Red Hat OpenShift on AWS, commonly known as ROSA, is a fully managed enterprise-ready Kubernetes platform jointly engineered and supported by Red Hat and AWS. As a managed service, ROSA reduces complexity for IT teams that build and manage their own application platforms. Consequently, ROSA empowers developers to focus on what they know best—writing quality code—which leads to faster deployment and increased productivity.
[ See Kubernetes: Everything you need to know ]
In this article, I will walk you through a ROSA cluster's simplest and default architecture and briefly explain the components and functions of the different cluster resources. The article summarizes my video covering the same topic, which you can watch below.
Get started with ROSA
Getting started with ROSA is easy. It runs natively on AWS infrastructure and uses the high availability and resiliency of the AWS cloud.
To create a public ROSA cluster in a single Availability Zone, use the command:
$ rosa create cluster --cluster-name=<cluster-name>
This default deployment creates a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) with two subnets—one public and one private—within the same Availability Zone (a distinct physical location within an AWS region). A VPC is a logically isolated section of the AWS public cloud, and subnets are smaller segments of the VPC.
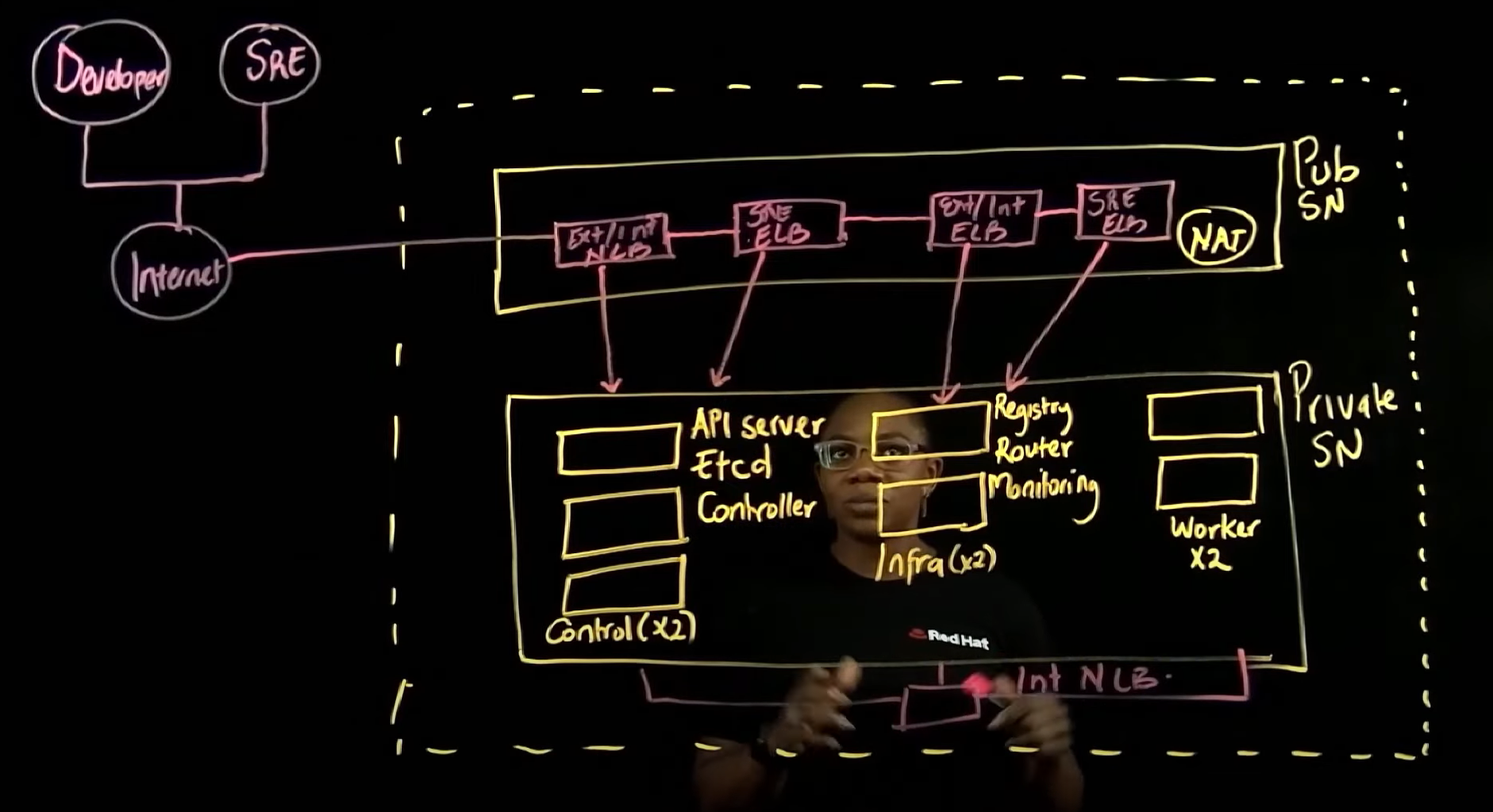
Each cluster gets deployed with three control plane nodes, a minimum of two infrastructure nodes, and at least two worker nodes inside the private subnet.
Each control plane node consists of three elements: an API server, an etcd database, and controllers. The control plane manages the entire cluster.
The infrastructure nodes each contain a built-in OpenShift container registry, router layer, and monitoring layer. The presence of at least two infrastructure nodes ensures the resiliency of the OpenShift router layer.
The worker or "compute" nodes contain agent runtimes for pod networking, monitoring, and DNS resolution. Application workloads run on the worker nodes.
The private subnet uses a network address translation (NAT) gateway that resides in the public subnet to access the internet.
[ When you're ready, start building in the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console. ]
The ROSA installer also deploys a series of AWS load balancers in the public subnet, allowing access to the cluster resources in the private subnet. The first load balancer is known as the external/internal API network load balancer (NLB), and it allows access to the control plane nodes through Kubernetes API.
The second load balancer is an external/internal API Elastic Load Balancer (ELB), and it allows access to end-user applications. This load balancer sits in front of the OpenShift HAProxy and routes requests to the application pods.
Manage the cluster
The Red Hat Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) team gets access to the cluster through the SRE API ELB for cluster administration and management. The SRE team also uses the Red Hat SRE Console ELB to manage the cluster.
The control plane nodes, infrastructure nodes, and worker nodes communicate with each other through an internal API NLB.
This default deployment is the simplest way for a new user or developer to begin understanding ROSA. Single Availability Zone deployments are not recommended for scale, resilience, or production.
Wrap up
The architecture of OpenShift on AWS (ROSA) is robust, but perhaps most importantly, it is architecture you don't have to build yourself. ROSA is a cloud service running on AWS cloud that's ready for your services. Understanding that architecture, in turn, gives you the power and confidence to adjust it if and when it's necessary.
For more detail on ROSA and its components, please watch this YouTube video.
[ Learn how to build a flexible foundation for your organization. Download An architect's guide to multicloud infrastructure. ]
Über den Autor
Charlotte is a Manage OpenShift Black Belt focusing on Red Hat Managed OpenShift offerings on AWS, Microsoft Azure and other public clouds. Charlotte has several years of IT experience helping customers build resilient, highly-available and cost-optimized solutions in the cloud. In her current role, Charlotte is focused on removing organizational, technical and competitive blockers of customer’s adoption of Managed OpenShift as a preferred platform for application workload deployments. Charlotte enjoys providing business value as well as having technical deep dive conversations with customers.
Ähnliche Einträge
AI in telco – the catalyst for scaling digital business
Simplify Red Hat Enterprise Linux provisioning in image builder with new Red Hat Lightspeed security and management integrations
Can Kubernetes Help People Find Love? | Compiler
Scaling For Complexity With Container Adoption | Code Comments
Nach Thema durchsuchen
Automatisierung
Das Neueste zum Thema IT-Automatisierung für Technologien, Teams und Umgebungen
Künstliche Intelligenz
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die es Kunden ermöglichen, KI-Workloads beliebig auszuführen
Open Hybrid Cloud
Erfahren Sie, wie wir eine flexiblere Zukunft mit Hybrid Clouds schaffen.
Sicherheit
Erfahren Sie, wie wir Risiken in verschiedenen Umgebungen und Technologien reduzieren
Edge Computing
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die die Operations am Edge vereinfachen
Infrastruktur
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von der weltweit führenden Linux-Plattform für Unternehmen
Anwendungen
Entdecken Sie unsere Lösungen für komplexe Herausforderungen bei Anwendungen
Virtualisierung
Erfahren Sie das Neueste über die Virtualisierung von Workloads in Cloud- oder On-Premise-Umgebungen
