In this article, I demonstrate how to leverage the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes console for the creation of a Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform cluster with bare-metal nodes.
Specifically, our focus will be on setting up a three-node bare-metal cluster with the addition of an external load balancer. Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management utilizes the assisted Installer to deploy new clusters. This installation method is compatible with a range of CPU architectures, including x86_64, ppc64le, s390x, and arm64. It is presumed that the infrastructure environment satisfies all the prerequisites as specified in the official documentation to cater to your environmental requirements. Additionally, I cover the steps required to fulfill the prerequisites before proceeding with the cluster creation.
Prerequisites
Before starting cluster creation, ensure these prerequisites are met:
- Load balancer configuration: Your load balancer is configured with *.apps, api, and api-int VIPs for the bare-metal cluster. In this article, I'm not running Keepalived on the nodes, because I'm using an external load balancer.
- Network connectivity: Your bare-metal servers and Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management hub network must be able to communicate, with all necessary ports open.
- Pull secret and SSH key: You have a pull secret and SSH key.
Creating your cluster with the web console
Let's get started with the cluster creation process using the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management console:
Create a host inventory
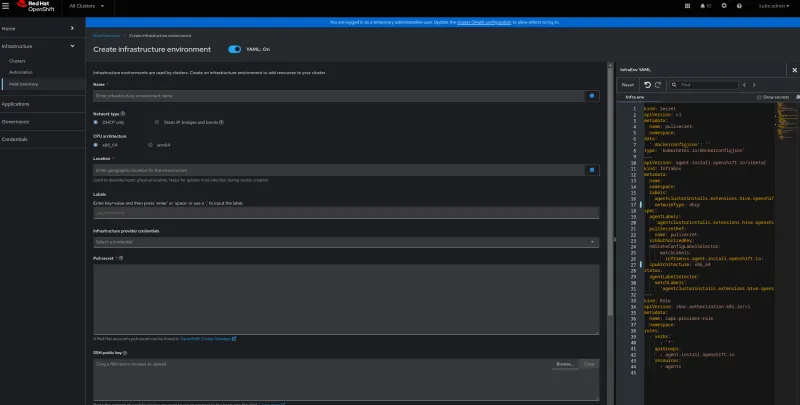
- Navigate to Infrastructure > Host inventory and click on Create infrastructure environment and fill in the required fields like Name and Location.
- Provide the pull secret and provide an SSH key to be able to connect to the hosts for debugging purposes during the discovery process.
- If your hosts are behind a firewall that requires a proxy, provide the necessary proxy information.
- Add your NTP sources for time synchronization among the hosts in this environment.
Create your cluster discovery ISO
- On the clusters page, click Create cluster and follow the steps in the console.
- Select the new host inventory and click Add hosts. choose With Discovery ISO, and download the discovery ISO.
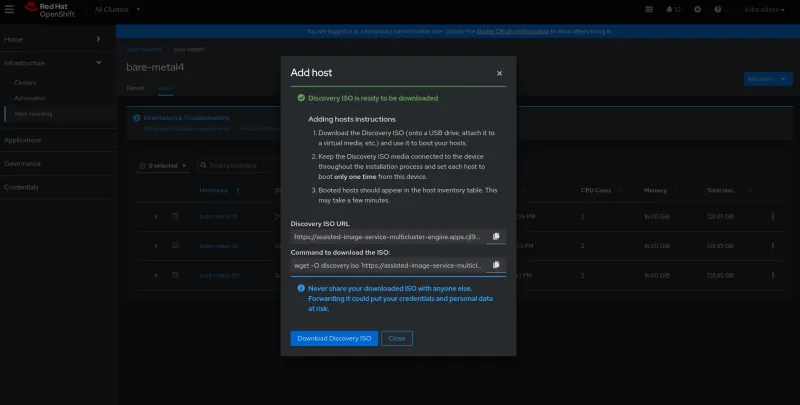
Prepare your bare-metal servers
- Ensure that your bare-metal servers can obtain DHCP IPs, and your Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management hub cluster has access to that DHCP network for host discovery.
- If you use static IP, bridges, or bonded networking, verify your configurations are correct.
- Power on each host and make sure they boot from the discovery ISO.
Add hosts
- After the hosts have booted from the discovery ISO, they are listed in the Hosts tab on the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management web console.
- Select all three hosts and approve them.
- Consider changing the hostname for easy identification later.

Create your cluster
- Go to Infrastructure > Clusters and click Create cluster.
- Select Host inventory from the list.
- Choose Standalone control plane and then Use existing hosts.
- Provide cluster details like cluster name, base domain, and pull secret. Skip automation for now.

- Select all three hosts and click Next to bind them. Wait for the binding to complete.


Networking configuration
Under networking, choose User-Managed Networking instead of the default Cluster-Managed Networking. This is essential when using an external load balancer. Opting for this lets you deploy OpenShift Container Platform with a custom network setup. You can use an external load balancer instead of internal keepalived and VRRP. User-managed networking also allows you to distribute cluster nodes across different L2 network segments as needed. You can find additional information about cluster-managed networking and user-managed networking in the Red Hat OpenShift documentation.

Why select user-managed networking instead of the default option? Cluster-managed networking prompts you to specify API and Ingress IPs, and it attempts to create internal API and Ingress configurations. This can result in troublesome errors that jeopardize your cluster deployment when using external load balancers.

You can also define the cluster network CIDR and service network CIDR by selecting the advanced networking feature.

If your hosts are behind a firewall using a proxy, enable Show proxy settings and define HTTP, HTTPS, and No Proxy.

Create your cluster
- Finally, click Create cluster. The cluster creation process takes approximately 40 minutes, depending on your network speed.
Common troubleshooting
When things aren't working, here are some things to look at:
- If your hosts aren't available in the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management web console, make sure they have access to the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management network.
- Verify that the discovery agent is running with the correct parameters. Directly SSH to one of the bare-metal nodes with the ssh-key to verify.
- To see the agent's status, use
ps -ef | grep agent. - Review logs for the agent using
sudo journalctl -u agent.servicefrom the same bare-metal node. - Ensure the proxy settings are correct and the assisted installer service is connected to the network.
- To see the agent's status, use
- During cluster deployment, ensure hosts have internet access to download necessary images.
- Log in using SSH to the node and verify that
podman pullcan fetch images from the registry. If you're using a proxy, ensure that HTTPS proxy is configured and has access to the registry.
I hope this guide simplifies the process of deploying a bare-metal cluster with an external load balancer using the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management console. For more details, refer to the official documentation.
Learn more
Über den Autor
Sohidur Rahman is a dedicated Red Hat Senior Consultant, driven by a passion for helping clients overcome their strategic technology and business challenges using open source methods and technologies.
Ähnliche Einträge
2025 Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform: A year in review
New observability features in Red Hat OpenShift 4.20 and Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management 2.15
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
Ready To Launch | Compiler
Nach Thema durchsuchen
Automatisierung
Das Neueste zum Thema IT-Automatisierung für Technologien, Teams und Umgebungen
Künstliche Intelligenz
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die es Kunden ermöglichen, KI-Workloads beliebig auszuführen
Open Hybrid Cloud
Erfahren Sie, wie wir eine flexiblere Zukunft mit Hybrid Clouds schaffen.
Sicherheit
Erfahren Sie, wie wir Risiken in verschiedenen Umgebungen und Technologien reduzieren
Edge Computing
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die die Operations am Edge vereinfachen
Infrastruktur
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von der weltweit führenden Linux-Plattform für Unternehmen
Anwendungen
Entdecken Sie unsere Lösungen für komplexe Herausforderungen bei Anwendungen
Virtualisierung
Erfahren Sie das Neueste über die Virtualisierung von Workloads in Cloud- oder On-Premise-Umgebungen
