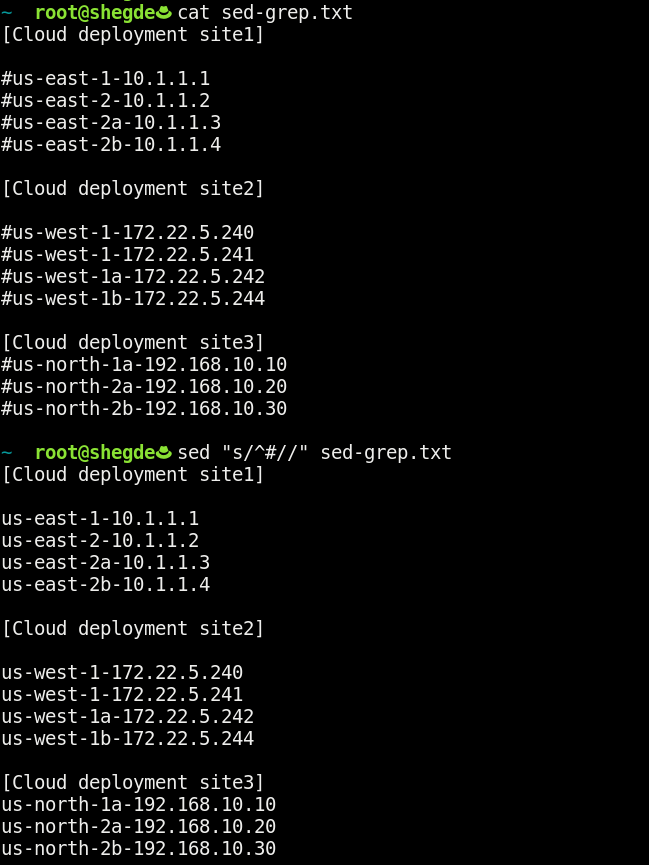
This command says that if # appears as a line’s first character, to replace that line with blank space. As a result, this command does the job of removing the comments from the file.
Group 2: /etc/passwd
Let’s look at some more use cases, this time involving /etc/passwd.
Use case 1
Assume you want to grab the users from the file /etc/passwd file. You can use sed as follows:
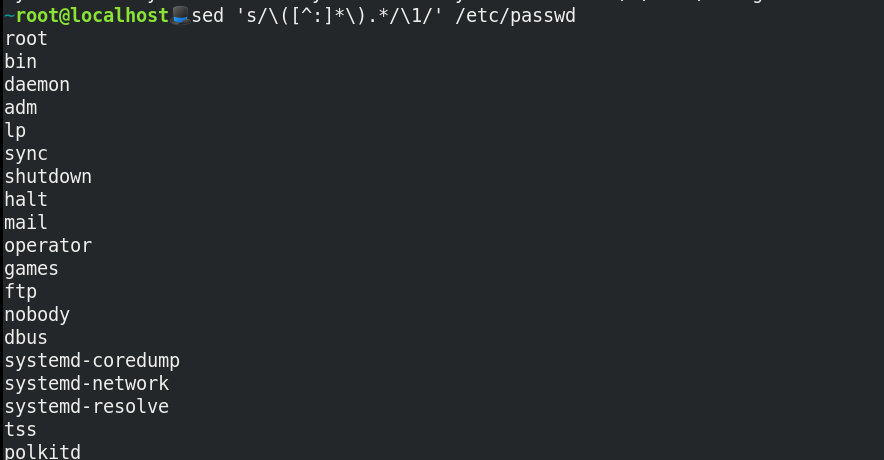
Use case 2
What if you only want to grab the first 10 users from /etc/passwd? You can use sed and awk for this purpose (please bear with me here):
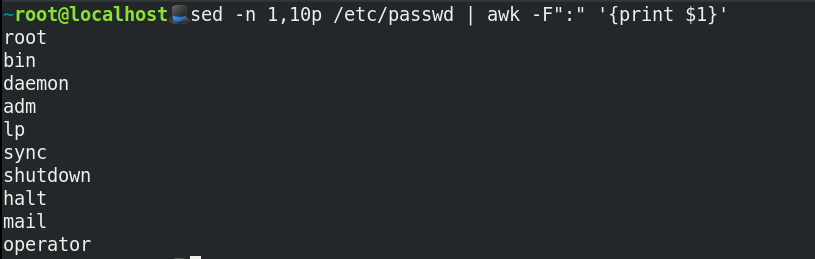
This command breaks down as:
sed -nmeans don’t print everything.pprints the lines one to 10.awkhere uses:as a field separator and prints the first column.
Use case 3
Delete a particular range of lines in text files using sed:

SELinux use case
Here is an example sed command for manipulating SELinux:

Conclusion
This is my attempt to give you readers just a sneak peek of the possibilities of using sed and grep. You can do many text manipulations using these commands. Refer to different options using the man page to learn more.
[Want to try out Red Hat Enterprise Linux? Download it now for free.]
Über den Autor
I work as a Solutions Engineer at Red Hat and my day-to-day work involves OpenShift and Ansible. I'm highly passionate about open source software, cloud, security, and networking technologies.
Ähnliche Einträge
More than meets the eye: Behind the scenes of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 10 (Part 6)
Red Hat Enterprise Linux now available on the AWS European Sovereign Cloud
The Overlooked Operating System | Compiler: Stack/Unstuck
Linux, Shadowman, And Open Source Spirit | Compiler
Nach Thema durchsuchen
Automatisierung
Das Neueste zum Thema IT-Automatisierung für Technologien, Teams und Umgebungen
Künstliche Intelligenz
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die es Kunden ermöglichen, KI-Workloads beliebig auszuführen
Open Hybrid Cloud
Erfahren Sie, wie wir eine flexiblere Zukunft mit Hybrid Clouds schaffen.
Sicherheit
Erfahren Sie, wie wir Risiken in verschiedenen Umgebungen und Technologien reduzieren
Edge Computing
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die die Operations am Edge vereinfachen
Infrastruktur
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von der weltweit führenden Linux-Plattform für Unternehmen
Anwendungen
Entdecken Sie unsere Lösungen für komplexe Herausforderungen bei Anwendungen
Virtualisierung
Erfahren Sie das Neueste über die Virtualisierung von Workloads in Cloud- oder On-Premise-Umgebungen
