Have you always wanted to configure your local or development Red Hat OpenShift cluster with self-signed certificates but found it too difficult and nerve-wracking?
Many articles and tutorials assume you are working with a certificate authority (CA) organization–but what if you're not? You probably don't want to purchase a domain name and pay fees to your CA just for local development. This article covers custom certificates with a private CA within the boundaries of your home lab or LAN, free and simple.
Its official page describes mkcert as "a simple tool for making locally trusted development certificates. It requires no configuration." mkcert creates a local CA in your system truststore and is probably available for your favorite operating system.
Getting ready to deploy mkcert
Here's how to use the tools below to configure an OpenShift cluster with local trusted certificates:
Requirements:
- mkcert binary
- OpenShift cluster with version >= 4.10
- oc binary
- OpenSSL
Note: OpenSSL is a powerful tool for managing certificates. It is available by default on Linux and macOS. You need little to no knowledge of OpenSSL for this article.
Workflow:
- Install mkcert
- Create a certificate signing request using OpenSSL
- Create and patch OpenShift's resources
mkcert deployment and configuration steps
Step 1: Install mkcert. This step creates a local CA in your system truststore:
% mkcert -installNext, create a certificate signing request with the OpenShift default ingress wildcard domain. This typically follows the pattern: *.apps.cluster-name.example.com.
% openssl req -out ingress.csr -new -newkey rsa:4096 -nodes -keyout ingresskey.pem -subj "/C=US/ST=College Station/L=Texas/O=Home/OU=lab/CN=*.apps.sno.homelab.com"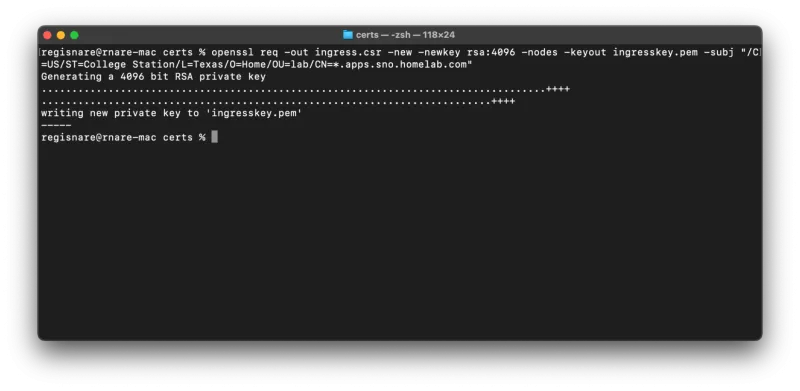
The following files are created:
- Ingress.csr - My certificate signing request.
- Ingresskey.pem - The csr associated private key.
Step 2: Sign the CSR with mkcert. This will produce your public key:
% mkcert -csr ingress.csr
You're done with certificates!
Configure the cluster
Next, make your cluster aware of your certs. You will create secrets and patch your proxy and ingress controller. You can check the prerequisites for configuring a cluster with custom certificates here (but you should be fine with what you have if you've followed along).
Step 3: Create your local rootCA configmap. This is your mkcert rootCA public key. Find its location directory with the mkcert -CAROOT command. It is named rootCA.pem:
% oc create configmap homelab-ca --from-file=ca-bundle.crt=../../Library/Application\ Support/mkcert/rootCA.pem -n openshift-configStep 4: Create the secret containing your wildcard domain key pair:
% oc create secret tls homelab-cert --cert=_wildcard.apps.sno.homelab.com.pem --key=ingresskey.pem -n openshift-ingressStep 5: Patch both the default proxy and ingress controller, respectively:
% oc patch proxy/cluster --type=merge --patch='{"spec":{"trustedCA":{"name":"homelab-ca"}}}' && oc patch ingresscontrollers.operator.openshift.io default --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"defaultCertificate": {"name": "homelab-cert"}}}' -n openshift-ingress-operatorYou're done!
Give your cluster a little time to reconcile the changes, and then you should be able to log into the UI via HTTPS. Verify your certificate, and confirm that it is trusted and issued by mkcert.

Wrap up
You may find it impractical to configure OpenShift clusters with certificates from public certificate authorities. The process is expensive and can be tedious. This article showed you how to use mkcert to create and manage self-signed certificates for internal use. This is perfect for home labs or test environments in small businesses. The configuration is straightforward, and the prerequisites are light—just mkcert, OpenShift and OpenSSL.
Try the steps above on your own OpenShift cluster configuration today to experience the ease and practicality of mkcert certificate management.
Sobre os autores
Abdoul Djire is a Senior OpenShift Engineer and Red Hat Certified Specialist in OpenShift Administration with a background in hybrid platforms and infrastructure automation. He is also a GitOps enthusiast and passionate about open source.
Mais como este
Introducing OpenShift Service Mesh 3.2 with Istio’s ambient mode
From if to how: A year of post-quantum reality
Data Security 101 | Compiler
AI Is Changing The Threat Landscape | Compiler
Navegue por canal
Automação
Últimas novidades em automação de TI para empresas de tecnologia, equipes e ambientes
Inteligência artificial
Descubra as atualizações nas plataformas que proporcionam aos clientes executar suas cargas de trabalho de IA em qualquer ambiente
Nuvem híbrida aberta
Veja como construímos um futuro mais flexível com a nuvem híbrida
Segurança
Veja as últimas novidades sobre como reduzimos riscos em ambientes e tecnologias
Edge computing
Saiba quais são as atualizações nas plataformas que simplificam as operações na borda
Infraestrutura
Saiba o que há de mais recente na plataforma Linux empresarial líder mundial
Aplicações
Conheça nossas soluções desenvolvidas para ajudar você a superar os desafios mais complexos de aplicações
Virtualização
O futuro da virtualização empresarial para suas cargas de trabalho on-premise ou na nuvem

